Polmacoxib
Polmacoxib (trade name Acelex) is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) used to treat osteoarthritis. It was developed as CG100649 and approved for use in South Korea in February 2015.[1] It inhibits the enzymes carbonic anhydrase and COX-2. A study in healthy volunteers showed drug effects on urinary prostaglandin metabolites for both polmacoxib and celecoxib that suggest a similar cardiovascular risk profile.[2] Further work by this group developed dose-exposure relationships of polmacoxib to guide clinical development strategies.[3]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Acelex |
| Other names | CG100649 |
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
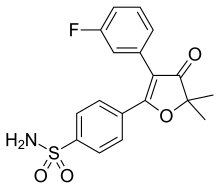
| Formula | C18H16FNO4S |
| Molar mass | 361.39 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
References
- "CrystalGenomics Receives MFDS Approval for Acelex (Polmacoxib)". PR Newswire.
- Skarke C, Alamuddin N, Lawson JA, Cen L, Propert KJ, Fitzgerald GA (June 2012). "Comparative impact on prostanoid biosynthesis of celecoxib and the novel nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug CG100649". Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics. 91 (6): 986–93. doi:10.1038/clpt.2012.3. PMC 3740579. PMID 22278334.
- Hirankarn S, Barrett JS, Alamuddin N, FitzGerald GA, Skarke C (October 2013). "GCG100649, A Novel Cyclooxygenase-2 Inhibitor, Exhibits a Drug Disposition Profile in Healthy Volunteers Compatible With High Affinity to Carbonic Anhydrase-I/II: Preliminary Dose-Exposure Relationships to Define Clinical Development Strategies". Clinical Pharmacology in Drug Development. 2 (4): 379–86. doi:10.1002/cpdd.47. PMID 27121942. S2CID 35992507.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.