This article was co-authored by Pouya Shafipour, MD, MS. Dr. Pouya Shafipour is a Family Medicine Specialist, Primary Care Physician, and a Weight Loss Specialist based in Santa Monica, California. Dr. Shafipour specializes in dietary, nutritional, behavioral, and exercise counseling to manage obesity and medical conditions related to excessive weight gain or loss. Dr. Shafipour received a BS in Molecular and Cell Biology from the University of California, Berkeley, an MS in Physiology and Biophysics from Georgetown University, and an MD from the Loma Linda University School of Medicine. He completed his internship in general surgery at UC Irvine and a residency in family medicine at the University of California, Los Angeles, and became board certified in family medicine in 2008.
There are 19 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page.
wikiHow marks an article as reader-approved once it receives enough positive feedback. In this case, 100% of readers who voted found the article helpful, earning it our reader-approved status.
This article has been viewed 410,418 times.
Humans carry body fat in a variety of places — around the hips and thighs, waist or all over multiple body parts. However, there are different types of fat within the body — subcutaneous and visceral. Subcutaneous fat is the layer of fat found right underneath the skin and generally doesn't impose a huge health risk.[1] Visceral fat, however, is a type of fat that's found in and around the organs especially in the abdominal or belly cavity. It surrounds the stomach, liver and intestines.[2] Visceral body fat is very harmful to your health. It's metabolically active producing harmful substances to the body. In addition, it has be linked to: insulin resistance (which can lead to type 2 diabetes), heart attack, stroke, high blood pressure and certain types of cancers (like breast and colon cancers).[3] However, levels of visceral fat can be managed and reduced with a few diet and lifestyle changes.
Steps
Changing Your Eating Habits
-
1Monitor your total fat intake. Limit dietary fat to about 20–30% of your total caloric intake. This is equal to about 40–70 g of fat daily (based on a 2,000 calorie diet).[4] Higher levels of fat may increase your risk of weight gain or levels of visceral fat.
- Eliminate trans-fats completely. Trans-fats are a type of fat that's man made and has been shown to cause hardening of the coronary arteries and increase visceral fat.[5]
- Reduce saturated fat intake to less than 7% of your total caloric intake. Although saturated fat is not as unhealthy as trans fat, it's important to moderate your intake to an appropriate level. In general, limit your intake to 15–20 g daily (this is based on a 2,000 calorie diet).[6]
-
2Consume heart-healthy fats. Although it's important to monitor your overall fat intake, it's also important to make sure you're consuming the types of dietary fat will improve your health and help support your desire to decrease visceral fat.[7] Some dietary fat — monounsaturated fatty acids (MUFAs) — have been shown to help decrease visceral fat levels.[8]Advertisement
-
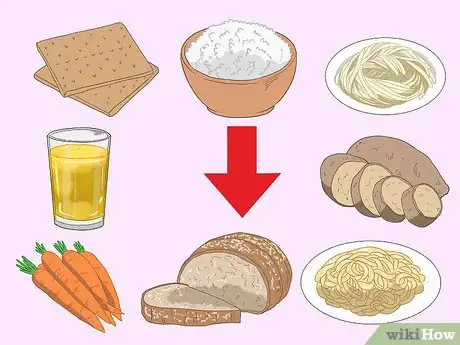
3Limit your carbohydrate intake. A low carbohydrate diet has been shown to be an effective eating pattern to help reduce levels of visceral fat.[11] Reduce the amount of carbohydrate rich foods in your diet to help promote the reduction of visceral fat.
- Carbohydrate rich foods include: bread, rice, pasta, crackers, tortillas, bagels, sweets and sugary beverages. Limit these foods to one to two servings maximum each day.[12]
- Foods like dairy, fruit and starchy vegetables also contain carbs, but have other beneficial nutrients like protein, fiber, vitamins and minerals.
- Keep carbohydrates from sweets or sweetened beverages to an absolute minimum if possible.[13]
-
4Consume adequate fiber daily.[14] Studies have shown that those who consumed adequate fiber daily had lower (and had an easier time lowering) visceral fat levels.[15] Women should consume 25 g of fiber daily and men should consume 38 g of fiber daily.[16]
- Outside of grains (like bread, rice or quinoa), you can consume a significant amount of fiber from fruits and vegetables.
- Fruits that are high in fiber include: apples, blackberries, raspberries and pears.[17]
- Vegetables that are high in fiber include: beans, artichokes, spinach, broccoli and cabbage.[18]
-
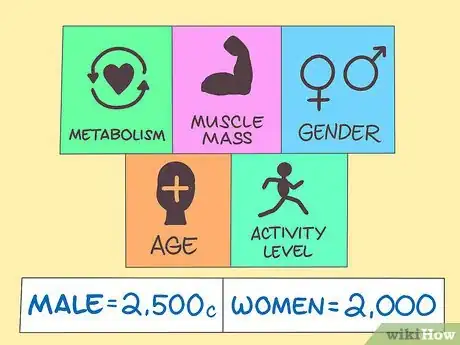
5Monitor your total calorie intake. Consuming a moderate- to low-calorie diet has been shown to support the loss of visceral fat.[19] In general, men should consume around 2,000-2,500 calories daily and women should consume 1,600-2,000 calories daily.[20]
- Your total calorie level can vary greatly based on your metabolism, muscle mass, gender, age and activity level.
- Note that a low-calorie diet alone has shown to have little effect on visceral fat levels. However, a low-calorie, moderate-carbohydrate diet along with exercise showed the best reduction in visceral fat levels.[21]
Incorporating Other Lifestyle Changes to Reduce Visceral Fat
-
1Engage in cardio exercises.[22] Cardio exercises have been shown to be one of the most effective methods at reducing visceral fat. It's recommended to include 150 minutes or 2 1/2 hours of moderate-intensity aerobic activity each week to help reduce visceral fat levels.[23]
- Aerobic activities can include exercises like: walking, jogging, swimming, biking or hiking.
- If you can do more than the recommended 150 minutes weekly, that may help you reach your goal faster.[24]
-
2Incorporate strength training. Weight lifting or resistance training is another important part of your exercise routine. It's recommended to include one to two days of strength training each week.
- Strength training includes activities like: weight lifting, Pilates or isometric exercises like push-ups or crunches.
- Note that spot training (trying to reduce fat in a specific area) does not rid the body of visceral fat. To lose fat, diet and cardio are key. However, the more muscle you build with strength training, the more calories you will burn.
-
3Try different types of exercise. Keep your exercise routine fun and exciting by engaging in a variety of different exercises. This can also help prevent over-training or over-using certain muscle groups.[25]
- If exercising in a gym is not your thing, try a dance class or team sport instead. You will be more willing to stick to it if it is enjoyable for you.
- Try incorporating some outdoor activities like hiking, kayaking or biking.
- Keep your end goal in mind to help motivate you to stick to your exercise routine.
-
4Go to bed early. It's recommended adults sleep at least seven to nine hours each night. Sleep is essential to your overall health and wellness. Studies have shown that those who slept less than six hours nightly had higher levels of visceral fat.[26] Make sure you go to bed early enough that you can get a full night's sleep.
-
5Give up smoking and alcohol. Both smoking (or consuming any type of tobacco product) and drinking alcohol have been linked to higher amounts of visceral fat.[29] Give up both to help reduce your levels of visceral fat, decrease your weight and improve your overall health.
- If you need help giving up nicotine, speak to your primary care physician for further help. She may be able to prescribe you a medication or provide you with additional resources to help quit.
- Limiting alcohol is recommended.[30] At a maximum, women should have one alcoholic beverage daily and men may have up to two alcoholic beverages daily.[31] However, it's ideal to discontinue consumption while trying to reduce visceral fat.
Monitoring Your Progress
-
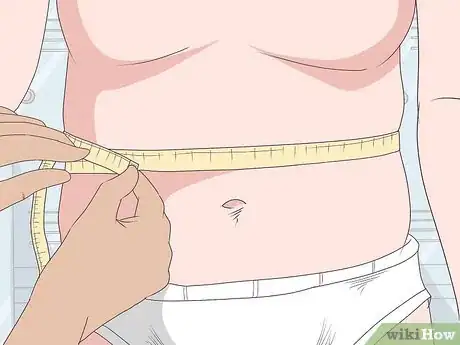
1Measure your waist circumference. Waist circumference is a measure that indicates your risk for obesity, metabolic syndrome and other chronic health conditions.[32] High waist circumference numbers may indicate an increased amount of visceral fat present.[33]
- To minimize risk, women's waist circumference should be 40" or less and men's waist circumference should be 35" or less.[34]
- To accurately measure your waist circumference, place a non-elastic tape measure around your waist — right above your hip bones. Measure as you breathe out, not as you inhale.[35]
-
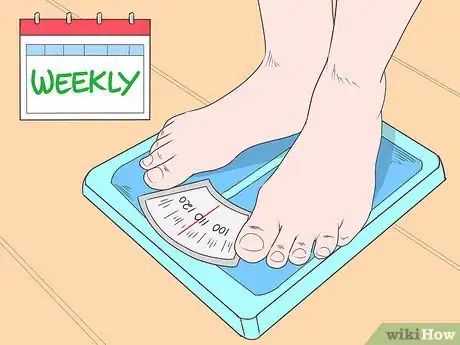
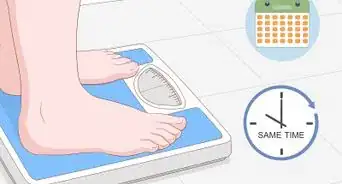
2Weigh yourself weekly. Although your main target goal is to reduce the amount of visceral fat, you will need to monitor the changes in your weight over time. Weight loss while modifying your diet and incorporating exercise can indicate your levels of visceral fat are decreasing.[36]
- Weigh yourself about one to two times weekly, and always at the same time (and nude, if possible) for the most accurate reflection of your progress over time.
- Safe weight loss (even when aiming to reduce visceral fat levels) is about one to two pounds weekly. Any more weight loss can result in nutrient deficiencies or may not be sustainable long-term.[37]
Expert Q&A
Did you know you can get expert answers for this article?
Unlock expert answers by supporting wikiHow
-
QuestionWhat are some mistakes I should avoid when trying to lose weight?
 Pouya Shafipour, MD, MSDr. Pouya Shafipour is a Family Medicine Specialist, Primary Care Physician, and a Weight Loss Specialist based in Santa Monica, California. Dr. Shafipour specializes in dietary, nutritional, behavioral, and exercise counseling to manage obesity and medical conditions related to excessive weight gain or loss. Dr. Shafipour received a BS in Molecular and Cell Biology from the University of California, Berkeley, an MS in Physiology and Biophysics from Georgetown University, and an MD from the Loma Linda University School of Medicine. He completed his internship in general surgery at UC Irvine and a residency in family medicine at the University of California, Los Angeles, and became board certified in family medicine in 2008.
Pouya Shafipour, MD, MSDr. Pouya Shafipour is a Family Medicine Specialist, Primary Care Physician, and a Weight Loss Specialist based in Santa Monica, California. Dr. Shafipour specializes in dietary, nutritional, behavioral, and exercise counseling to manage obesity and medical conditions related to excessive weight gain or loss. Dr. Shafipour received a BS in Molecular and Cell Biology from the University of California, Berkeley, an MS in Physiology and Biophysics from Georgetown University, and an MD from the Loma Linda University School of Medicine. He completed his internship in general surgery at UC Irvine and a residency in family medicine at the University of California, Los Angeles, and became board certified in family medicine in 2008.
Board Certified Family Medicine Specialist People usually try to lose weight using a mixture of intense exercise and a low-calorie diet, which often leaves them hungry and cranky. This can also lead to someone breaking their diet and either failing to lose weight or gaining more weight. Calorie counting without taking into consideration the quality of calories is another common mistake. To see results when trying to lose weight, follow a complex and comprehensive plan comprised of a whole food diet, exercise, and healthy eating behaviors.
People usually try to lose weight using a mixture of intense exercise and a low-calorie diet, which often leaves them hungry and cranky. This can also lead to someone breaking their diet and either failing to lose weight or gaining more weight. Calorie counting without taking into consideration the quality of calories is another common mistake. To see results when trying to lose weight, follow a complex and comprehensive plan comprised of a whole food diet, exercise, and healthy eating behaviors. -
QuestionIf present visceral fat is 30 percent and the ideal is 15 percent, how fast can a diet and exercise routine reduce it to the ideal?
 Chris M. Matsko, MDDr. Chris M. Matsko is a retired physician based in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. With over 25 years of medical research experience, Dr. Matsko was awarded the Pittsburgh Cornell University Leadership Award for Excellence. He holds a BS in Nutritional Science from Cornell University and an MD from the Temple University School of Medicine in 2007. Dr. Matsko earned a Research Writing Certification from the American Medical Writers Association (AMWA) in 2016 and a Medical Writing & Editing Certification from the University of Chicago in 2017.
Chris M. Matsko, MDDr. Chris M. Matsko is a retired physician based in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. With over 25 years of medical research experience, Dr. Matsko was awarded the Pittsburgh Cornell University Leadership Award for Excellence. He holds a BS in Nutritional Science from Cornell University and an MD from the Temple University School of Medicine in 2007. Dr. Matsko earned a Research Writing Certification from the American Medical Writers Association (AMWA) in 2016 and a Medical Writing & Editing Certification from the University of Chicago in 2017.
Family Medicine Physician
Warnings
- Always speak to your doctor prior to starting any new diet or exercise program. He will be able to guide you on what is the most safe, healthy and appropriate program for you.⧼thumbs_response⧽
References
- ↑ http://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/gim/core_resources/Patient%20Handouts/Handouts_May_2012/The%20Skinny%20on%20Visceral%20Fat.pdf
- ↑ http://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/gim/core_resources/Patient%20Handouts/Handouts_May_2012/The%20Skinny%20on%20Visceral%20Fat.pdf
- ↑ http://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/gim/core_resources/Patient%20Handouts/Handouts_May_2012/The%20Skinny%20on%20Visceral%20Fat.pdf
- ↑ http://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/nutrition-and-healthy-eating/in-depth/fat/art-20045550?pg=2
- ↑ http://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/nutrition-and-healthy-eating/in-depth/fat/art-20045550?pg=2
- ↑ http://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/nutrition-and-healthy-eating/in-depth/fat/art-20045550?pg=2
- ↑ Pouya Shafipour, MD, MS. Weight Loss Specialist. Expert Interview. 8 May 2020.
- ↑ https://www.heart.org/en/healthy-living/healthy-eating/eat-smart/fats/monounsaturated-fats
- ↑ http://www.heart.org/HEARTORG/GettingHealthy/NutritionCenter/HealthyEating/Monounsaturated-Fats_UCM_301460_Article.jsp
- ↑ http://www.heart.org/HEARTORG/GettingHealthy/NutritionCenter/HealthyEating/Monounsaturated-Fats_UCM_301460_Article.jsp
- ↑ http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15331203
- ↑ http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15331203
- ↑ Pouya Shafipour, MD, MS. Weight Loss Specialist. Expert Interview. 8 May 2020.
- ↑ Pouya Shafipour, MD, MS. Weight Loss Specialist. Expert Interview. 8 May 2020.
- ↑ http://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2011/06/110627123032.htm
- ↑ http://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/nutrition-and-healthy-eating/in-depth/fiber/art-20043983
- ↑ http://www.fruitsandveggiesmorematters.org/fiber-in-fruits-and-vegetables
- ↑ http://www.fruitsandveggiesmorematters.org/fiber-in-fruits-and-vegetables
- ↑ http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15331203
- ↑ https://health.gov/our-work/food-nutrition/2015-2020-dietary-guidelines/guidelines/appendix-2/
- ↑ http://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/gim/core_resources/Patient%20Handouts/Handouts_May_2012/The%20Skinny%20on%20Visceral%20Fat.pdf
- ↑ Pouya Shafipour, MD, MS. Weight Loss Specialist. Expert Interview. 8 May 2020.
- ↑ http://health.gov/paguidelines/
- ↑ http://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/gim/core_resources/Patient%20Handouts/Handouts_May_2012/The%20Skinny%20on%20Visceral%20Fat.pdf
- ↑ http://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/fitness/in-depth/overuse-injury/art-20045875?pg=2
- ↑ http://www.today.com/health/3-ways-get-rid-worst-kind-body-fat-1C6943603
- ↑ http://sleepfoundation.org/sleep-tools-tips/healthy-sleep-tips
- ↑ http://sleepfoundation.org/sleep-tools-tips/healthy-sleep-tips
- ↑ http://www.diabetes.co.uk/body/visceral-fat.html
- ↑ Pouya Shafipour, MD, MS. Weight Loss Specialist. Expert Interview. 8 May 2020.
- ↑ http://www.cdc.gov/alcohol/fact-sheets/alcohol-use.htm
- ↑ https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/educational/lose_wt/risk.htm
- ↑ https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/educational/lose_wt/risk.htm
- ↑ http://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/gim/core_resources/Patient%20Handouts/Handouts_May_2012/The%20Skinny%20on%20Visceral%20Fat.pdf
- ↑ https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/educational/lose_wt/risk.htm
- ↑ http://www.health.harvard.edu/staying-healthy/abdominal-fat-and-what-to-do-about-it
- ↑ http://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/weight-loss/basics/weightloss-basics/hlv-20049483
About This Article
If you want to get rid of visceral fat, try reducing trans-fat and saturated fats in your diet which are found in sugary and fried foods. Instead, try consuming heart-healthy fats, like olive oil, avocados, and nuts. You should also limit carbohydrate-rich foods like bread, pasta, and sweets, which only increase visceral fat in your body. In addition to a good diet, aim to do 2 ½ hours of cardio a week, like biking, swimming, or running. If you get bored with going to the gym, try different types of exercise, like dancing or hiking, to keep you motivated to lose fat. To learn how to measure your progress, read more from our Physician co-author!













-Step-14.webp)
-Step-14.webp)


-Step-14-Version-3.webp)