Glucose-galactose malabsorption
| Glucose-galactose malabsorption | |
|---|---|
| Other names: SGLT1 deficiency | |
_(1)_(1).jpg.webp) | |
| Glucose-galactose malabsorption due to a genetic defect in SGLT1 expression[1] | |
| Treatment | avoidance of glucose and galactose |
Glucose-galactose malabsorption is a rare condition in which the cells lining the intestine cannot take in the sugars glucose and galactose, which prevents proper digestion of these molecules and larger molecules made from them.
Glucose and galactose are called simple sugars, or monosaccharides. Sucrose and lactose are called disaccharides because they are made from two simple sugars, and are broken down into these simple sugars during digestion. Sucrose is broken down into glucose and another simple sugar called fructose, and lactose is broken down into glucose and galactose. As a result, lactose, sucrose and other compounds made from carbohydrates cannot be digested by individuals with glucose-galactose malabsorption.
Signs and symptoms
The presentation of Glucose-galactose malabsorption is as follows:[2]
- Diarrhea
Genetics
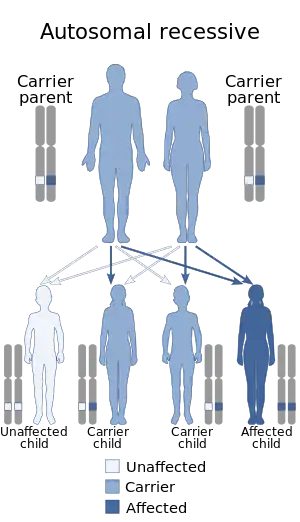
The SLC5A1 gene provides instructions for producing a sodium/glucose cotransporter protein called SGLT1.[3] This protein is found mainly in the intestinal tract and, to a lesser extent, in the kidneys, where it is involved in transporting glucose and the structurally similar galactose across cell membranes. The sodium/glucose cotransporter protein is important in the functioning of intestinal epithelial cells, which are cells that line the walls of the intestine. These cells have fingerlike projections called microvilli that absorb nutrients from food as it passes through the intestine. Based on their appearance, groups of these microvilli are known collectively as the brush border. The sodium/glucose cotransporter protein is involved in the process of glucose uptake in the instesinal cells due to a sodium gradient across the membrane. This is a secondary active transport because the sodium gradient generated for the functioning of the sodium/calcium exchanger is created by the sodium/potassium pump which requires ATP. Sodium and water are transported across the brush border along with the sugars in this process.
Mutations that prevent the sodium/glucose cotransporter protein from performing this function result in a buildup of glucose and galactose in the intestinal tract. This failure of active transport prevents the glucose and galactose from being absorbed and providing nourishment to the body. In addition, the water that normally would have been transported across the brush border with the sugar instead remains in the intestinal tract to be expelled with the stool, resulting in dehydration of the body's tissues and severe diarrhea.
This condition is inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern, which means two copies of the gene in each cell are altered. Most often, the parents of an individual with an autosomal recessive disorder each carry one copy of the altered gene but do not show signs and symptoms of the disorder. In some cases, individuals with one altered gene have reduced levels of glucose absorption capacity as measured in laboratory tests, but this has not generally been shown to have significant health effects.
Diagnosis
Glucose-galactose malabsorption generally becomes apparent in the first few weeks of a baby's life. Affected infants experience severe diarrhea resulting in life-threatening dehydration, increased acidity of the blood and tissues (acidosis), and weight loss when fed breast milk or regular infant formulas. However, they are able to digest fructose-based formulas that do not contain glucose or galactose. Some affected children are better able to tolerate glucose and galactose as they get older.
Small amounts of glucose in the urine (mild glucosuria) may occur intermittently in this disorder. Affected individuals may also develop kidney stones or more widespread deposits of calcium within the kidneys.
Glucose-galactose malabsorption is a rare disorder; only a few hundred cases have been identified worldwide. However, as many as 10 percent of the population may have a somewhat reduced capacity for glucose absorption without associated health problems. This condition may be a milder variation of glucose-galactose malabsorption.[4]
Treatment
Treatment mainly consists of introducing formulas that are based on fructose and a regular diet deficient in glucose and galactose (and the disaccharides sucrose and lactose) products and ingredients.[5]
See also
References
- ↑ Berni Canani, Roberto; Pezzella, Vincenza; Amoroso, Antonio; Cozzolino, Tommaso; Di Scala, Carmen; Passariello, Annalisa (10 March 2016). "Diagnosing and Treating Intolerance to Carbohydrates in Children". Nutrients. 8 (3): 157. doi:10.3390/nu8030157. ISSN 2072-6643. Archived from the original on 23 January 2023. Retrieved 19 November 2023.
- ↑ "Entry - #606824 - GLUCOSE/GALACTOSE MALABSORPTION; GGM - OMIM". omim.org. Archived from the original on 15 March 2023. Retrieved 19 November 2023.
- ↑ Wright EM, Turk E, Martin MG (2002). "Molecular basis for glucose-galactose malabsorption". Cell Biochem. Biophys. 36 (2–3): 115–21. doi:10.1385/CBB:36:2-3:115. PMID 12139397. S2CID 25248625.
- ↑ "Orphanet: Glucose galactose malabsorption". Archived from the original on 2017-12-01. Retrieved 2023-05-07.
- ↑ Glucose galactose malabsorption. National Center for Biotechnology Information (US). 1998. Archived from the original on 2022-08-14. Retrieved 2023-05-07.
External links
- National Library of Medicine. Genetics Home Reference- Glucose-galactose malabsorption Archived 2010-04-08 at the Wayback Machine
| Classification | |
|---|---|
| External resources |
|