Thumbprint sign
| Thumbprint sign | |
|---|---|
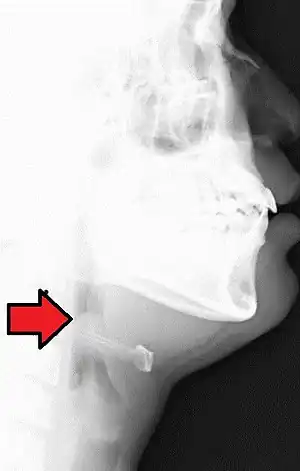 | |
| Lateral radiograph showing the "thumb sign". The diagnosis of epiglottitis was confirmed on subsequent imaging and laryngoscopy. The patient recovered following treatment with predonine and ceftriaxone | |
| Differential diagnosis | epiglottitis |
In radiology, the thumbprint sign, or thumbprinting, is a radiologic sign found on a radiograph that suggests the diagnosis of either epiglottitis or intestinal ischemia.
In a lateral C-spine radiograph, the sign is caused by a thickened free edge of the epiglottis, which causes it to appear more radiopaque than normal, resembling the distal thumb.
In an abdominal radiography, thumbprinting has an appearance of thumbs protruding into the intestinal lumen, and is caused by thickened edematous mucosal folds.[1] Abdominal thumbprinting is a non-specific finding, though one potential cause is intestinal ischemia.[2]
References
- ↑ Page 111 in:Elizabeth D Agabegi; Agabegi, Steven S. (2008). Step-Up to Medicine (Step-Up Series). Hagerstwon, MD: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. ISBN 978-0-7817-7153-5.
- ↑ Acute epiglottitis at eMedicine
External links
This article is issued from Offline. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.