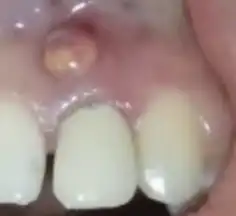
Intraoral dental sinus
| Intraoral dental sinus | |
|---|---|
| Other names: Parulis, intraoral dental sinus | |
 | |
| Intraoral dental sinus | |
| Specialty | Dentistry |
| Symptoms | Toothache, small bump on gum, leaking fluid[1] |
| Causes | Response to an infected sinus discharging from a longterm dental abscess from a dead tooth[2] |
| Diagnostic method | Appearance, X-rays[2] |
| Treatment | Tooth extraction[1] |
| Medication | Antibiotics[1] |
Intraoral dental sinus, also termed gum boil or parulis, is a small bump on the gum.[2] There is usually a history of toothache and leaking fluid in the mouth.[1]
It is formed of inflammed granulation tissue in response to an infected sinus discharging from a longterm dental abscess from a dead tooth.[2]
Diagnosis is by its appearance and X-rays.[2] Treatment is by removing the affected tooth.[1] Antibiotics such as metronidazole or penicillin may be considered.[1] It can take a couple of weeks for the sinus to heal, and may leave a mark or scar.[1]
Cause and mechanism
It develops on the alveolar process in association with a non-vital tooth and accompanying dental abscess.[3] It is made up of inflamed granulation tissue.[2]
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 "Dental sinus | DermNet NZ". dermnetnz.org. Archived from the original on 7 April 2022. Retrieved 19 April 2022.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Gupta, Ruchi; Hegde, Jayshree; Prakash, Vijay; Srirekha, A. (2019). "31. Periodical pathology". Concise Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics. New Delhi: Elsevier. pp. 505–506. ISBN 978-81-312-5343-4. Archived from the original on 2022-04-19. Retrieved 2022-04-17.
- ↑ Rapini, Ronald P.; Bolognia, Jean L.; Jorizzo, Joseph L. (2007). Dermatology: 2-Volume Set. St. Louis: Mosby. ISBN 978-1-4160-2999-1.
This article is issued from Offline. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.