This article was co-authored by wikiHow staff writer, Travis Boylls. Travis Boylls is a Technology Writer and Editor for wikiHow. Travis has experience writing technology-related articles, providing software customer service, and in graphic design. He specializes in Windows, macOS, Android, iOS, and Linux platforms. He studied graphic design at Pikes Peak Community College.
The wikiHow Tech Team also followed the article's instructions and verified that they work.
This article has been viewed 441,747 times.
Learn more...
Do you want to disable certain memory options in your PC's BIOS? Disabling RAM speed caps and frequency limiting options may get you better performance from your RAM. If you are experiencing blue screen errors related to memory, disabling memory caching can fix some of these issues. If your computer doesn't have a lot of RAM, you may want to disable shadow memory to free up much-needed memory. This wikiHow article teaches how to enter the BIOS menu and disable options for memory on a Windows PC.
Things You Should Know
- You can usually find the memory options in the "Advanced" section of the BIOS menu.
- The BIOS menu is different from one computer's manufacturer to the next. Not all BIOS menus have the same RAM options.
- Disabling options in the BIOS may cause performance issues or damage your computer.
Steps
Memory & BIOS: The Basics
-
1Memory is where your computer stores data before processing. The most common type of memory that is used in a computer is Random Access Memory, or RAM. The RAM is stored in removable chips that are inserted into your computer's motherboard. These chips are removable so that you can upgrade your RAM and improve your computer's performance. Your computer can access the data on your RAM much more quickly than the data on your hard drive. But unlike the data stored on your hard drive, the data stored in your RAM is temporary and disappears when you reboot your computer.[1]
-
2BIOS stands for Basic Input/Output System. The BIOS is a ROM chip on your motherboard that contains basic instructions that test your computer's hardware for errors, locate your operating system and pass control of the computer's hardware to the operating system. It also contains a configuration program you can use to configure your computer's hardware settings, including settings related to memory.
How to Access the BIOS
-
1Access the BIOS using the setup key. One way to enter the BIOS is to use the setup key. To do this, you will need to restart your computer and press the BIOS setup key when prompted as your computer is booting up.
- The key you press is different from one computer model to the next. Common BIOS setup keys include; F2, DEL, Esc or one of the other function keys.
- Unfortunately for many newer computers, the bootup process happens so quickly that it's hard to press the Setup key on time. If this is the case, you can boot into the BIOS from within Windows.
-
2Access the BIOS from within Windows. If you are having a tough time accessing the BIOS as your computer boots up, you can boot into the BIOS from within Windows. Use the following steps to boot into the BIOS from within Windows 10 and 11:
- Click the Windows Start menu.
- Click the Gear/Settings icon.
- Click System (Windows 11) or Update & Security (Windows 10).
- Click Recovery.
- Click Restart Now below or next to "Advanced Options".
- Click Troubleshoot.
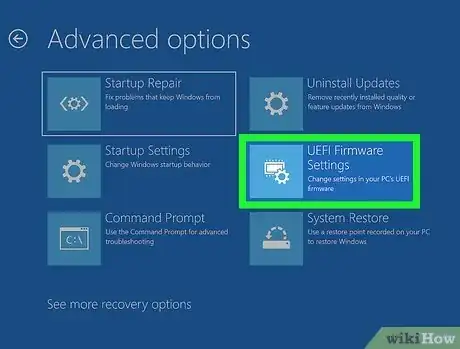
- Click Advanced Options (Windows 11).
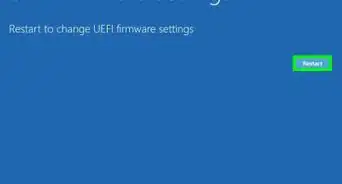
- Click UEFI Firmware Settings.
- Click Restart.
How to Disable Memory Options
-
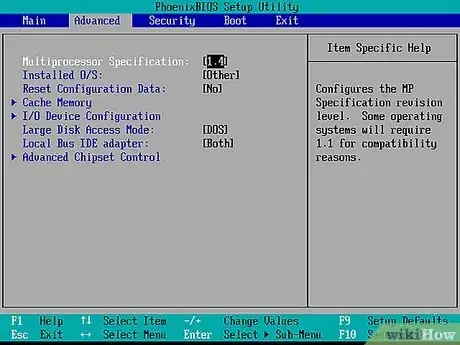
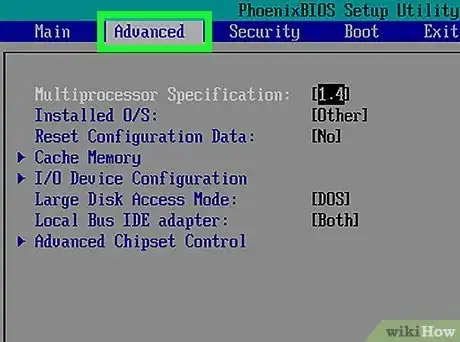
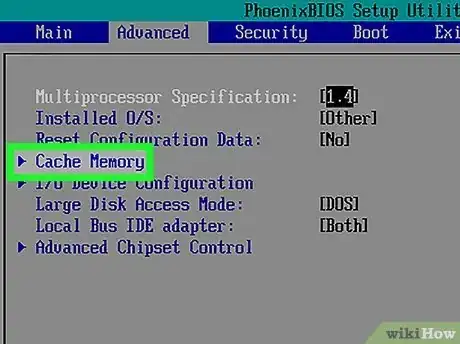
1Go to the "Advanced" page. The BIOS menu is going to look different depending on your computer's make and model. The memory options are usually listed in the "Advanced" section of the BIOS menu. Look for the "Advanced" option at the top of the BIOS menu or in one of the other menus.
- If the memory options are not found in the Advanced menu, check other menus, such as "General," "Settings, "Memory," or "XMP."
- Use the arrow keys on your keyboard to navigate the BIOS menu. Then press Enter to select a menu item.
-
2Look for the memory option you want to disable. Available memory options will vary from one computer's BIOS menu to the next. You may have several memory options that other computers don't have, and vice versa. The following are some memory options that you may find in your BIOS menu:
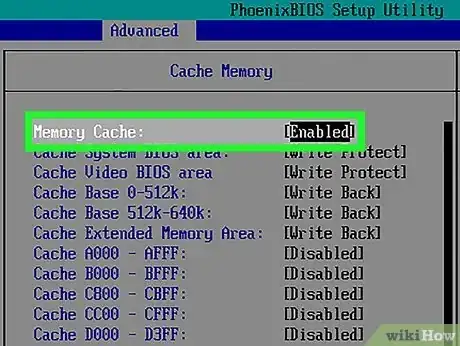
- Memory Caching — Memory caching allows computer programs and applications to store bits of data in the RAM so that it can be quickly accessed. If you are having issues with blue-screen crashes, disabling memory caching may fix the problem.[2]
- Shadow Memory — Shadow memory (also known as "Shadow RAM" or "Shadowing") is when a copy of BIOS routines are saved to the RAM for quicker access. This is useful for many older operating systems (such as DOS), which rely on BIOS for normal operations in addition to the boot-up process. Most newer operating systems (such as Windows) do not use this function. However, it could be useful if your BIOS is ever corrupted and you need to restore your BIOS. If you have a computer that does not have a lot of memory, you may want to consider turning this function off or limiting the amount of RAM it uses.[3]
- Disable RAM — If any of the RAM chips installed on your motherboard aren't working, you may be able to disable them from the BIOS without physically removing it from your computer.
- Frequency Limiter — Memory Frequency Limiter or RAM Frequency Limiter limits your computer's memory and CPU transfer speed. This often lowers your RAM speed below the manufacturer's specifications. Not all BIOS menus have this option or allow you to disable it. If you are not getting the full potential out of your RAM, disabling the frequency limiter and entering your own RAM speed may improve your RAM's performance.
- XMP — Some motherboards support XMP (extreme memory profiles). These profiles allow users to increase select different memory speeds and voltage consumption settings. This allows you to overclock your RAM. If you are using an XMP and your RAM is not behaving properly, you may want to disable this function. You can usually find memory profiles in the XMP section of the BIOS.
- DRAM Settings — DRAM stands for Dynamic Random Access Memory. This is the type of RAM that most computers use. A lot of motherboards limit the speed of your RAM by default. You may be able change the speed and voltage consumption of your RAM in the DRAM settings.[4]
-
3Select a memory item you want to disable. Use the arrow keys to move the selection box onto the "Enabled" or similar text to the right of a memory item. This will select it.
- If you cannot find the option you want to disable in the BIOS menu, you may be able to use third-party apps that change your RAM settings.
-
4Press the "Change" key. The key you use to change options will be different from one BIOS menu to the next. This may be the Enter key or the left and right arrow keys. Doing so will disable your selected memory option.
-
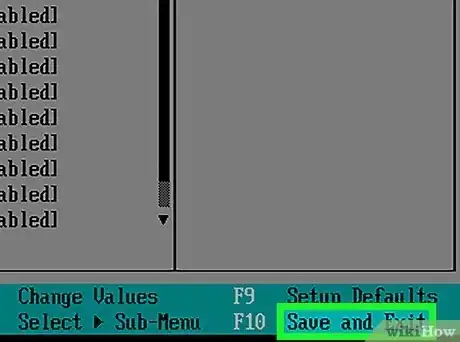
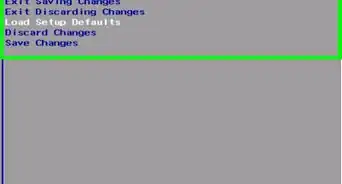
5Save your settings. After you are finished making the changes you want, locate the option to save your settings. This may be a tab that says Save & Exit at the top or another option or a button you press to save your settings.
-
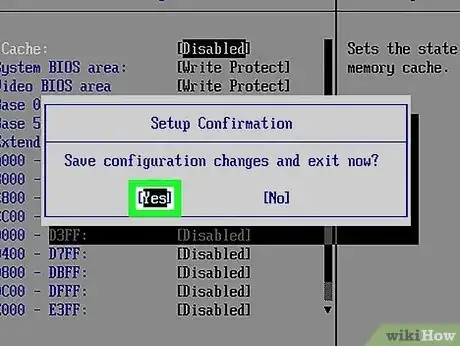
6Confirm that you want to save your settings. You will most likely be asked if you are sure you want to save your settings. Select the option to confirm that you want to save your BIOS and press Enter.
- If you have issues with your RAM or computer after changing your BIOS settings, you may need to reset your BIOS back to it's default settings.
Community Q&A
-
QuestionWhat if I don't have a tab called "advanced?"
 Community AnswerEvery motherboard has a BIOS that is configured uniquely. If you are unfamiliar with your BIOS, maybe you can get a friend who knows a lot about computers to help you. If you have the make and model of the motherboard, you might be able to download information that includes the BIOS.
Community AnswerEvery motherboard has a BIOS that is configured uniquely. If you are unfamiliar with your BIOS, maybe you can get a friend who knows a lot about computers to help you. If you have the make and model of the motherboard, you might be able to download information that includes the BIOS. -
QuestionWhy is it important for the instructions in the BIOS to be permanent?
 Community AnswerIn the BIOS, there are settings, accompanied by instructions that explain each setting. The settings are up to you, but if you pick the wrong ones, your computer may not boot. If you have never accessed the BIOS before, get a geeky friend to help you.
Community AnswerIn the BIOS, there are settings, accompanied by instructions that explain each setting. The settings are up to you, but if you pick the wrong ones, your computer may not boot. If you have never accessed the BIOS before, get a geeky friend to help you. -
QuestionHow can I find my BIOS memory options?
 Community AnswerPress one of the function keys on startup. Once you are in BIOS, find the Advanced tab and find Memory Cache.
Community AnswerPress one of the function keys on startup. Once you are in BIOS, find the Advanced tab and find Memory Cache.
Warnings
- Disabling any components in the BIOS can damage your computer. Be extremely careful not to disable anything you don't need to disable.⧼thumbs_response⧽
References
About This Article
1. Restart your PC.
2. Press and hold Del or F2 to enter BIOS.
3. Select the Advanced tab.
4. Select a memory option to disable.
5. Toggle the option off.
6. Press the Esc key.
7. Save and exit.