Batik kawung
Kawung batik (Indonesian: Batik Kawung) is an Indonesian batik motif[1] whose shape is in the form of a circle similar to a kawung fruit (a type of coconut or sometimes also considered as sugar palm or palm fruit) which is neatly arranged geometrically. Sometimes, this motif is also interpreted as an image of a lotus flower with four flower crowns that are open. Lotus is a flower that symbolizes longevity and purity.[2][3][4]
 Kawung batik motif | |
| Type | Art fabric |
|---|---|
| Material | Cambrics, silk, cotton |
| Place of origin | Indonesia |
| Batik | |
|---|---|
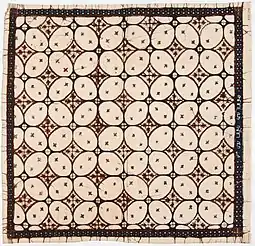 Kawung batik made in the 19th century | |
| Country | Indonesia |
| Domains | Traditional craftsmanship, oral traditions and expressions, social practices, rituals and festive events |
| Reference | 170 |
| Region | Asia and the Pacific |
| Inscription history | |
| Inscription | 2009 (4th session) |
| List | Representative List |
 Written batik (batik tulis) and stamped batik (batik cap) | |
Etymology
There are several opinions regarding the origin of the word kawung, including the following:
History

Batik kawung is one of the oldest batik motifs in Indonesia. Its existence is often mentioned and appears in various written historical sources and oral culture since the days of the Mataram Sultanate in the 16th century. There are 2 theories that explain the origin of this batik.
- The first theory states that this batik motif was created by the fourth Sultan of Mataram who ruled from 1613-1645, namely Sultan Agung of Mataram. Where the sultan said that he was inspired by the palm tree.[5]

- For the second theory, this often appears in folklore which tells of an authoritative young man who is also known to be very polite and wise. Until one day, rumors about this young man reached the royal circle. The royal party also sent a spy to observe the daily life of the young man, until finally he was summoned to appear before the king. The mother, who received news that her son was called by the king, prepared the best clothes for her child in the form of a kawung motif in the hope that her son could become a useful person for the community.[7]
Type

Usually the Kawung motifs are named based on the size of the oval shape contained in a certain motif and/or in combination with other batik motifs.[8]
Kawung picis
Kawung Picis is a kawung motif composed of small circles. Picis is a small 10-cent currency. Although it is said to come from the form of a 10-cent coin, other sources state that the word picis is interpreted as simply something small.[9][8]
Kawung Bribil/Gidril
Kawung Bribil are kawung motifs composed of a larger shape than the kawung Picis. This is in accordance with the name bribil, a currency whose shape is larger than the picis. Bribil means half a penny in the Javanese dictionary. Other sources state that the bribil or gidril motif is the name of a currency made of nickel, its value equal to five cents. Another source says bribil is worth 25 cents.[9][8]
Kawung Sen
Kawung Sen is an oval-shaped kawung larger than the Kawung Bribil, in accordance with the colonial era one penny coin which was larger than the bribil. However, other sources state that Kawung Sen, Kawung Bribil and Kawung Gidril are the same kawung motif, and are said to be inspired by the sen coin, while the kawung Picis motif is not.[9][8]
Kawung Beton
The shape of the Kawung Beton batik motif is decorated with the shape of four circles with two rectangular points. Between the four circles there are four parts that seem to be bounded by a cross line. Understanding Concrete on the Kawung Beton motif comes from the name of the jackfruit seed in Javanese, the jackfruit that is inside has a symbolic meaning of good deeds not always displayed on the outside.[8]
Kawung Cacah Gori
Kawung-patterned batik with chopped gori isen-isen.
Kawung Geger
Kawung Geger is a large kawung motif filled with smaller kawung motifs inside. Batik with this motif is considered sacred and can only be worn by kings and their close families. This has something to do with historical events, namely the Ponorogo agreement in 1813 which split the sultanate into the Ngayogyakarto Hadiningrat Sultanate and the Pakualaman Duchy.[8]
Kawung Kopi/Sari
Consists of the main ornament in the form of an oval, and on each part of the kawung motif. given the shape of a line that divides into two parts as if it resembles the shape of a broken coffee fruit. So this kawung motif is often also referred to as Kawung Kopi. The main ornament, which consists of four oval circles, is arranged based on a crossed slash or a slanted diagonal line, also arranged in a horizontal or vertical straight line. The shape of the lines seems like a cross in the visual form of the kawung motif. The color composition in this form of kawung motif consists of white, yellowish white, on the main ornament, red soga as the color of the contour, while black is to give the background color in the Kawung Sari motif.[8]
Kawung Sekar Ageng
Consists of the main ornamental elements in the form of four oval spheres that have undergone changes to a slightly square or square shape. In each main ornament there are three lines (sawut) followed by three dots (cecek). This form in terms of batik is often referred to as cecek sawut. The kawung motif element also contains isen motifs in the form of four small rhombus shapes as variations in the composition of the visual form. While the color composition consists of white, yellowish white as the color for the main ornament, red soga to color the contours of the motif and isen motif, and black is the background for the Kawung SekarAgeng motif.[8]
Kawung Semar
Consists of the main ornamental elements in the form of four oval spheres with a large size as in Kawung Beton, but in the main ornament there is an oval shape with a smaller size. The Isen motif in Kawung Semar consists of an Indonesian: cecek (dot) shape found in a circle inside the Kawung circle. In the middle of the main ornament, there is an isen motif in the form of a rhombus filled with Indonesian: cecekcecek (dots) and several dots in the form of a circular series.[8]
Kawung Buntal
Consists of the main ornament in the form of a mixture of Kawung Pecis combined with floral motifs. The floral motif found on Kawung Buntal is in the form of kenikir flowers, so the shape of the mixture of motifs is the hallmark of the Kawung Buntal motif. Isen batik motifs on Kawung Buntal consist of a small oval shape which is divided into two parts placed in the main ornament, and a rhombus with small, medium, and rather large sizes placed in the middle of the main ornament. The color composition of the Kawung Buntal motif consists of white, yellowish white as the color of kawung, red soga for the background color of Kawung Buntal and black as the contour and background color of the kenikir flower motif.[8]
Kawung Bunga
Consisting of the main ornament in the form of four oval spheres made to resemble the shape of bunga (flower), so this motif is called Kawung Kembang. The main ornament consisting of oval circles with isen motifs in the form of lines is placed at each end of the kawung circle. In the middle between the kawung circles, there is an isen motif in the form of a row of dots in a circular direction, forming a small circle with four dots outside the circle. The color composition of the Kawung Kembang motif consists of white, yellowish white as the main ornament color, red soga as the contour color and black for the background color of the Kawung Kembang motif.[8]
Kawung Seling
Consists of the main ornament that is shaped almost the same as Kawung Kembang, namely the shape of an oval circle interspersed with a flower shape. But the size and variety of flowers are not the same and are made with striking color differences. The isen motif in Kawung Seling consists of a dotted isen shaped like a line (palm), placed on a flower motif. The color composition in Kawung Seling consists of white as the color for the main ornament, black as the color for floral motifs and contours, red soga for the background color for the Kawung motif.
Other types of kawung motifs include Kawung Prabu, Kawung Putri, Kawung Putro, Kawung Ndil, and others.[10][11]
Design
The shape of the kawung is generally thought to be inspired by a circle similar to a kawung fruit (a type of coconut or sometimes also considered a fruit of kolang-kaling) which is split in half so that four hollows appear in the four corners.
Meaning
The kawung motif means perfection, purity and holiness. In relation to the word suwung which means empty, the kawung motif symbolizes the emptiness of worldly passions and desires, resulting in perfect self-control. This emptiness makes a person neutral, impartial, not wanting to stand out, following the flow of life, letting everything around him run according to the will of nature. Semar, the incarnation of a god who has a very good and wise character, always wears this kawung motif.[12]
References
- "Let's Get to Know 7 Indonesian Batik Patterns and their Philosophical Meanings", Wisma Bahasa, 6 October 2020
- "NILAI KEARIFAN LOKAL DALAM BATIK TRADISIONAL KAWUNG", Jurnal.ugm
- "Mengenal Motif Batik Kawung, Sejarah, Filosofi, dan Jenisnya", Kompas, 10 January 2022
- "Kawung", Iware Batik
- "Mengenal Kawung, Salah Satu Motif Batik Tertua di Nusantara", Detik
- "7 Enchanting Stories behind Indonesia's Famous Batik", Indonesia.Travel
- "Sejarah dan Makna Motif Batik Kawung", Kelaspintar, 24 April 2021
- "Motif Kawung sebagai Simbolisme Busana Para Abdi dalam Wayang Kulit Purwa Gaya Surakarta". Journal Unnes. Retrieved 3 October 2022.
- "Indonesia Batik". Batik Indonesia. Retrieved 3 October 2022.
- "8 types of batik kawung motif", Infobatik
- Kusrianto, Adi (11 November 2021), "MOTIF BATIK KLASIK LEGENDARIS DAN TURUNANNYA", Adi Kusrianto, ISBN 9786230118814
- "Batik Kawung, Motif Batik Bermakna Kesucian dan Panjang Umur", Fimale, 28 May 2015



.svg.png.webp)
.jpeg.webp)
