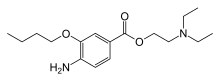
Oxybuprocaine
Oxybuprocaine (INN), also known as benoxinate or BNX, is an ester-type local anesthetic, which is used especially in ophthalmology and otolaryngology. Oxybuprocaine is sold by Novartis under the brand names Novesine or Novesin.
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Novesin(e) |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | Topical |
| ATC code | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Metabolism | Esterases in blood plasma and liver |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C17H28N2O3 |
| Molar mass | 308.422 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| (verify) | |
Safety for use in pregnancy and lactation has not been established.
Uses
- In ophthalmology in order to numb the surface of the eye (the outermost layers of the cornea and conjunctiva) for the following purposes:[1]
- in order to perform a contact/applanation tonometry,
- for small operations,
- in order to remove small foreign objects from the uppermost layer of the cornea or conjunctiva;
- in otolaryngology for numbing the mucous membranes of the nostrils and pharynx, for diagnostic purposes and small operations,[2]
- for numbing the mucous membranes of bronchi, for example in bronchoscopy,[2]
Pharmacokinetics
Anaesthesia starts with a latency of 30 to 50 seconds and lasts for about 10 to 30 minutes, depending on perfusion. The drug is metabolised by esterases in blood plasma and liver.[2]
Adverse effects
When used excessively, oxybuprocaine like any other topical anesthetic used in the eye and on mucous membranes (like for example tetracaine, proxymetacaine and proparacaine) can cause irritation, hypersensitivity, anaphylaxis, irreversible corneal damage and even complete destruction of the cornea.[1][3] (Excessive use means several times a day during several days or even weeks.)
Interactions
Oxybuprocaine is incompatible with silver and mercury salts, as well as basic substances. It also reduces the antimicrobial action of sulfonamides.[2]
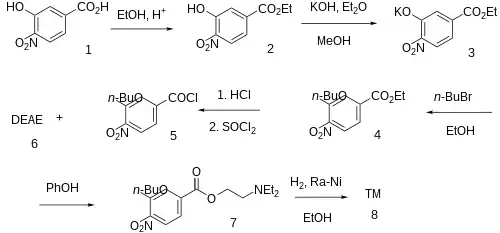
Synthesis
The nitration of 3-hydroxybenzoic acid [99-06-9] (0) gives 3-hydroxy-4-nitrobenzoic acid [619-14-7] (1). Fischer esterification with ethanol gives ethyl 3-hydroxy-4-nitrobenzoate [717-01-1] (2). The phenoxide ion was then prepared from potash (3). Alkylation with 1-bromobutane supplied ethyl 3-butoxy-4-nitrobenzoate, CID:13346201 (4). The product is crystallized from hydrochloric acid, and then halogenation with thionyl chloride gives 3-butoxy-4-nitrobenzoyl chloride [23442-21-9] (5). Esterification with diethylaminoethanol [100-37-8] (6) gives 2-(diethylamino)ethyl 3-butoxy-4-nitrobenzoate, CID:13346204 (7) Lastly, catalytic hydrogenation over Raney-Nickel completes the synthesis of Oxybuprocaine (8).
See also
References
- Drugs.com: Minims Oxybuprocaine Hydrochloride 0.4%
- Jasek W, ed. (2007). Austria-Codex (in German) (2007/2008 ed.). Vienna: Österreichischer Apothekerverlag. ISBN 978-3-85200-181-4.
- McGee HT, Fraunfelder FW (November 2007). "Toxicities of topical ophthalmic anesthetics". Expert Opinion on Drug Safety. 6 (6): 637–40. doi:10.1517/14740338.6.6.637. PMID 17967152. S2CID 44377478.
- Büchi, J.; Stünzi, Elisabeth; Flury, M.; Hirt, R.; Labhart, P.; Ragaz, L. (1951). "Über lokalanästhetisch wirksame basische Ester und Amide verschiedener Alkoxy-amino-benzoesäuren". Helvetica Chimica Acta. 34 (4): 1002–1013. doi:10.1002/hlca.19510340404.
- Anon., GB 654484 (1951 to Wander AG).
- Lai Fuping, CN 106810463 (2017 to Shenzhen Oasis Pharmaceutical Co Ltd).
- 叶芳, CN 105669462A (2016).