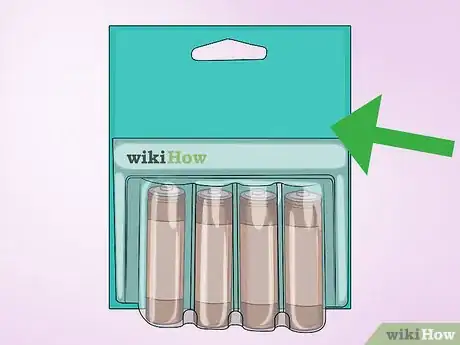This article was co-authored by Ricardo Mitchell. Ricardo Mitchell is the CEO of CN Coterie, a fully licensed and insured Lead EPA (Environmental Protection Agency) Certified construction company located in Manhattan, New York. CN Coterie specializes in full home renovation, electrical, plumbing, carpentry, cabinetry, furniture restoration, OATH/ECB (Office of Administrative Trials and Hearings/Environmental Control Board) violations removal, and DOB (Department of Buildings) violations removal. Ricardo has over 10 years of electrical and construction experience and his partners have over 30 years of relevant experience.
There are 12 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page.
wikiHow marks an article as reader-approved once it receives enough positive feedback. This article received 17 testimonials and 96% of readers who voted found it helpful, earning it our reader-approved status.
This article has been viewed 405,216 times.
Batteries come in many different shapes, sizes, and applications, and it can be very helpful to have several different kinds stored in your home for later use. Proper storage extends the life of the batteries and prevents them from becoming a safety hazard, and allows you to easily find them when you need them.
Steps
Storing Batteries
-
1Keep batteries in the original packaging if possible. Storing batteries sealed in their packaging ensures that they remain protected from environmental factors such as humidity. It also ensures that you do not confuse new, fully charged batteries with older ones, and it prevents the terminals from coming into contact with other metals.
- If you don't have the original packaging, keep your batteries in a plastic container.[1]
-
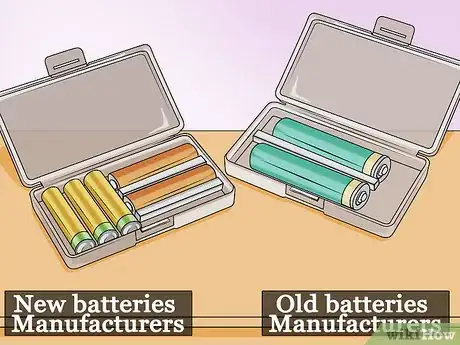
2Separate batteries by make and age. Batteries of different types or from different manufacturers can react with each other, causing leakage or other damage. If you are storing disposable (non-rechargeable) batteries, avoid storing new and used batteries together.[2] Separate containers are ideal. If you plan to use one container, place each type of battery in its own plastic bag.Advertisement
-
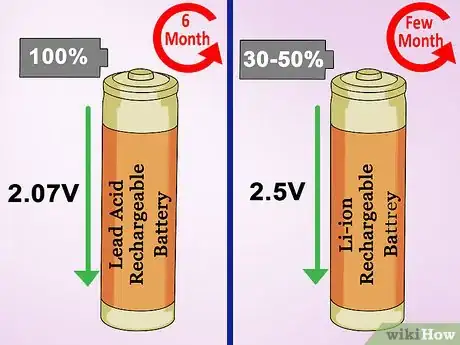
3Check the charge levels on rechargeable batteries. Many rechargeable batteries will permanently damage themselves if kept in a discharged state. The ideal level of charge depends on the technology:Lead Acid
Store at full charge to avoid sulfation, which lowers capacity.Lithium Ion (Li-ion)
For best results, store at 30–50% maximum charge.[3]
If you will be unable to recharge within a few months, store at full charge instead.[4] [5]Nickel-based (NiMH, NiZn, NiCd)
Can be stored at any state of charge.[6] -
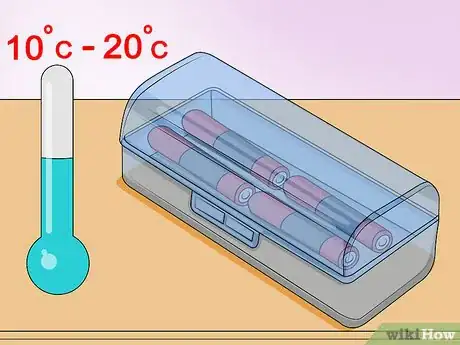
4Store your batteries at room temperature or below. In most cases, any cool room away from direct sun is fine—just avoid storing your batteries in high temperatures.[7] Even at relatively warm temperatures of 77ºF (25ºC), a typical battery only loses a few percent of its charge capacity each year. Storing batteries in the refrigerator (or anywhere between 34–60ºF / 1–15ºC) causes minor improvements in this area, but is not necessary unless you have no good alternative or maximum performance is vital. For most consumers, the refrigerator is not worth the risk of water damage and the inconvenience of waiting for batteries to warm up before use.
- Do not put a battery in a freezer unless the manufacturer recommends it.Traditional nickel-based batteries lose their charge quickly even at low temperatures. They recharge faster at cool temperatures, but not below 50ºF (10°C) for consumer-grade chargers.
More recent LSD (Low Self-Discharge) NiMH batteries are designed to maintain their charge at room temperature.
- Do not put a battery in a freezer unless the manufacturer recommends it.
-
5Control humidity. Keep your batteries in a vapor-proof container if they are in a high-humidity environment or if there is risk of condensation (including in the fridge). Alkaline batteries can be safely stored in moderately humid conditions (35 to 65% relative humidity).[8] Most other batteries prefer drier environments.[9]
- In addition, don't store your batteries down on the ground.[10]
-
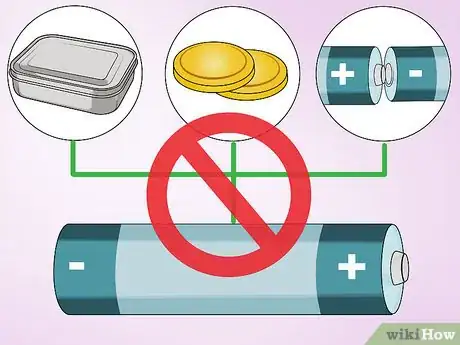
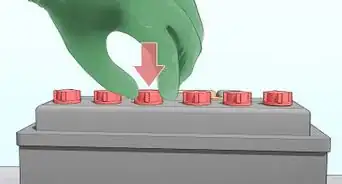
6Prevent electrical conduction. Your batteries may start conducting electricity if they come into contact with metal. This will drain your batteries quickly, and create heat. Take steps to prevent this problem and reduce fire risk:[11] [12]
- Do not store batteries in a metal container. Use a sealed plastic container or a specialized battery storage box.
- Do not store coins or other metal objects in the same container.
- Align batteries so the positive terminals cannot contact the negative terminals of other batteries. Cover the terminals with masking tape or plastic caps if you cannot guarantee this.
Maintaining Rechargeable Batteries
-
1Recharge lead acid and lithium-ion batteries periodically. Storing a lead-acid battery at a very low charge state can cause permanent crystal formation (sulfation) that reduces capacity.[13] Lithium-ion batteries at low charge can develop copper structures that short the battery, making it dangerous to use.[14] The exact recharge instructions depend on the battery design. Follow these guidelines if you do not have access to manufacturer instructions:
-
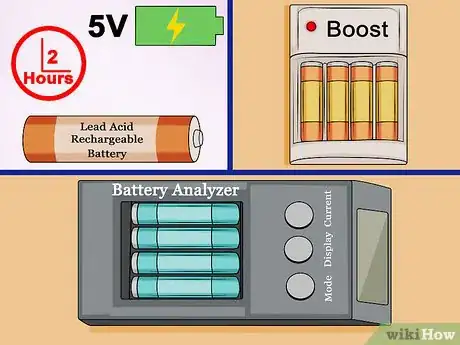
2Restore discharged batteries. If your rechargeable batteries drop to low charge levels for more than a few days, they will likely require special treatment before you can use them again:Lead Acid
The battery will usually recharge, but with permanently reduced capacity. If a small lead acid battery fails to recharge, apply a very low amount of current at a high voltage (~5V) for two hours.
Anti-sulfation devices are not recommended without an experienced operator.Lithium Ion (Li-ion)
The battery may enter "sleep mode" and fail to recharge. Use a charger with a "boost" feature, taking care to apply the voltage with the correct polarity.
Never boost a battery that falls below 1.5V/cell for a week or more, as it is permanently damaged and dangerous to use.
Expert Q&A
Did you know you can get expert answers for this article?
Unlock expert answers by supporting wikiHow
-
QuestionIs there a wrong way to store batteries?
 Ricardo MitchellRicardo Mitchell is the CEO of CN Coterie, a fully licensed and insured Lead EPA (Environmental Protection Agency) Certified construction company located in Manhattan, New York. CN Coterie specializes in full home renovation, electrical, plumbing, carpentry, cabinetry, furniture restoration, OATH/ECB (Office of Administrative Trials and Hearings/Environmental Control Board) violations removal, and DOB (Department of Buildings) violations removal. Ricardo has over 10 years of electrical and construction experience and his partners have over 30 years of relevant experience.
Ricardo MitchellRicardo Mitchell is the CEO of CN Coterie, a fully licensed and insured Lead EPA (Environmental Protection Agency) Certified construction company located in Manhattan, New York. CN Coterie specializes in full home renovation, electrical, plumbing, carpentry, cabinetry, furniture restoration, OATH/ECB (Office of Administrative Trials and Hearings/Environmental Control Board) violations removal, and DOB (Department of Buildings) violations removal. Ricardo has over 10 years of electrical and construction experience and his partners have over 30 years of relevant experience.
Electrician & Construction Professional, CN Coterie
Warnings
- Storing wet (flooded) lead-acid batteries long-term is not recommended. These batteries require regular maintenance to top up water levels and prevent corrosion.⧼thumbs_response⧽
Things You'll Need
- Batteries
- Plastic bag (optional)
- Battery storage box (optional)
References
- ↑ Ricardo Mitchell. Electrician & Construction Professional, CN Coterie. Expert Interview. 6 May 2020.
- ↑ https://www.sparefoot.com/self-storage/blog/7433-how-to-store-batteries/
- ↑ http://www.mpoweruk.com/storage.htm
- ↑ http://www.newark.com/pdfs/techarticles/tektronix/LIBMG.pdf
- ↑ http://batteryuniversity.com/learn/article/how_to_prolong_lithium_based_batteries
- ↑ http://www.mpoweruk.com/storage.htm
- ↑ Ricardo Mitchell. Electrician & Construction Professional, CN Coterie. Expert Interview. 6 May 2020.
- ↑ https://www.fdk.com/battery/alkaline_e/caution/
- ↑ http://batteryuniversity.com/learn/article/how_to_store_batteries
- ↑ Ricardo Mitchell. Electrician & Construction Professional, CN Coterie. Expert Interview. 6 May 2020.
- ↑ http://dnr.wi.gov/files/pdf/pubs/wa/wa1736.pdf
- ↑ http://www.energizer.com/about-batteries/battery-care
- ↑ http://www.mpoweruk.com/storage.htm
- ↑ http://batteryuniversity.com/learn/article/low_voltage_cut_off
- ↑ http://www.dalitech.com/Resources/Lithium%20Ion.pdf
- ↑ http://www.mpoweruk.com/storage.htm
- ↑ http://batteryuniversity.com/learn/article/how_to_restore_nickel_based_batteries
About This Article
If you want to store batteries, try to keep them in their original packaging to prevent exposure to humidity. For batteries you've already removed from the packaging, sort them into different types to reduce the risk of them reacting with each other. Place your batteries in a vapor-tight container, then keep them at room temperature away from direct sunlight. To avoid losing charge and causing a fire risk, don't store coins or other metal objects with your batteries. For tips on how to store rechargeable batteries, keep reading!