This article was co-authored by Patricia Somers, RD, PhD. Patricia Somers is a Registered Dietitian and an Associate Professor of the Department of Educational Leadership and Policy at the University of Texas at Austin. She received her RD from the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics in 1979 and her PhD in Educational Administration (Higher Education Specialization) from the University of New Orleans. She received an Emerging Scholar Award from the American Association of University Women and the Faculty Excellence Award in Research from the University of Arkansas, Little Rock.
There are 20 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page.
This article has been viewed 23,560 times.
Artichoke leaf extract is an herbal supplement and complementary medicine that is thought to lower cholesterol, reduce stomach problems, and increase bile production. You can take artichoke leaf extract up to three times a day. You should, however, check with your doctor to make sure that it will not interfere with your current medications or medical conditions. To find artichoke leaf extract, you may need to do a little bit of research to make sure that the supplement you purchase is safe to consume.
Steps
Taking the Extract
-
1Swallow a pill up to three times a day. The typical dose for a standardized pill is 300 – 640 mg. It is recommended that you take this dose three times a day. You may need to take it for up to six weeks to see effects.[1]
- The typical daily dosage of artichoke extract is between 1,240 and 1,800 mg for most people. Ask your doctor what might be the best dosage for you.
- Take the pill with water if you have difficulty swallowing pills dry.
- To help you remember to take it three times a day, you might want to take it when you eat breakfast, lunch, and dinner. Artichoke leaf extract does not need to be taken with food, although it can be if you want.
-
2Consume dried leaves as a substitute. It can be difficult to find a standardized artichoke leaf extract pill. If you cannot take a pill, you can weigh between 1 and 4 grams of dried artichoke leaves.You can powder the leaves using a mortar and pestle.[2] Consume each dose up to three times a day.
- If eating the leaves does not appeal to you, you can brew them as a tea. Place the leaves in a tea strainer, and pour hot water over them. Let them steep for a few minutes.[3]
- You can buy dried leaves online or at an herbal supply store. You can also dry your own by placing them in an oven or dehydrator for between one and four hours. Set the temperature to between 95 °F (35 °C) and 115 °F (46 °C).[4]
Advertisement -
3Continue with your other medication. Artichoke leaf extract is a complementary medicine. This means that it has modest health benefits on its own, but it is not a good substitute for medication. If you have a medical condition that you can think can be treated with artichoke leaf extract, talk to your doctor. Make sure that it will not interfere with your normal medication. Continue taking your medication as directed.
Determining if Artichoke Leaf Extract is Right for You
-
1Talk to your doctor. Before starting any supplement or complementary medicine, always speak to your doctor first. Explain to them why you want to take artichoke leaf extract, and ask them if they think it will interfere with any of your current medications.
- While there are few known side effects of artichoke leaf extract, it can worsen bile duct problems, increase bleeding, or cause a rash.
-
2Research your condition. Artichoke leaf extract can help reduce the symptoms of certain medical conditions and diseases. If you are suffering from a particular condition, you may find that artichoke leaf extract provides relief when taken with your normal medication. These conditions include:
-
3Get a cholesterol test. Artichoke leaf extract is most often used to lower cholesterol levels. If you have high cholesterol or if you have a cholesterol-related condition, such as hyperlipoproteinemia, an artichoke leaf extract can help you manage it.[10] If you’re not sure about your cholesterol levels, ask your doctor to do a cholesterol test.
- You may not be able to eat for twelve hours before your test. This is a type of blood test, which means that your blood will be drawn.[11]
- If your mean cholesterol levels are 5.17 mmol/L (200 mg/dL), you may have hypercholesterolemia. Artichoke leaf extract may be able to help manage your levels slightly as a complementary medicine, but you should still take the medication prescribed to you by your doctor.[12]
-
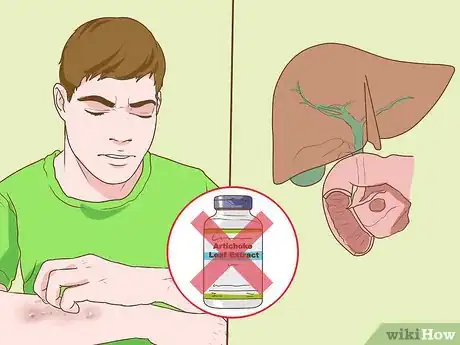
4Avoid artichoke leaf extract if you have an allergy or bile duct condition. While most people will not have an adverse reaction to artichoke leaf extract, you should avoid it if you have an allergy to artichoke or to any plants related to the artichoke (such as daisies). Furthermore, those who have bile duct obstructions, such as gallstones, may find that it worsens their condition.[13]
- Allergies to artichoke often manifest as skin rashes (dermatitis).
- Its safety for use during pregnancy has never been tested. If you are pregnant or lactating, you may want to avoid artichoke leaf extract just in case.[14]
Finding a Reputable Extract
-
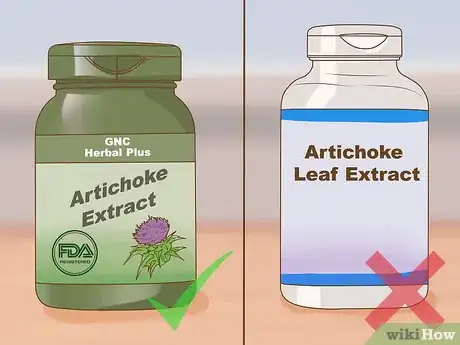
1Trust verified brands. There are many brands on the internet offering artichoke leaf extract, but you should exercise caution when ordering from the internet. Look for brands that you recognize and trust. Order from their official website. These brands may be manufactured in registered facilities, such as an FDA registered facility. Some good brands include:
- GNC Herbal Plus Artichoke Extract
- Good n Natural Artichoke Extract Capsules
- Superior Labs Artichoke Leaf Extract
-
2Look for seals of verification. Supplements are not subject to the same FDA regulations as medications, meaning they are not tested for safety and efficacy. This means it is possible that supplements do not contain the advertised dose or even the advertised ingredients. Some companies choose to have their products verified by independent organizations, who will test for dangerous contaminants and make sure the product contains the amounts as advertised.[15] Look for seals from the following organizations:
- U.S. Pharmacopeia ("USP Verified")
- NSF International
- ConsumerLab.com
- UL
-
3Read the ingredients. The FDA requires that all ingredients on an herbal supplement are listed on the label (though, keep in mind, it has been shown that not all companies comply with this).[16] When taking artichoke leaf extract, you may not want other ingredients interfering with the dosage. Some extract companies may try to dilute the extracts with other ingredients. Make sure you always read the label before purchasing.
- The artichoke may be listed under one of its scientific names. These include Cynara scolymus L. and C. cardunculus L.[17]
- If you are shopping online and the store does not offer an ingredients list, do not buy the extract.
-
4Avoid foreign products. Products manufactured and imported from abroad are not subject to FDA regulations, and therefore it is impossible to tell if you are actually receiving artichoke leaf extract or a cheaper substitute. Some foreign supplements may also contain toxic substances that are not included on the label. Always buy domestic products to make sure that you are receiving the highest quality supplement that you can.[18]
-
5Find the right dosage. Your doctor can provide you guidance as to the proper amount you need a day. If you’re still uncertain about how much you need, look for pills that offer between 300 – 640 mg in each dose. This is the recommended amount for most healthy adults.[19]
Warnings
- The studies completed thus far on the effectiveness of artichoke leaf extract have been limited and small in size. This means that the effects, benefits, and consequences of artichoke leaf extract are poorly understood. Take it at your own risk.⧼thumbs_response⧽
- Do not take artichoke leaf extract if you have gallstones.⧼thumbs_response⧽
- Do not any extracts before surgery as they may interfere with clotting or anesthesia.⧼thumbs_response⧽
References
- ↑ https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/herbal-report/superseded-assessment-report-cynara-scolymus-l-folium_en.pdf
- ↑ http://scialert.net/qredirect.php?doi=pjn.2006.147.151&linkid=pdf
- ↑ http://www.therighttea.com/artichoke-tea.html
- ↑ http://nchfp.uga.edu/how/dry/herbs.html
- ↑ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15353023
- ↑ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18424099
- ↑ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15581909
- ↑ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10758778
- ↑ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/14653829
- ↑ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10758778
- ↑ http://www.mayoclinic.org/tests-procedures/cholesterol-test/details/what-you-can-expect/rec-20169541
- ↑ http://www.sld.cu/galerias/pdf/sitios/mednat/artichoke_leaf_extract_for_treating_hypercholesterolaemia.pdf
- ↑ https://www.drugs.com/npp/artichoke.html
- ↑ https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/herbal-report/superseded-assessment-report-cynara-scolymus-l-folium_en.pdf
- ↑ http://www.consumerreports.org/vitamins-supplements/what-usp-verified-and-other-supplement-seals-mean/
- ↑ http://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/nutrition-and-healthy-eating/in-depth/herbal-supplements/art-20046714?pg=1
- ↑ https://www.drugs.com/npp/artichoke.html#ref2
- ↑ http://www.fda.gov/ForConsumers/ConsumerUpdates/ucm466588.htm
- ↑ http://www.uofmhealth.org/health-library/hn-2038002#hn-2038002-how-it-works
- ↑ http://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/nutrition-and-healthy-eating/in-depth/herbal-supplements/art-20046714?pg=2







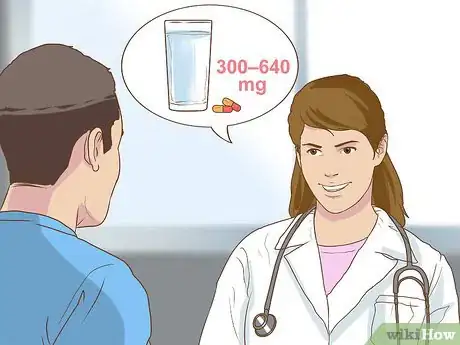












































Medical Disclaimer
The content of this article is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, examination, diagnosis, or treatment. You should always contact your doctor or other qualified healthcare professional before starting, changing, or stopping any kind of health treatment.
Read More...