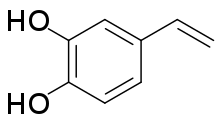
3,4-Dihydroxystyrene
3,4-Dihydroxystyrene (DHS) is a centrally-acting inhibitor of the enzyme phenylalanine hydroxylase (PH).[1] It is likely that DHS and other PH inhibitors will never have clinical applications on account of their capacity for inducing hyperphenylalaninemia and phenylketonuria.
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C8H8O2 |
| Molar mass | 136.150 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| | |
See also
References
- Koizumi S, Matsushima Y, Nagatsu T, Iinuma H, Takeuchi T, Umezawa H (September 1984). "3,4-dihydroxystyrene, a novel microbial inhibitor for phenylalanine hydroxylase and other pteridine-dependent monooxygenases". Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Protein Structure and Molecular Enzymology. 789 (2): 111–8. doi:10.1016/0167-4838(84)90194-8. PMID 6148105.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.