Dental fluorosis
| Dental fluorosis | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Mottled enamel[1] |
.png.webp) | |
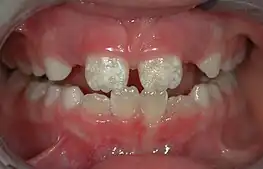
| Mild fluorosis: in its usual mildest form, fluorosis appears as opaque white patches on the enamel | |
| Specialty | Dentistry |
Dental fluorosis is a common[2] disorder, characterized by hypomineralization of tooth enamel caused by ingestion of excessive fluoride during enamel formation.[3]
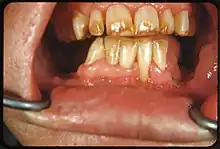
It appears as a range of visual changes in enamel[4] causing degrees of intrinsic tooth discoloration, and, in some cases, physical damage to the teeth. The severity of the condition is dependent on the dose, duration, and age of the individual during the exposure.[1] The "very mild" (and most common) form of fluorosis, is characterized by small, opaque, "paper white” areas scattered irregularly over the tooth, covering less than 25% of the tooth surface. In the "mild" form of the disease, these mottled patches can involve up to half of the surface area of the teeth. When fluorosis is moderate, all of the surfaces of the teeth are mottled and teeth may be ground down and brown stains frequently "disfigure" the teeth. Severe fluorosis is characterized by brown discoloration and discrete or confluent pitting; brown stains are widespread and teeth often present a corroded-looking appearance.[1]
People with fluorosis are relatively resistant to dental caries (tooth decay caused by bacteria),[2] although there may be cosmetic concern.[2] In moderate to severe fluorosis, teeth are weakened and suffer permanent physical damage.[5]
Diagnosis

The adequate diagnosis of fluorosis can be diagnosed by visual clinical examination. This requires inspection of dry and clean tooth surfaces under a good lighting.[6] There are individual variations in clinical fluorosis manifestation which are highly dependent on the duration, timing, and dosage of fluoride exposure.There are different classifications to diagnose the severity based on the appearances. The clinical manifestation of mild dental fluorosis is mostly characterised a snow flaking appearance that lack a clear border, opaque, white spots, narrow white lines following the perikymata or patches as the opacities may coalesce with an intact, hard and smooth enamel surface on most of the teeth.[7] With increasing severity, the subsurface enamel, all along the tooth becomes more porous. Enamel may appear yellow/ brown discolouration and/ or many and pitted white-brown lesions that look like cavities. They are often described as “mottled teeth”.[8] Fluorosis does not cause discolouration to the enamel directly, as upon eruption into the mouth, affected permanent teeth are not discoloured yet. In dental enamel, fluorosis causes subsurface porosity or hypomineralizations, which extend toward the dentinal-enamel junction as the condition progresses and the affected teeth become more susceptible to staining. Due to diffusion of exogenous ions (e.g., iron and copper), stains develop into the increasingly and abnormally porous enamel.[7]
The differential diagnosis for this condition includes:
- Turner's hypoplasia (although this is usually more localized)
- Enamel defects caused by an undiagnosed and untreated celiac disease.[9]
- Some mild forms of amelogenesis imperfecta and enamel hypoplasia
- Enamel defects caused by infection of a primary tooth predecessor
- Dental caries: Fluorosis-resembling enamel defects are often misdiagnosed as dental caries.[10]
- Dental Trauma: Mechanical trauma to the primary tooth may cause disturbance to the maturation phase of enamel formation, which may result in enamel opacities on the permanent successors.[11]
Classification

The two main classification systems are described below. Others include the tooth surface fluorosis index (Horowitz et al. 1984), which combines Deans index and the TF index; and the fluorosis risk index (Pendrys 1990), which is intended to define the time at which fluoride exposure occurs, and relates fluorosis risk with tooth development stage.[12]
Dean's index
Dean's fluorosis index was first published in 1934 by H. Trendley Dean. The index underwent two changes, appearing in its final form in 1942.[5] An individual's fluorosis score is based on the most severe form of fluorosis found on two or more teeth.[6]
| Classification | Code | Criteria – description of enamel |
|---|---|---|
| Normal | 0 | The enamel represents the usual translucent semivitriform (glass-like) type of structure. The surface is smooth, glossy and usually of pale creamy white color |
| Questionable | 1 | The enamel discloses slight aberrations from the translucency of normal enamel, ranging from a few white flecks to occasional white spots. This classification is utilised in those instances where a definite diagnosis is not warranted and a classification of ‘normal’ not justified |
| Very Mild | 2 | Small, opaque, paper white areas scattered irregularly over the tooth but not involving as much as approximately 25% of the tooth surface. Frequently included in this classification are teeth showing no more than about 1 – 2mm of white opacity at the tip of the summit of the cusps, of the bicuspids or second molars. |
| Mild | 3 | The white opaque areas in the enamel of the teeth are more extensive but do involve as much as 50% of the tooth. |
| Moderate | 4 | All enamel surfaces of the teeth are affected and surfaces subject to attrition show wear. Brown stain is frequently a disfiguring feature |
| Severe | 5 | All enamel surfaces are affected and hypoplasia is so marked that the general form of the tooth may be affected. The major diagnostic sign of this classification is discrete or confluent pitting. Brown stains are widespread and teeth often present a corroded-like appearance. |
TF index
Proposed by Thylstrup and Fejerskov in 1978, the TF index represents a logical extension of Dean's index, incorporating modern understanding of the underlying pathology of fluorosis.[12] It scores the spectrum of fluorotic changes in enamel from 0 to 9, allowing more precise definition of mild and severe cases.[13]
Causes
Dental fluorosis is caused by a higher than normal amount of fluoride ingestion whilst teeth are forming. Primary dentine fluorosis and enamel fluorosis can only happen during tooth formation, so fluoride exposure occurs in childhood. Enamel fluorosis has a white opaque appearance which is due to the surface of the enamel being hypomineralised.[14]
The most superficial concern in dental fluorosis is aesthetic changes in the permanent dentition (the adult teeth). The period when these teeth are at highest risk of developing fluorosis is between when the child is born up to 6 years old, though there has been some research which proposes that the most crucial course is during the first 2 years of the child's life.[15][16] From roughly 7 years old thereafter, most children's permanent teeth would have undergone complete development (except their wisdom teeth), and therefore their susceptibility to fluorosis is greatly reduced, or even insignificant, despite the amount of intake of fluoride.[17] The severity of dental fluorosis depends on the amount of fluoride exposure, the age of the child, individual response, weight, degree of physical activity, nutrition, and bone growth.[18] Individual susceptibility to fluorosis is also influenced by genetic factors.[19]
Many well-known sources of fluoride may contribute to overexposure including dentifrice/fluoridated mouthrinse (which young children may swallow), excessive ingestion of fluoride toothpaste, bottled waters which are not tested for their fluoride content, inappropriate use of fluoride supplements, ingestion of foods especially imported from other countries, and public water fluoridation.[20] The last of these sources is directly or indirectly responsible for 40% of all fluorosis, but the resulting effect due to water fluoridation is largely and typically aesthetic.[20][21] Severe cases can be caused by exposure to water that is naturally fluoridated to levels above the recommended levels, or by exposure to other fluoride sources such as brick tea or pollution from high fluoride coal.[22]
Dental fluorosis has been growing in the United States concurrent with fluoridation of municipal water supplies, although disproportionately by race.[23] A 2010 CDC report acknowledges an overall incidence of dental fluorosis of 22% from 1986-87 increased to 41% in the early 21st century, with an increase in moderate to severe dental fluorosis from 1% to 4%.[24] The 2011-12 NHANES figures documented another 31% overall increase among American teens since the previous decade, with a total adolescent population impact of 61% afflicted. More than one in five American teens (23%) have moderate to severe dental fluorosis on at least two teeth.[25]
Mechanism
Teeth are the most studied body tissues to examine the impact of fluoride to human health. There are a few possible mechanisms that have been proposed. It is generally believed that the hypomineralization of affected enamel is mainly due to in-situ toxic effects of the fluoride on the ameloblasts in the enamel formation, and not caused by the general effects of fluoride on the calcium metabolism, or by the poisoning effects that suppress the fluoride metabolism. However, despite decades of research and studies, there have yet to be any studies that substantiates the believed mechanism whereby dental fluorosis is a result of alteration in the mineralisation that takes place when fluroide interacts with mineralising tissues.[26]
In the extra-cellular environment of maturing enamel, an excess of fluoride ions alters the rate at which enamel matrix proteins (amelogenin) are enzymatically broken down and the rate at which the subsequent breakdown products are removed.[2][12] Fluoride may also indirectly alter the action of protease via a decrease in the availability of free calcium ions in the mineralization environment.[12] This results in the formation of enamel with less mineralization. This hypomineralized enamel has altered optical properties and appears opaque and lusterless relative to normal enamel.[2]
Traditionally severe fluorosis has been described as enamel hypoplasia, however, hypoplasia does not occur as a result of fluorosis.[12] The pits, bands, and loss of areas of enamel seen in severe fluorosis are the result of damage to the severely hypomineralized, brittle and fragile enamel which occurs after they erupt into the mouth.[12]
Hydroxyapatite is converted to fluoroapatite in a three step process. Dental fluorosis can be prevented at a population level through defluoridation. It is the downward adjustment of the level of fluoride in drinking water.
Management
Dental fluorosis may or may not be of cosmetic concern. In some cases, there may be varying degrees of negative psychosocial effects. The treatment options are:
- Mild cases: Tooth bleaching[14]
- Moderate cases: Enamel microabrasion (outer affected layer of enamel is abraded in an acidic environment)[14]
- Severe cases: Composite fillings, Micro-abrasion, Veneers, Crowns[14]
Epidemiology
Fluorosis is extremely common, with 41% of adolescents having definite fluorosis, and another 20% "questionably" having fluorosis according to the Centers for Disease Control.[27] As of 2005 surveys conducted by the National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research in the USA between 1986 and 1987[28] and by the Center of Disease Control between 1999 and 2004[27] are the only national sources of data concerning the prevalence of dental fluorosis. Before the 1999-2004 study was published, CDC published an interim report covering data from 1999 to 2002.[29]
| Deans Index | 2002 |
|---|---|
| Questionable fluorosis | 11.5% |
| Very mild fluorosis | 21.68% |
| Mild fluorosis | 6.59% |
| Moderate to severe fluorosis | 3.26% |
| Total confirmed fluorosis prevalence | 31.65% |
| Total confirmed and questionable fluorosis prevalence | 43.15% |
The U.S. Centers for Disease Control found a 9 percentage point increase in the prevalence of confirmed dental fluorosis in a 1999-2002 study of American children and adolescents than was found in a similar survey from 1986-1987 (from 22.8% in 1986-1987 to 32% in 1999-2002). In addition, the survey provides further evidence that African Americans suffer from higher rates of fluorosis than Caucasian Americans.
The condition is more prevalent in rural areas where drinking water is derived from shallow wells or hand pumps. It is also more likely to occur in areas where the drinking water has a fluoride content greater than 1 ppm (part per million).
| Age group | Reference weight kg (lb) | Adequate intake (mg/day) | Tolerable upper intake (mg/day) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Infants 0–6 months | 7 (16) | 0.01 | 0.7 |
| Infants 7–12 months | 9 (20) | 0.5 | 0.9 |
| Children 1–3 years | 13 (29) | 0.7 | 1.3 |
| Children 4–8 years | 22 (48) | 1.0 | 2.2 |
| Children 9–13 years | 40 (88) | 2.0 | 10 |
| Boys 14–18 years | 64
(142) |
3.0 | 10 |
| Girls 14–18 years | 57 (125) | 3.0 | 10 |
| Males 19 years and over | 76 (166) | 4.0 | 10 |
| Females 19 years and over | 61 (133) | 3.0 | 10 |
If the water supply is fluoridated at the level of 1 ppm, one must consume one litre of water in order to take in 1 mg of fluoride. It is thus improbable a person will receive more than the tolerable upper limit from consuming optimally fluoridated water alone.
Fluoride consumption can exceed the tolerable upper limit when someone drinks a lot of fluoride-containing water in combination with other fluoride sources, such as swallowing fluoridated toothpaste, consuming food with a high fluoride content, or consuming fluoride supplements. The use of fluoride supplements as a prevention for tooth decay is rare in areas with water fluoridation, but was recommended by many dentists in the UK until the early 1990s.
In November 2006 the American Dental Association published information stating that water fluoridation is safe, effective and healthy; that enamel fluorosis, usually mild and difficult for anyone except a dental health care professional to see, can result from ingesting more than optimal amounts of fluoride in early childhood; that it is safe to use fluoridated water to mix infant formula; and that the probability of babies developing fluorosis can be reduced by using ready-to-feed infant formula or using water that is either free of fluoride or low in fluoride to prepare powdered or liquid concentrate formula. They go on to say that the way to get the benefits of fluoride but minimize the risk of fluorosis for a child is to get the right amount of fluoride, not too much and not too little. "Your dentist, pediatrician or family physician can help you determine how to optimize your child’s fluoride intake."[30]
Prevention
Dental fluorosis can be prevented by lowering the amount of fluoride intake to below the tolerable upper limit. This can be achieved by consuming de-fluorinated water and improving the general nutritional status of the people.[31]
History
In ancient times, Galen describes what is thought to be dental fluorosis.[12] However, it was not until the early 20th century that dental fluorosis became increasingly recognized and scientifically studied.
In 1901 Eager published the first description of the "mottled enamel" of immigrants from a small village near Naples, Italy.[32] He writes that the condition is called "Denti di Chiaie" (Chiaie teeth), named after Stefano Chiaie, an Italian professor.[32] In the United States of America, a dentist, Frederick McKay, set up practice in Colorado Springs in 1901 and discovered a high proportion of the residents had stained teeth, locally termed the "Colorado brown stain".[12] He took this information to Greene Vardiman Black, a prominent American dentist of the time. After examining specimens of affected enamel, in 1916 Black described the condition as "[a]n endemic imperfection of the enamel of the teeth, heretofore unknown in the literature of dentistry."[12] They made the interesting observation that although the mottled enamel was hypomineralized, and therefore should be more susceptible to decay, this was not the case.[12] Gradually, they became aware of existing and further reports of a similar condition worldwide.[12]
In 1931, 3 different groups of scientists around the world published their discoveries that this condition was caused by fluoride in drinking water during childhood.[33][34][35][36] The condition then started to become termed "dental fluorosis".[36] Through epidemiological studies in the US, Henry Trendley Dean helped to identify a causal link between high concentrations of fluoride in the drinking water and mottled enamel.[12] He also produced a classification system for dental fluorosis that is still used in modern times, Dean's Index.[12] As research continued, the protective effect of fluoride against dental decay was demonstrated.[12]
References
- 1 2 3 Dean JA (10 August 2015). McDonald and Avery's Dentistry for the Child and Adolescent (10th ed.). Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 132. ISBN 978-0-323-28746-3.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Neville BW, Chi AC, Damm DD, Allen CM (13 May 2015). Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology (4th ed.). Elsevier Health Sciences. pp. 52–54. ISBN 978-1-4557-7052-6.
- ↑ Wong MC, Glenny AM, Tsang BW, Lo EC, Worthington HV, Marinho VC (January 2010). "Topical fluoride as a cause of dental fluorosis in children". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (1): CD007693. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD007693.pub2. PMC 8078481. PMID 20091645.
- ↑ Bergc JH, Slayton RL (26 October 2015). Early Childhood Oral Health. John Wiley & Sons. p. 113. ISBN 978-1-118-79210-0.
- 1 2 Meiers P. "HT Dean´s epidemiology of Mottled Teeth". The History of Fluorine, Fluoride and Fluoridation. Retrieved 12 November 2015.
- 1 2 Whelton H, Browne D, Felicia P, Whelton J. "E-training for Dean's Index Version 2". Oral Health Services Research Centre, University College Cork, Ireland. Archived from the original on 4 June 2016. Retrieved 12 November 2015.
- 1 2 Abanto Alvarez J, Rezende KM, Marocho SM, Alves FB, Celiberti P, Ciamponi AL (February 2009). "Dental fluorosis: exposure, prevention and management" (PDF). Medicina Oral, Patologia Oral y Cirugia Bucal. 14 (2): E103–7. PMID 19179949.
- ↑ Ritter AV (2005). "Dental fluorosis". Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry. 17 (5): 326–7. doi:10.1111/j.1708-8240.2005.tb00139.x. PMID 16225799.
- 1 2 Dental Enamel Defects and Celiac Disease Archived March 5, 2016, at the Wayback Machine National Institute of Health (NIH)
- ↑ Sabokseir A, Golkari A, Sheiham A (2016-02-25). "Distinguishing between enamel fluorosis and other enamel defects in permanent teeth of children". PeerJ. 4: e1745. doi:10.7717/peerj.1745. PMC 4782718. PMID 26966672.
- ↑ Skaare AB, Maseng Aas AL, Wang NJ (April 2013). "Enamel defects in permanent incisors after trauma to primary predecessors: inter-observer agreement based on photographs". Dental Traumatology. 29 (2): 79–83. doi:10.1111/j.1600-9657.2012.01153.x. PMID 22676308.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 Fejerskov O, Kidd E (16 March 2009). Dental Caries: The Disease and Its Clinical Management. John Wiley & Sons. pp. 299–327. ISBN 978-1-4443-0928-7.
- ↑ Wagner BM (1993). Health effects of ingested fluoride. Washington, D.C. : National Academy Press. p. 171. ISBN 9786610211333.
- 1 2 3 4 Denbesten P, Li W (2011). "Chronic fluoride toxicity: dental fluorosis". Monographs in Oral Science. 22: 81–96. doi:10.1159/000327028. ISBN 978-3-8055-9659-6. PMC 3433161. PMID 21701193.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ↑ Hong L, Levy SM, Broffitt B, Warren JJ, Kanellis MJ, Wefel JS, Dawson CV (2006). "Timing of fluoride intake in relation to development of fluorosis on maxillary central incisors". Community Dentistry and Oral Epidemiology. 34 (4): 299–309. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0528.2006.00281.x. PMID 16856950.
- ↑ Buzalaf MAR, Levy SM (2011): Fluoride intake of children: considerations for dental caries and dental fluorosis in Fluoride and the Environment. Editor: MAR Buzalaf, Karger, Basel. Pages 1-19
- ↑ "Dental Fluorosis" (PDF).
- ↑ Abanto Alvarez J, Rezende KM, Marocho SM, Alves FB, Celiberti P, Ciamponi AL (February 2009). "Dental fluorosis: exposure, prevention and management" (PDF). Medicina Oral, Patologia Oral y Cirugia Bucal. 14 (2): E103–7. PMID 19179949.
- ↑ Clark MB, Slayton RL (September 2014). "Fluoride use in caries prevention in the primary care setting". Pediatrics. 134 (3): 626–33. doi:10.1542/peds.2014-1699. PMID 25157014.
- 1 2 United States Environmental Protection Agency (2010). "Comment-Response Summary Report for the Peer Review of the Fluoride: Dose-Response Analysis for Non-Cancer Effects Document". Lay summary (PDF) – EPA (2010).
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help); Cite uses deprecated parameter|lay-url=(help) - ↑ Yeung CA (2008). "A systematic review of the efficacy and safety of fluoridation". Evidence-Based Dentistry. 9 (2): 39–43. doi:10.1038/sj.ebd.6400578. PMID 18584000. Lay summary (PDF) – NHMRC (2007).
{{cite journal}}: Cite uses deprecated parameter|lay-date=(help) - ↑ Fawell J, Bailey K, Chilton J, Dahi E, Fewtrell L, Magara Y (2006). "Environmental occurrence, geochemistry and exposure" (PDF). Fluoride in Drinking-water. World Health Organization. pp. 5–27. ISBN 92-4-156319-2. Retrieved 2009-01-24.
- ↑ Beltrán-Aguilar ED, et al. (August 26, 2005). "Surveillance for Dental Caries, Dental Sealants, Tooth Retention, Edentulism, and Enamel Fluorosis — United States, 1988–1994 and 1999–2002". Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report. Surveillance Summaries. 54 (3): 1–44. PMID 16121123.
- ↑ Beltrán-Aguilar, E. D; Barker, L; Dye, B. A (2010). "Prevalence and severity of dental fluorosis in the United States, 1999-2004" (PDF). NCHS Data Brief (53): 1–8. PMID 21211168.
- ↑ Wiener, R. C; Shen, C; Findley, P; Tan, X; Sambamoorthi, U (2018). "Dental Fluorosis over Time: A comparison of National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey data from 2001-2002 and 2011-2012". Journal of Dental Hygiene. 92 (1): 23–29. PMC 5929463. PMID 29500282.
- ↑ Aoba, T; Fejerskov, O (2016). "Dental Fluorosis: Chemistry and Biology". Critical Reviews in Oral Biology & Medicine. 13 (2): 155–70. doi:10.1177/154411130201300206. PMID 12097358.
- 1 2 Beltrán-Aguilar, Eugenio D.; Barker, Laurie; Dye, Bruce A. (2010). "Prevalence and Severity of Dental Fluorosis in the United States, 1999–2004" (PDF). National Center for Health Statistics. PMID 21211168. NCHS data brief, no 53. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2016-06-16. Retrieved 2011-04-26.
- 1 2 Fluoridation Facts (PDF). American Dental Association. 2005. p. 29.
- ↑ "Table 23, Surveillance for Dental Caries, Dental Sealants, Tooth Retention, Edentulism, and Enamel Fluorosis --- United States, 1988--1994 and 1999--2002". Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 2005. Retrieved 2006-10-29.
- ↑ Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ), American Dental Association Website accessed February 4, 2012 Archived January 12, 2016, at the Wayback Machine
- ↑ "Fluorosis: Causes, Diagnosis, Management and Prevention". AIMU.us. August 15, 2017.
- 1 2 Eager JM (November 1, 1901). "Denti di Chiaie (Chiaie teeth)". Public Health Reports. 16 (44): 2576–2577. Reprinted in "Public Health Reports, November 1, 1901: Denti di Chiaie (Chiaie teeth), by J.M. Eager". Public Health Reports. 91 (3): 284–5. 1976. PMC 1438998. PMID 818673.
- ↑ Velu H, Balozet L (1931). "Reproduction experimentale chez Ie mouton de la dystrophie dentaire des animaux des zones phosphates". Bull Acad Vet France. 4: 373.
- ↑ Churchill HV (1931). "Occurrence of fluorides in some water of the United States". Ind Eng Chem. 23 (9): 996–998. doi:10.1021/ie50261a007.
- ↑ Smith MC, Lantz EM, Smith HV (September 1931). "The Cause of Mottled Enamel". Science. 74 (1914): 244. Bibcode:1931Sci....74..244C. doi:10.1126/science.74.1914.244. PMID 17755565.
- 1 2 Teotia SP (1999). "Dental fluorosis" (PDF). The National Medical Journal of India. 12 (3): 96–8. PMID 10492579. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2016-03-04.