City of Westminster
The City of Westminster is a city and borough in Greater London. It is the site of the United Kingdom's Houses of Parliament and much of the British government. It occupies a large area of central London, including most of the West End. Many London landmarks are within the borough, including Buckingham Palace, Westminster Abbey, Whitehall, Westminster Cathedral, 10 Downing Street, and Trafalgar Square.
City of Westminster | |
|---|---|
 Trafalgar Square, an open plaza in the city | |
 Coat of arms  Council logo | |
 Westminster shown within Greater London | |
| Coordinates: 51°30′44″N 00°09′48″W | |
| Sovereign state | United Kingdom |
| Country | England |
| Region | London |
| Ceremonial county | Greater London |
| Created | 1 April 1965 |
| Admin HQ | City Hall, Victoria Street |
| Government | |
| • Type | London borough council |
| • Body | Westminster City Council |
| • Leadership | Leader & Cabinet (Labour) |
| • Lord Mayor | Hamza Taouzzale |
| • London Assembly | Tony Devenish (Conservative) |
| • MPs |
|
| Area | |
| • Total | 8.29 sq mi (21.48 km2) |
| • Rank | 288th (of 296) |
| Population (2021) | |
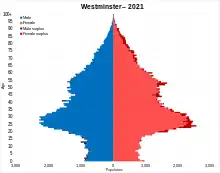
| • Total | 205,087 |
| • Rank | 96th (of 296) |
| • Density | 25,000/sq mi (9,500/km2) |
| Time zone | UTC (GMT) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+1 (BST) |
| Postcodes | |
| Area code | 020 |
| ISO 3166 code | GB-WSM |
| ONS code | 00BK |
| GSS code | E09000033 |
| Police | Metropolitan Police |
| Website | www.westminster.gov.uk |
Westminster became a city in 1540, and historically, it was a part of the ceremonial county of Middlesex. Its southern boundary is the River Thames. To the City of Westminster's east is the City of London near Temple Bar, and to its west is the Royal Borough of Kensington and Chelsea. To its north is the London Borough of Camden. Charing Cross in Westminster is the notional centre of London, and the point from which distances from London are measured.
The borough is divided into a number of localities including the ancient political district of Westminster; the shopping areas around Oxford Street, Regent Street, Piccadilly and Bond Street; and the night-time entertainment district of Soho. Much of the borough is residential, and in 2019 it was estimated to have a population of 261,000. Despite large swaths of parks and open spaces, including Hyde Park and most of Regent's Park, the population density of the district is high.
The London Westminster borough was created with the 1965 establishment of Greater London. Upon the creation, it inherited the city status previously held by the then Metropolitan Borough of Westminster from 1900, which was first awarded to Westminster in 1540. The local government body is Westminster City Council, and there has been a Lord Mayor of the City of Westminster since 1966, while the area is also within authority of the Mayor of London, an office created in 2000.
History
After the depopulation of Roman London in the 5th century, an Anglo Saxon agricultural and trade settlement likely developed to its west, associated with the Middle Saxons, sometimes called Lundenwic ('London village' or London port'). Over time, Lundenburh ('London fort'), the former Roman city with its still-existing Roman walls, was repopulated and Lundenwic declined, becoming pastoral and partly known as Aldwych (Aldwic—'old village'), the name of which lives on for a section of Westminster.[1]
The origins of the City of Westminster pre-date the Norman Conquest of England. In the mid-11th century, King Edward the Confessor began the construction of an abbey at Westminster, only the foundations of which survive today. Between the abbey and the river he built a palace, thereby guaranteeing that the seat of Government would be fixed at Westminster, and inevitably drawing power and wealth west out of the old City of London.[2]
For centuries Westminster and the City of London were geographically quite distinct. It was not until the sixteenth century that houses began to be built over the adjoining fields, eventually absorbing nearby villages such as Marylebone and Kensington, and gradually creating the vast Greater London that exists today.
Henry VIII's dissolution of the monasteries abolished the abbey at Westminster, although the former abbey church is still called Westminster Abbey. The church was briefly the cathedral of the Diocese of Westminster created from part of the Diocese of London in 1540, by letters patent which also granted city status to Westminster, a status retained after the diocese was abolished in 1550.[3] The Westminster Court of Burgesses was formed in 1585 to govern the Westminster area, previously under the Abbey's control. The City and Liberties of Westminster were further defined by Letters Patent in 1604, and the court of burgesses and liberty continued in existence until 1900, and the creation of the Metropolitan Borough of Westminster.[4][5]
The present-day City of Westminster as an administrative entity with its present boundaries dates from 1965, when the City of Westminster was created from the former area of three metropolitan boroughs: St Marylebone, Paddington, and the smaller Metropolitan Borough of Westminster, which included Soho, Mayfair, St James's, Strand, Westminster, Pimlico, Belgravia, and Hyde Park. This restructuring took place under the London Government Act 1963, which significantly reduced the number of local government districts in London, resulting in local authorities responsible for larger geographical areas and greater populations.
The Westminster Metropolitan Borough was itself the result of an administrative amalgamation which took place in 1900. Sir John Hunt O.B.E was the First Town Clerk of the City of Westminster, 1900–1928.
In addition to the Westminster Court of Burgesses, prior to 1900, the area that would become the Metropolitan Borough of Westminster had been administered by five separate local bodies: the Vestry of St George Hanover Square, the Vestry of St Martin in the Fields, Strand District Board of Works, Westminster District Board of Works and the Vestry of Westminster St James.
The boundaries of the City of Westminster today, as well as those of the other London boroughs, have remained more or less unchanged since the Act of 1963.
Demographics
| Year | Pop. | ±% |
|---|---|---|
| 1801 | 220,188 | — |
| 1811 | 245,254 | +11.4% |
| 1821 | 288,851 | +17.8% |
| 1831 | 344,200 | +19.2% |
| 1841 | 368,910 | +7.2% |
| 1851 | 422,850 | +14.6% |
| 1861 | 446,263 | +5.5% |
| 1871 | 469,677 | +5.2% |
| 1881 | 493,090 | +5.0% |
| 1891 | 462,837 | −6.1% |
| 1901 | 441,857 | −4.5% |
| 1911 | 421,865 | −4.5% |
| 1921 | 396,406 | −6.0% |
| 1931 | 372,566 | −6.0% |
| 1941 | 334,448 | −10.2% |
| 1951 | 300,461 | −10.2% |
| 1961 | 267,126 | −11.1% |
| 1971 | 237,614 | −11.0% |
| 1981 | 163,893 | −31.0% |
| 1991 | 187,526 | +14.4% |
| 2001 | 181,279 | −3.3% |
| 2011 | 219,396 | +21.0% |
| Source: A Vision of Britain through time, citing Census population | ||
Ethnicity

The following table shows the ethnic group of respondents in the 1991 to 2021 censuses in Westminster.
| Ethnic group | 1981 estimations[6] | 1991[7] | 2001[8] | 2011[9] | 2021[10] | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | % | Number | % | Number | % | Number | % | Number | % | |
| White: Total | 132,613 | 87.5% | 137,375 | 78.5% | 132,715 | 73.12% | 135,330 | 61.68% | 112,732 | 55.1% |
| White: British | – | – | – | – | 87,938 | 48.51% | 77,334 | 35.25% | 57,162 | 28.0% |
| White: Irish | – | – | – | – | 6,574 | 3.63% | 4,960 | 2.26% | 3,742 | 1.8% |
| White: Gypsy or Irish Traveller | – | – | – | – | – | – | 76 | 0.03% | 49 | 0.0% |
| White: Roma | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | 1,503 | 0.7% |
| White: Other | – | – | – | – | 38,203 | 21.07% | 52,960 | 24.14% | 50,276 | 24.6% |
| Asian or Asian British: Total | – | – | 16,421 | 9.4% | 20,184 | 11.13% | 31,862 | 14.52% | 34,242 | 16.7% |
| Asian or Asian British: Indian | – | – | 3,410 | 1.9% | 5,665 | 3.12% | 7,213 | 3.29% | 7,965 | 3.9% |
| Asian or Asian British: Pakistani | – | – | 1,173 | 0.7% | 1,828 | 1.01% | 2,328 | 1.06% | 2,461 | 1.2% |
| Asian or Asian British: Bangladeshi | – | – | 3,997 | 2.3% | 5,000 | 2.76% | 6,299 | 2.87% | 7,533 | 3.7% |
| Asian or Asian British: Chinese | – | – | 2,831 | 1.6% | 4,077 | 2.25% | 5,917 | 2.70% | 6,625 | 3.2% |
| Asian or Asian British: Other Asian | – | – | 5,010 | 2.9% | 3,614 | 1.99% | 10,105 | 4.61% | 9,658 | 4.7% |
| Black or Black British: Total | – | – | 13,475 | 7.7% | 13,481 | 7.44% | 16,472 | 7.51% | 16,456 | 8% |
| Black or Black British: African | – | – | 4,963 | 2.8% | 5,613 | 3.10% | 4,449 | 2.03% | 10,451 | 5.1% |
| Black or Black British: Caribbean | – | – | 6,535 | 3.7% | 6,678 | 3.68% | 9,141 | 4.17% | 4,307 | 2.1% |
| Black or Black British: Other Black | – | – | 1,977 | 1.1% | 1,190 | 0.66% | 2,882 | 1.31% | 1,698 | 0.8% |
| Mixed or British Mixed: Total | – | – | – | – | 7,480 | 4.13% | 11,395 | 5.19% | 13,335 | 6.5% |
| Mixed: White and Black Caribbean | – | – | – | – | 1,382 | 0.76% | 1,869 | 0.85% | 2,061 | 1.0% |
| Mixed: White and Black African | – | – | – | – | 1,204 | 0.66% | 1,927 | 0.89% | 2,089 | 1.0% |
| Mixed: White and Asian | – | – | – | – | 2,436 | 1.34% | 3,584 | 1.63% | 3,718 | 1.8% |
| Mixed: Other Mixed | – | – | – | – | 2,458 | 1.36% | 4,015 | 1.83% | 5,467 | 2.7% |
| Other: Total | – | – | 7,543 | 4.3% | 7,426 | 4.10% | 24,337 | 11.09% | 27,471 | 13.5% |
| Other: Arab | – | – | – | – | – | – | 15,724 | 7.17% | 15439 | 7.6% |
| Other: Any other ethnic group | – | – | 7,543 | 4.3% | 7,426 | 4.1% | 8,613 | 3.93% | 12032 | 5.9% |
| Ethnic minority: Total | 18,891 | 12.5% | 37,439 | 21.4% | 48,571 | 26.79% | 84,066 | 38.32% | 91,504 | 44.9% |
| Total | 151,504 | 100% | 174,814 | 100% | 181,286 | 100.00% | 219,396 | 100.00% | 204,236 | 100% |
Religion
| Religion | 2001[11] | 2011[12] | 2021[13] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | Of total | Number | Of total | Number | Of total | |
| Christian | 99,797 | 55.05% | 97,877 | 44.61% | 76,245 | 37.3% |
| No religion | 29,300 | 16.16% | 44,542 | 20.30% | 52,936 | 25.9% |
| Muslim | 21,346 | 11.77% | 40,073 | 18.27% | 40,873 | 20.0% |
| Religion not stated | 15,877 | 8.76% | 20,519 | 9.35% | 19,179 | 9.4% |
| Jewish | 7,732 | 4.27% | 7,237 | 3.30% | 5,628 | 2.8% |
| Hindu | 3,497 | 1.93% | 4,178 | 1.90% | 4,457 | 2.2% |
| Buddhist | 2,392 | 1.32% | 3,194 | 1.46% | 2,603 | 1.3% |
| Other religion | 945 | 0.52% | 1,280 | 0.58% | 1,741 | 0.9% |
| Sikh | 400 | 0.22% | 496 | 0.23% | 573 | 0.3% |
| Total | 181,286 | 100.00% | 219,396 | 100.00% | 204,300 | 100.0% |
Housing
The borough ranks highest on one standard criteria in analysing housing supply and demand, the proportion of private rented accommodation relative to other types of housing in England.[14]
Income inequality
A study in 2017 by Trust for London and The New Policy Institute found that Westminster has the third-highest pay inequality of the 32 London boroughs. It also has the second-least affordable private rent for low earners in London, behind only Kensington and Chelsea.
Education
In education, 82% of adults and 69% of 19-year-olds having Level 3 qualifications.[15]
Governance

Westminster City Council

The city is divided into 18 wards, each electing three councillors. As of 2022, Westminster City Council is currently composed of 31 Labour Party councillors and 23 Conservative Party councillors.[16]
A lord mayor is elected annually to serve as the official representative of the city for one year. See List of mayors of Westminster for a list of former mayors (1900–1965) and lord mayors (1965 to date).
Coat of arms

The current Westminster coat of arms was given by an official grant on 2 September 1964.[17]
Westminster had other arms before, which had a chief identical to the chief in the present arms. The symbols in the lower two thirds of the shield stand for former municipalities now merged with the city, Paddington and St Marylebone. The original arms had a portcullis as the main charge, which now forms the crest.[17]
UK Parliament
| 1918 | 1950 | 1974 | 1983 | 1997 | 2010 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| St Marylebone | Westminster North | Regent's Park and Kensington North | Westminster North | ||
| Paddington North | Paddington | ||||
| Paddington South | Cities of London and Westminster | ||||
| Westminster St George's | Cities of London and Westminster | Cities of London and Westminster | |||
| Westminster Abbey | |||||
| City of London | |||||
Greater London representation
For elections to the Greater London Council, the borough formed part of the Westminster and the City of London electoral division, electing three members. In 1973 it was divided into the single-member City of London and Westminster South, St Marylebone and Paddington electoral divisions. The Greater London Council was abolished in 1986.
Since 2000, for elections to the London Assembly, the borough forms part of the West Central constituency.
Districts
The City of Westminster covers all or part of the following areas of London:
- "Albertopolis" (shared with the Royal Borough of Kensington and Chelsea)
- Bayswater
- Belgravia (shared with the Royal Borough of Kensington and Chelsea)
- Covent Garden (shared with the London Borough of Camden)
- Fitzrovia (shared with the London Borough of Camden)
- Hyde Park
- Knightsbridge (shared with the Royal Borough of Kensington and Chelsea)
- Lisson Grove
- Maida Vale
- Mayfair
- Marylebone
- Millbank
- Paddington
- Pimlico
- St James's
- St John's Wood
- Soho, including Chinatown
- "Theatreland"
- Victoria
- Westbourne Green (shared with the Royal Borough of Kensington and Chelsea)
- West End (shared with the London Borough of Camden)
- Westminster City Centre
Economy
Many global corporations have their global or European headquarters in the City of Westminster. Mayfair and St James's within the City of Westminster also have a large concentration of hedge fund and private equity funds. The West End is known as the Theatre District and is home to many of the leading performing arts businesses. Soho and its adjoining areas house a concentration of media and creative companies. Oxford Street is a busy shopping destination.
Landmarks


The City of Westminster contains some of the most famous sites in London, including Buckingham Palace, Westminster Abbey, the Palace of Westminster (Houses of Parliament) and Big Ben.
Centre of London
Charing Cross is the notional centre of London and the location where distinances from London are measured. This custom appears to have begun with the set distances of the 12 Eleanor crosses to Lincoln, England in the north, and expanded even after destruction of most the crosses.[18]
Parks and open spaces
These include Green Park, Hyde Park, Kensington Gardens, Regent's Park and St James's Park. In addition to parks and open spaces within the borough, the City owns and maintains East Finchley Cemetery and crematorium in the London Borough of Barnet.
Transport
National Rail stations
Four National Rail stations serve the City of Westminster:
London Underground
The City of Westminster is served by 27 London Underground stations and 10 of the 11 lines.
Electric charging points
By 2009 Westminster City Council had electric vehicle charging points in 15 locations through the city (13 car parks and two on-street points). Users pay an annual fee to cover administration costs to register and use the points.[25] By 2018 there were 60 electric vehicle charging locations.[26]
Travel to work
In March 2011, the main forms of transport that residents used to travel to work were: underground, metro, light rail, tram, 21.0% of all residents aged 16–74; on foot, 9.3%; bus, minibus or coach, 9.3%; driving a car or van, 6.0%; work mainly at or from home, 5.5%; bicycle, 3.1%; train, 3.0%.[27]
Education

Westminster Children's Services administers many primary and secondary schools. In addition, there are several state-funded faith schools, primarily Church of England (CE), and Roman Catholic (RC), but Christian non-denominational (ND) schools are also in the borough,[28] and there are several non-profit-making junior and senior independent schools.
Universities and colleges
- The University of Westminster has its three campuses in the borough; 309 Regent Street (with 4–12 / 16 Little Titchfield Street and 32 / 38 Wells Street buildings uniting under the same campus), 115 New Cavendish Street, and 29 / 35 Marylebone Road.
- The Strand campus of King's College London is located within the district.
- The London Business School, in Regent's Park.
- The London School of Economics, at Clare Market, near Aldwych.
- The Royal Academy of Music, on Marylebone Road.
- University of the Arts London has constituent colleges in Millbank (Chelsea College of Art and Design) and Oxford Street (London College of Fashion).
- The Courtauld Institute of Art, in Somerset House, Strand.
- Brigham Young University London Centre, on Palace Court.
- The northern half of Imperial College London's main South Kensington campus lies within the borough.
- City of Westminster College is a further education college with campuses on Paddington Green and at Queens Park. It also owns the Cockpit Theatre, which is used as a training and performance venue.
- Regent's College, whose campus is within the grounds of Regent's Park, which houses: European Business School London; Regent's American College London; Regent's Business School; School of Psychotherapy and Counselling; Webster Graduate School; Internexus, a provider of English language courses.
- Westminster Kingsway College is a further education college with centres in Soho and Victoria in Westminster. It also has centres in Camden.
- The Royal College of Art in Kensington Gore.
Public libraries

The London Library, an independent lending library, is at 14 St James Square.[29][30]
The city operates two reference libraries; Westminster Reference Library and Marylebone Information Service.[31] Westminster Reference Library holds several special collections: of which the Sherlock Holmes, Arts and Business collections are the most comprehensive.[32] In addition to the collections in Westminster Reference Library the city has two specialist libraries: the Westminster Music Library, the largest music library in the UK[33] and the Westminster Chinese Library in the Charing Cross Library.[34]
Free City of Westminster operated public lending libraries in Westminster include:
Embassies and High Commissions
Many countries' embassies or High Commissions are in Westminster.
Notable people
Freedom of the City
The following people and military units have received the Freedom of the City of Westminster.
Individuals
- Sir Winston Churchill: 1946.[45]
- Sir Robert Mark: 22 June 1977.[46]
- Margaret Thatcher: 12 December 1990.[47]
Military units
- HMS Westminster, RN: 11 December 2005.[48]
See also
Notes
- Cowie, Robert; Whitehead, Robert (1989). "Lundenwic: The archaeological evidence for middle Saxon London". Antiquity. 63 (241): 706–18. doi:10.1017/S0003598X00076845.
- Gray, p. 68
- Coke, Edward; Hale, Matthew; Nottingham, Heneage Finch, Earl of; Francis Hargrave, Charles Butler (1853). "109b, Note (3) [124]". A commentary upon Littleton. The Institutes of the laws of England. Vol. 1 (1st American, from 19th London ed.). Philadelphia: R. H. Small. Vol. 1 p.164. Archived from the original on 20 May 2016. Retrieved 17 May 2010.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link); "December 1540; Grants, No.30". Letters and Papers, Foreign and Domestic, Henry VIII. Vol. 16: 1540–1541. London: Her Majesty's Stationery Office. 1898. pp. 174–175. Archived from the original on 24 September 2018. Retrieved 5 June 2018 – via British History Online. - "City of Westminster". www.londonancestor.com. Archived from the original on 4 March 2016. Retrieved 30 January 2016.
- Lewis, Samuel, Topographical Dictionary of England, Vol. III, London, 1831
- Equality, Commission for Racial (1985). "Ethnic minorities in Britain: statistical information on the pattern of settlement". Commission for Racial Equality: Table 2.2.
- Data is taken from United Kingdom Casweb Data services of the United Kingdom 1991 Census on Ethnic Data for England, Scotland and Wales (Table 6)
- "Office of National Statistics; 2001 Census Key Statistics". webarchive.nationalarchives.gov.uk. Retrieved 7 September 2021.
- "2011 Census: Ethnic Group, local authorities in England and Wales". webarchive.nationalarchives.gov.uk. Retrieved 15 December 2021.
- "Ethnic group - Office for National Statistics". www.ons.gov.uk. Retrieved 29 November 2022.
- "KS007 - Religion". Retrieved 30 January 2016.
- "2011 census – theme tables". Archived from the original on 4 March 2016. Retrieved 8 January 2016.
- "Religion - Office for National Statistics".
- Office for National Statistics 2011 Census Key Statistics: Tenure Archived 11 February 2003 at the Wayback Machine.
- "London's Poverty Profile". Trust for London. Archived from the original on 19 June 2018. Retrieved 19 June 2018.
- Councillors by political party Archived 8 August 2016 at the Wayback Machine at westminster.gov.uk
- "Westminster (London)". Heraldry of the world. Archived from the original on 2 February 2018. Retrieved 25 October 2015.
- BBC (15 August 2005). "Where Is The Centre Of London?". www.bbc.co.uk. Retrieved 5 July 2023.
- "London's Rail and Tube Services" (PDF). Transport for London. Archived from the original (PDF) on 10 April 2019.
- "Explore our Network". Southeastern. Archived from the original on 18 April 2019.
- "Route Map". Chiltern Railways. Archived from the original on 27 April 2019.
- "Network Map" (PDF). Great Western Railway. Archived from the original (PDF) on 27 April 2019.
- "Elizabeth line Map". Transport for London.
- "Route Map" (PDF). Southern. Archived from the original (PDF) on 27 April 2019.
- "City of Westminster: Additional on street charging points for electric vehicles". Archived from the original on 5 May 2009. Retrieved 4 April 2012.
- "Electric Vehicles". Archived from the original on 23 December 2018. Retrieved 22 December 2018.
- "2011 Census: QS701EW Method of travel to work, local authorities in England and Wales". Office for National Statistics. Archived from the original on 15 September 2013. Retrieved 23 November 2013. Percentages are of all residents aged 16–74 including those not in employment. Respondents could only pick one mode, specified as the journey's longest part by distance.
- Westminster Education service accessed 17 May 2007
- "Libraries Archived 8 May 2009 at the Wayback Machine." City of Westminster. Retrieved on 21 January 2009.
- "Visit Archived 3 March 2016 at the Wayback Machine." The London Library. Retrieved on 21 January 2009.
- "Westminster Find a Library Archived 24 September 2018 at the Wayback Machine." City of Westminster. Retrieved on 25 September 2015.
- "Westminster Reference Library Archived 13 March 2016 at the Wayback Machine." City of Westminster. Retrieved on 25 September 2015.
- ";Westminster Music Library Archived 14 April 2009 at the Wayback Machine." City of Westminster. Retrieved on 21 January 2009.
- "Westminster Chinese Library Archived 7 February 2009 at the Wayback Machine." City of Westminster. Retrieved on 21 January 2009.
- "Charing Cross Library Archived 31 January 2009 at the Wayback Machine." City of Westminster. Retrieved on 21 January 2009.
- "Church Street Library Archived 5 February 2009 at the Wayback Machine." City of Westminster. Retrieved on 21 January 2009.
- "Maida Vale Library Archived 5 February 2009 at the Wayback Machine." City of Westminster. Retrieved on 21 January 2009.
- "Marylebone Library Archived 7 February 2009 at the Wayback Machine." City of Westminster. Retrieved on 21 January 2009.
- "Mayfair Library Archived 5 February 2009 at the Wayback Machine." City of Westminster. Retrieved on 21 January 2009.
- "Paddington Library Archived 29 January 2009 at the Wayback Machine." City of Westminster. Retrieved on 21 January 2009.
- "Pimlico Library Archived 5 February 2009 at the Wayback Machine." City of Westminster. Retrieved on 21 January 2009.
- "Queen's Park Library Archived 31 January 2009 at the Wayback Machine." City of Westminster. Retrieved on 21 January 2009.
- "St. John's Wood Library Archived 15 February 2009 at the Wayback Machine." City of Westminster. Retrieved on 21 January 2009.
- "Victoria Library Archived 17 February 2009 at the Wayback Machine." City of Westminster. Retrieved on 21 January 2009.
- "Churchill Receives Freedom of Westminster". Archived from the original on 2 November 2021 – via YouTube.
- "Recognition & Awards". Archived from the original on 7 October 2019. Retrieved 7 October 2019.
- "Speech receiving Freedom of City of Westminster". Margaret Thatcher Foundation. 12 December 1990. Archived from the original on 30 November 2018. Retrieved 30 November 2018.
- "Ship is granted freedom of city". 11 December 2005. Archived from the original on 7 October 2019. Retrieved 7 October 2019 – via news.bbc.co.uk.
References
- Gray, Robert, A History of London, Hutchinson & Co, London, 1978, ISBN 0-09-133140-4
External links
- City of Westminster
- Westminster, by Sir Walter Besant and Geraldine Edith Mitton and A. Murray Smith, 1902, from Project Gutenberg
- Westminster City Council YouTube channel
- West End Extra: A local newspaper covering the City of Westminster