Thrombophlebitis
Thrombophlebitis is a phlebitis (inflammation of a vein) related to a thrombus (blood clot).[2] When it occurs repeatedly in different locations, it is known as thrombophlebitis migrans (migratory thrombophlebitis).[3]
| Thrombophlebitis | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Phlebitis[1] |
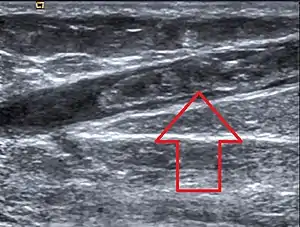 | |
| Ultrasonographic image showing thrombosis of the great saphenous vein. | |
| Specialty | Cardiology |
| Symptoms | Skin redness[1] |
| Risk factors | Smoking, Lupus[1] |
| Diagnostic method | Doppler ultrasound, Venography[1] |
| Treatment | Blood thinners, Pain medication[1] |
Signs and symptoms
The following symptoms or signs are often associated with thrombophlebitis, although thrombophlebitis is not restricted to the veins of the legs.[1][4]
- Pain (area affected)
- Skin redness/inflammation
- Edema
- Veins hard and cord-like
- Tenderness
Complications
In terms of complications, one of the most serious occurs when the superficial blood clot is associated with a deep vein thrombosis; this can then dislodge, traveling through the heart and occluding the dense capillary network of the lungs This is a pulmonary embolism which can be life-threatening.[5]
Causes

Thrombophlebitis causes include disorders related to increased tendency for blood clotting and reduced speed of blood in the veins such as prolonged immobility; prolonged traveling (sitting) may promote a blood clot leading to thrombophlebitis but this occurs relatively less. High estrogen states such as pregnancy, estrogen replacement therapy, or oral contraceptives are associated with an increased risk of thrombophlebitis.[1][4][6]
Specific disorders associated with thrombophlebitis include superficial thrombophlebitis which affects veins near the skin surface, deep vein thrombosis which affects deeper veins, and pulmonary embolism.[7]
Those with familial clotting disorders such as protein S deficiency, protein C deficiency, or factor V Leiden are also at increased risk of thrombophlebitis. Thrombophlebitis can be found in people with vasculitis including Behçet's disease. Thrombophlebitis migrans can be a sign of malignancy – Trousseau sign of malignancy.[8]
Diagnosis
The diagnosis for thrombophlebitis is primarily based on the appearance of the affected area. Frequent checks of the pulse, blood pressure, and temperature may be required. If the cause is not readily identifiable, tests may be performed to determine the cause, including the following:[1][4]
- Doppler ultrasound
- Extremity arteriography
- Blood coagulation studies (Blood clotting tests)
Prevention
Prevention consists of walking, drinking fluids and if currently hospitalized, changing of IV lines.[1] Walking is especially suggested after a long period seated, particularly when one travels.[9]
Treatment
In terms of treatment for this condition the individual may be advised to do the following: raise the affected area to decrease swelling, and relieve pressure off of the affected area so it will encounter less pain. In certain circumstances drainage of the clot might be an option. In general, treatment may include the following:[1][4][5]
- Low molecular weight heparin
- Warfarin
- Surgery
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications (NSAIDS) (Ibuprofen)
- Support stockings
Epidemiology
Thrombophlebitis occurs almost equally between women and men, though males do have a slightly higher possibility. The average age of developing thrombophlebitis, based on analyzed incidents, is 54 for men and 58 for women.[5]
See also
References
- "Thrombophlebitis: MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia". medlineplus.gov. Retrieved 23 September 2016.
- Torpy JM, Burke AE, Glass RM (July 2006). "JAMA patient page. Thrombophlebitis". JAMA. 296 (4): 468. doi:10.1001/jama.296.4.468. PMID 16868304.
- Jinna, Sruthi; Khoury, John (2020). "Migratory Thrombophlebitis". StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. PMID 31613482.
- "Thrombophlebitis Clinical Presentation: History, Physical Examination, Causes". emedicine.medscape.com. Retrieved 23 October 2016.
- Raval, P. (1 January 2014). "Thrombophlebitis☆". Reference Module in Biomedical Sciences. Elsevier. doi:10.1016/B978-0-12-801238-3.05368-X. ISBN 9780128012383. Retrieved 2 January 2021.
- Philbrick, John T.; Shumate, Rebecca; Siadaty, Mir S.; Becker, Daniel M. (23 October 2016). "Air Travel and Venous Thromboembolism: A Systematic Review". Journal of General Internal Medicine. 22 (1): 107–114. doi:10.1007/s11606-006-0016-0. ISSN 0884-8734. PMC 1824715. PMID 17351849.
- "Superficial Thrombophlebitis: Background, Pathophysiology, Etiology". eMedicine. Medscape. 12 July 2016. Retrieved 23 October 2016.
- Varki, Ajit (15 September 2007). "Trousseau's syndrome: multiple definitions and multiple mechanisms". Blood. 110 (6): 1723–1729. doi:10.1182/blood-2006-10-053736. ISSN 0006-4971. PMC 1976377. PMID 17496204.
- Tamparo, Carol D. (2016). Diseases of the Human Body. F.A. Davis. p. 292. ISBN 9780803657915. Retrieved 23 October 2016.
Further reading
- Sadick, Neil S.; Khilnani, Neil; Morrison, Nick (2012). Practical Approach to the Management and Treatment of Venous Disorders. Springer Science & Business Media. ISBN 9781447128915. Retrieved 23 October 2016.
- Mulholland, Michael W.; Lillemoe, Keith D.; Doherty, Gerard M.; Maier, Ronald V.; Simeone, Diane M.; Upchurch, Gilbert R. (2012). Greenfield's Surgery: Scientific Principles & Practice. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. ISBN 9781451152920. Retrieved 23 October 2016.