Brofaromine
Brofaromine (proposed brand name Consonar) is a reversible inhibitor of monoamine oxidase A (RIMA) discovered by Ciba-Geigy.[1] The compound was primarily researched in the treatment of depression and anxiety but its development was dropped before it was brought to market.[2]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Protein binding | 98% |
| Elimination half-life | 9-14 hours |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
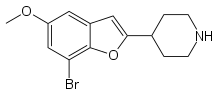
| Formula | C14H16BrNO2 |
| Molar mass | 310.191 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| (verify) | |
Brofaromine also acts as a serotonin reuptake inhibitor, and its dual pharmacologic effects offered promise in the treatment of a wide spectrum of depressed patients while producing less severe anticholinergic side effects in comparison with older standard drugs like the tricyclic antidepressants.
Pharmacology
Brofaromine is a reversible inhibitor of monoamine oxidase A (RIMA, a type of monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI)) and acts on epinephrine (adrenaline), norepinephrine (noradrenaline), serotonin, and dopamine. Unlike standard MAOIs, possible side effects do not include cardiovascular complications (hypertension) with encephalopathy, liver toxicity or hyperthermia.
See also
References
- US Patent 4210655
- Lotufo-Neto F, Trivedi M, Thase ME (1999). "Meta-analysis of the reversible inhibitors of monoamine oxidase type A moclobemide and brofaromine for the treatment of depression". Neuropsychopharmacology. 20 (3): 226–47. doi:10.1016/S0893-133X(98)00075-X. PMID 10063483. Free full text