wikiHow is a “wiki,” similar to Wikipedia, which means that many of our articles are co-written by multiple authors. To create this article, 23 people, some anonymous, worked to edit and improve it over time.
This article has been viewed 386,933 times.
Learn more...
Are you trying to get the best performance from your favorite games without shelling out the cash for a new graphics card? Overclocking can give you significant performance benefits, but there are some serious risks involved as well. Any time you start increasing speeds past what the manufacturer specifies, you run the risk of damaging the card. If you approach the process with caution and patience, however, you'll be able to do it safely without running into any serious issues.
Steps
Getting Ready
-
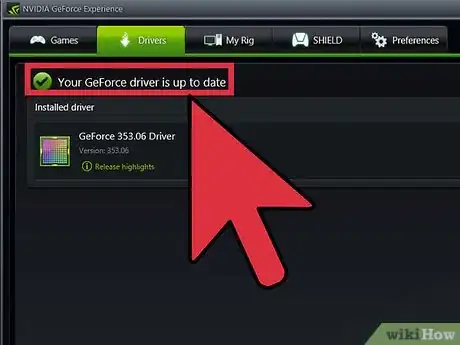
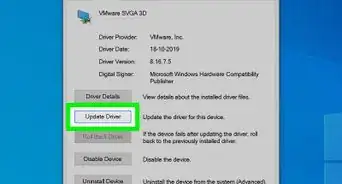
1Update your video card drivers. Before you start overclocking, you'll want to make sure you are running the latest drivers on your video card. You can download the latest drivers from the Nvidia or AMD site, depending on which manufacturer you have. Having the latest drivers will ensure that your card is running as stably as possible. Newer drivers often increase overclocking performance as well.[1]
-
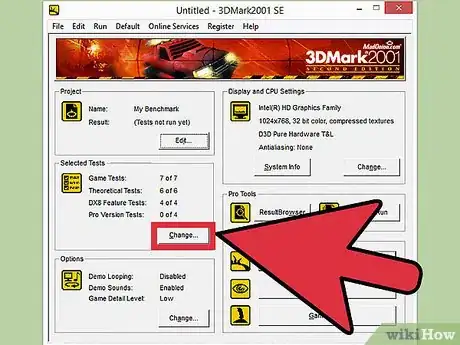
2Download your tools. To overclock, you will need a few different programs, all of which are available for free. These programs will give you performance benchmarks, allow you to adjust your card timing and voltage, and monitor temperature performance.
- Download a benchmark program - There are several available, but one of the quickest and most intuitive is Heaven. It is available for free from Unigine, the developers. Another popular program is 3DMark.
- Download an overclocking program. While both Nvidia and AMD have overclocking utilities of their own, MSI Afterburner is one of the most popular and widely-used programs. Despite it's name, it will work with virtually every graphics card from both Nvidia and AMD.[2]
- Download a monitoring program. Although benchmark and overclocking programs will report temperatures and speeds, sometimes it's good to have another monitor to make sure that all of your settings take. GPU-Z is a lightweight program that will monitor the temperature, clock speed, memory speed, and every other aspect of your graphics card.
Advertisement -
3Research your card. Going into your overclocking process without being informed can cost you a lot of time and cause you a lot of headaches later on. You want to find the clock speeds that other users who have your exact same card are getting. You also need to find what is generally considered to be your card's highest safe voltage.
- Do not immediately apply these numbers to your card. Since every card is different, there's no telling what could happen if you enter the wrong numbers. Instead, use them as a guide during the overclocking process to judge how effective your numbers are.
- Try forums such as Overclock.net to find other overclockers who have the same card that you do.
- Overclocking a laptop's GPU is not recommended. Laptops have a much harder time dissipating heat, and overclocking can quickly lead to dangerous temperatures.
Benchmarking Your Card
-
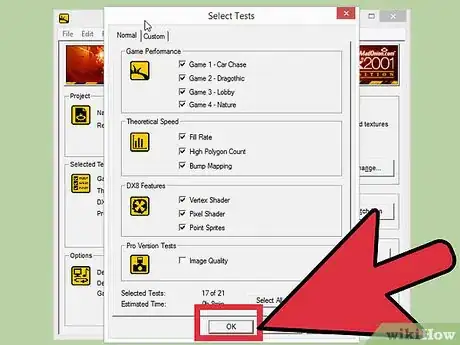
1Open your benchmark program. You will need to install it after downloading it. Most users will be able to leave the settings at their default during installation. Once your program is installed, open it to start the benchmarking process.
-
2Adjust the benchmark settings. Before you start the benchmarking, you will be able to adjust the graphics settings. Adjust them to whatever you would like, and make sure that Resolution is set to "Desktop". If the benchmark program does not perform well with the settings you pick, you can change them later.
-
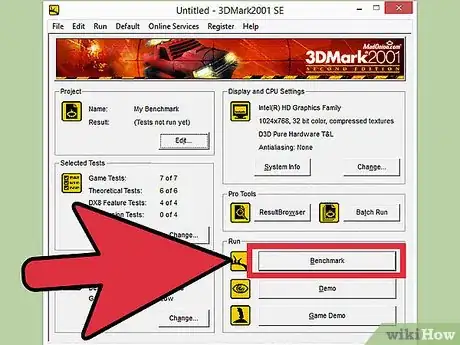
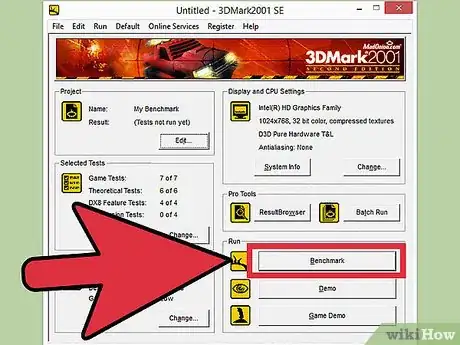
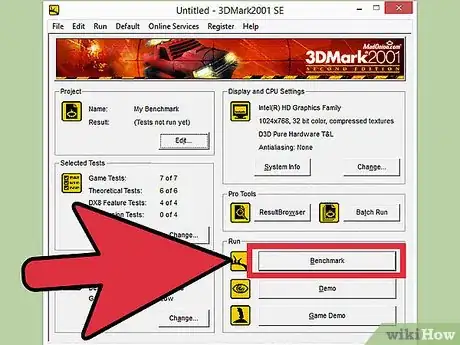
3Click Run. The benchmark program will begin, and after a few moments of loading scenes will begin playing on your monitor. If the performance is poor, you can exit and lower your settings, but this isn't necessary. During the overclocking process, you should see performance improve without having to adjust the settings.
-
4Click Benchmark. Once the scenes start playing, you will see a row of buttons at the top of the screen. Click the Benchmark button to start the benchmark process. In Heaven, this will run through 26 different scenes, and will take several minutes to complete. After the benchmark is over, you will be given a score based on your graphics card's performance.
-
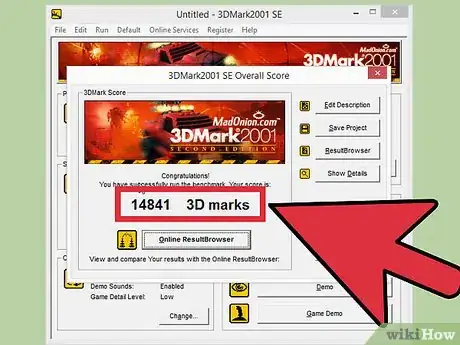
5Record your score. Write down the score that you get. This will help you easily compare results as you increase the speed of your card.
Raising Your Core Clock Speeds
-
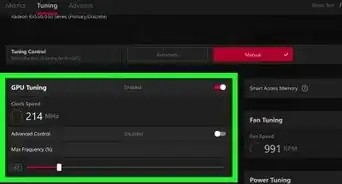
1Open MSI Afterburner. You will see a list of sliders on the left side of the program and a hardware monitor on the right. You can also run GPU-Z now to have an additional monitor to verify readings.
-
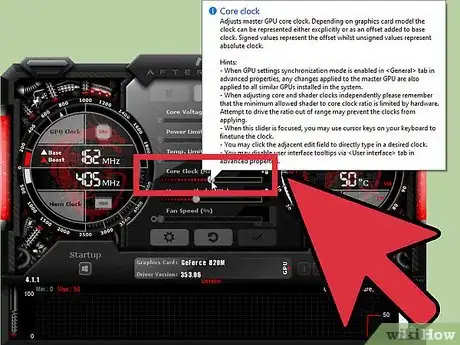
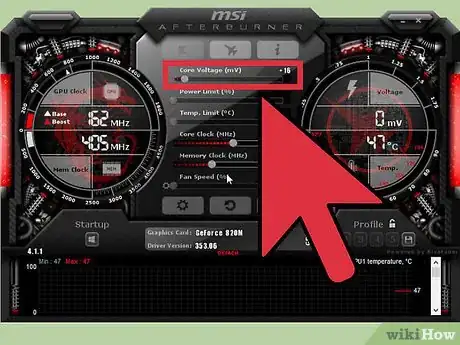
2Find the "Core Clock (MHz)" slider. This slider controls the core clock speed of your GPU. If your card has a Shader Clock slider, make sure that it is linked to the Core Clock slider. You will see a link icon between the two if they are linked.
-
3Raise the Core Clock speed by about 10MHz. When making adjustments to the speed of your clock for the first time, it is always advisable to go by small amounts, such as 10MHz. This amount allows you to see improvements, but not accidentally go overboard. If you do your game could crash.
-
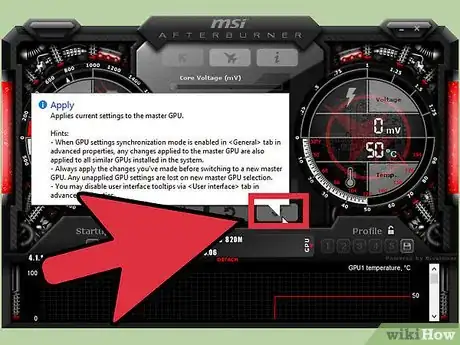
4Click Apply. The changes should take effect immediately. Look at your readings in GPU-Z to ensure that the new speed is showing.
-
5Run the benchmark program. Once you've made your first adjustment and verified it, it's time to run the benchmark program again and get your new score. When the benchmark program is running, pay attention to see if image quality or frame rate improves noticeably from the first time.
- If the benchmark program runs without any issue, then your overclock is stable so far and you can continue.
-
6Repeat the "raise and benchmark" process. Continue raising your speed in 10MHz intervals, checking the results in the benchmark program each time. Sooner or later, you'll start running into instabilities.
- Instabilities will manifest as black screens, graphical glitches, artifacts, bad colors, blotches, and more.
-
7Decide how to proceed. Once you hit an instability, you can either revert your settings to the last speed that was working well, or you can try increasing your voltage. If you've seen noticeable improvements, or you don't want to risk damaging your card due to increasing the power flow, revert to the last working speed and skip down to Part Five. If you want to keep pushing your card, leave the speed as it is and move on to the next section.
Raising Your Core Voltage
-
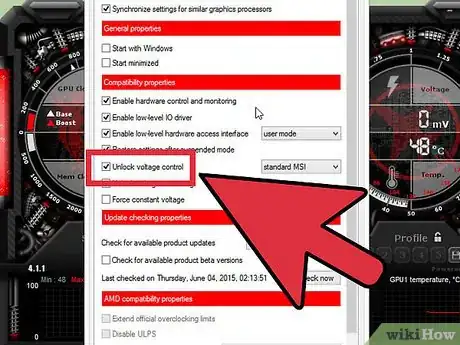
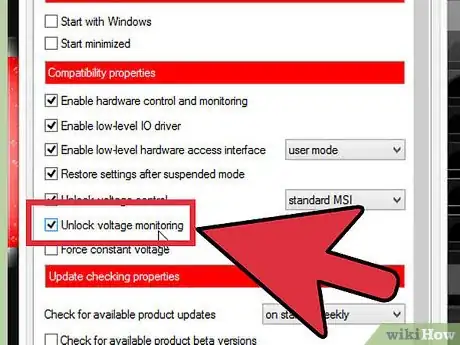
1Click the Settings button in MSI Afterburner. The Core Voltage sliders is locked by default to prevent accidental damage to your card. This alone should tell you how potentially serious doing this is. Check the "Unlock voltage control" box in the General tab and click OK.
-
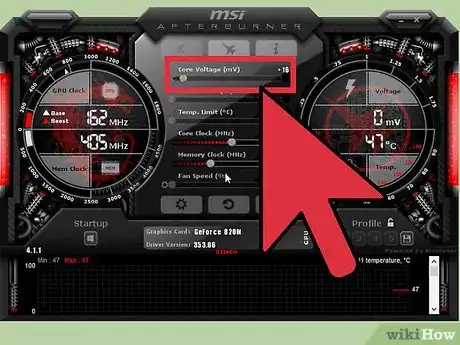
2Increase the "Core Voltage (mV)" slider by about 10mV. You will unlikely be able to select exactly 10mV, as voltages can only be increased by set amounts. Click Apply.
-
3Run your benchmark program. Once you've increased your voltage, run your benchmarking program to see if your overclock is stable now. Remember, you left your settings at a speed that was unstable, so if it is stable now after raising your voltage you can go back to increasing your clock speed.
-
4Repeat Part Three. If your overclock is stable now, start raising the Core Clock speed in 10MHz intervals again, running benchmarks each time. Repeat this until you reach the next instability.
-
5Watch your temperature. As voltage increases, the temperature of your GPU will start to go up. As you continue the process of increasing your voltage, keep an eye on your temperature readings in GPU-Z. It's recommended to keep temperatures below 90 °C (194 °F), but many enthusiasts prefer to keep it even cooler, such as 80° and below.
- Improving your case's and card's cooling can help you increase your overclocking capabilities, but can be expensive and time-consuming.
-
6Increase your voltage again. Once you reach your next plateau, raise the Core Voltage by 10mV again. Benchmark, and then repeat the Core Clock process. Remember to keep watching your temperature, as this will be one of the big limiting factors in how far you can take the overclock.
-
7Don't go over your safe voltage. Remember the notes you took about your card earlier? Make sure that you don't exceed the safe voltage limit for your card when you are making your adjustments.
-
8Know when to quit. At a certain point, your overclock will stop being effective. You may reach your temperature threshold, your maximum voltage, or your clock speeds may just not be stable no matter how much your voltage increases. If that's the case then you can move on to the next step.
-
9Repeat the entire thing with your "Memory Clock (MHz)" slider". Once you've hit the limit with your Core Clock, it's time to do the same with your Memory Clock. Repeat the process by raising the Memory Clock in 10MHz intervals, raising the voltage when you hit instabilities (if you haven't maxed out your safe voltage or temperature yet).
- Make sure to keep running the benchmark after each adjustment. Raising the Memory Clock can lead to increases, but at a certain point it will actually start hurting performance. Pay attention to your benchmark scores to get it just right.
-
10Overclock SLI cards. The process for overclocking SLI cards is pretty much the same as a single card. Each card needs to be overclocked individually, and the slower card will always dictate the overall speed. Since no two cards are the same, one of your cards will be held back a little by the other. Follow the above steps to overclock each individual card.
Testing Your Stability
-
1Start up your benchmark program. Performing your stress test is going to take a significant amount of time, so make sure you aren't going to need your computer for the next few hours. It's a fairly hands-off process, but you'll want to be able to check in and evaluate performance.
-
2Click the Run button. Instead of starting the "Benchmark" process in Heaven, click Run and just let it go. Heaven will continue to cycle through the scenes until you tell it otherwise.
-
3Watch for errors. As the scenes continue to play, keep your eyes open for any glitches, artifacts, or full-on crashes. These indicate an unstable overclock, and you'll need to go back and lower your settings. If you make it through the stress test without issue (4-5 hours), then it's game time.
-
4Get your game on. Benchmark programs are great, but they aren't the reason you're overclocking; the games are. Open up your favorite game and test out the performance. Your old settings should work much better, and you may be able to crank them up to something higher![3]
Community Q&A
-
QuestionI'm unable to move the sliders, why?
 Community AnswerIt is possible that your particular GPU can not be overclocked or some features are not available.
Community AnswerIt is possible that your particular GPU can not be overclocked or some features are not available. -
QuestionIf I don't see a difference, what do I do?
 Community AnswerNothing, if it's stable. You're just enabling the card to have better performance when under stress.
Community AnswerNothing, if it's stable. You're just enabling the card to have better performance when under stress. -
QuestionIs it possible to install an NVIDIA graphics card on an Intel where it was nonexistent?
 Community AnswerYes, if the motherboard has any free PCI-E x16 slots available. You will have to open your case to see the slots.
Community AnswerYes, if the motherboard has any free PCI-E x16 slots available. You will have to open your case to see the slots.
Warnings
- Overclocking can seriously damage your card. it is possible that your card may cease to function. Only overclock if you are aware of the risks and are comfortable with the programs.⧼thumbs_response⧽
References
About This Article
1. Update your video card drivers.
2. Use a benchmarking app to find your score.
3. Use MSI Afterburner to raise the core clock speed by 10MHz.
4. Run the benchmarking app again.
5. Keep raising until you reach an instability.
6. Raise the core voltage in MSI Afterburner.
7. Run a stability test in your benchmarking app.