This article was co-authored by Michael Lewis, MD, MPH, MBA, FACPM, FACN. Michael D. Lewis, MD, MPH, MBA, FACPM, FACN, is an expert on nutritional interventions for brain health, particularly the prevention and rehabilitation of brain injury. In 2012 upon retiring as a Colonel after 31 years in the U.S. Army, he founded the nonprofit Brain Health Education and Research Institute. He is in private practice in Potomac, Maryland, and is the author of "When Brains Collide: What every athlete and parent should know about the prevention and treatment of concussions and head injuries." He is a graduate of the U.S. Military Academy at West Point and Tulane University School of Medicine. He completed post-graduate training at Walter Reed Army Medical Center, Johns Hopkins University, and Walter Reed Army Institute of Research. Dr. Lewis is board certified and a Fellow of the American College of Preventive Medicine and American College of Nutrition.
There are 7 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page.
This article has been viewed 36,831 times.
The most complex organ of the human body is the brain. Part of the central nervous system, the brain is command central around which the body's intellect, senses, and nervous system all function. It is an extraordinary organ, and in this article, the four main sections of the brain will be explored.
Steps
Understanding the Cerebrum
-
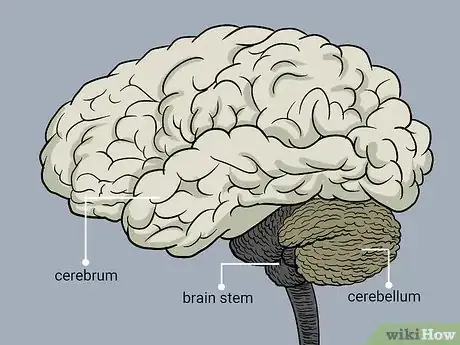
1Explore the largest section of the brain. The brain weighs approximately 3 pounds, and the cerebrum occupies 80% of this mass. Important brain functions such as thought, memory, judgement, and decision-making are all controlled in the cerebrum.
-
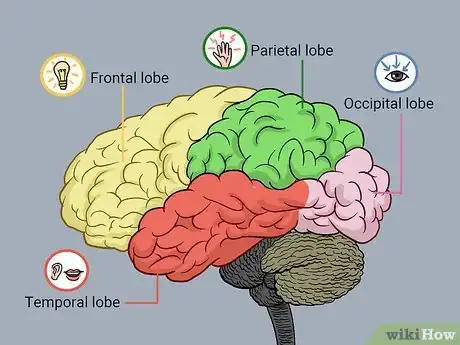
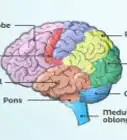
2Understand the sections of the cerebrum. The cerebrum is divided into four lobes, each with a specific function:[1]
- Frontal lobe: High levels of perception and motor skills are controlled by the frontal lobe. Encompassed in the frontal lobe is the body's power of planning, expression, reasoning and problem solving. The frontal lobe is located at the very front of the brain.
- Parietal lobe: This lobe is responsible for translating signals to the brain from tangible sources; touch, pain, pressure. The parietal lobe is also responsible orientation and recognition. Its location is in the center of the brain.
- Occipital lobe: The occipital lobe has but one responsibility; taking the information that we see, translating it, and sending appropriate signals to the brain for processing. The occipital lobe is located at the back of the brain.
- Temporal lobe: Located at the bottom of the brain, the temporal lobe is tasked with processing the sounds we hear, as well as memory and speech perception.[2]
Understanding the Cerebellum
-
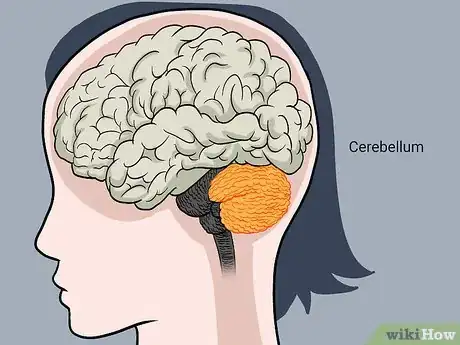
1Explain the cerebellum. The cerebellum occupies approximately 10% of the brain's mass. It is divided into two hemispheres and is located behind the top of the brain stem, where the brain connects to the spinal cord. Despite its small size, the cerebellum contains half of the neurons of the entire body. Neurons are specially designed cells that are responsible for transmitting information to other nerve and gland cells, as well as muscles throughout the body.
-
2Coordinate movements: The cerebellum is responsible for synchronizing voluntary muscle movements including balance, coordination, posture and speech.[3]
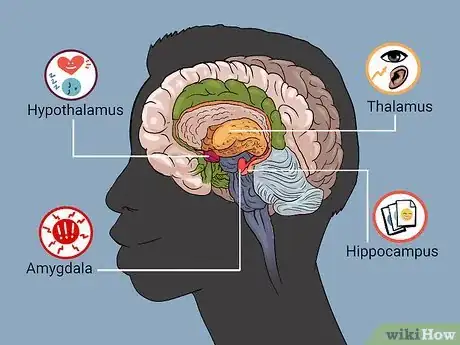
Understanding the Limbic System
-
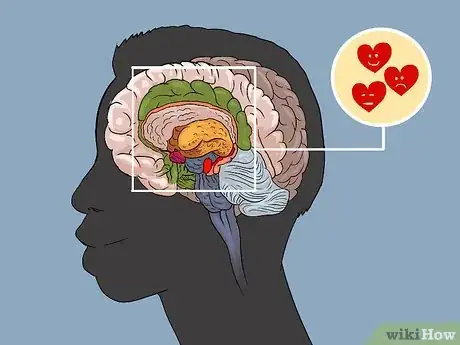
1Define the function: The limbic system is the portion of the brain that controls emotional response. It is positioned between the cerebrum and the brain stem, playing key roles in our ability to learn, long-term memory, emotion and reason.[4]
-
2Explain the function of each section: There are four sections of the limbic system.
- Thalamus: The thalamus is an integral component in relaying messages to the appropriate regions of the body. It is involved in functions such as pain perception and motor control. It processes auditory and visual signals, as well as our emotional expression.[5]
- Hypothalamus: While the thalamus is responsible for interpreting signals from outside stimulus, the hypothalamus is responsible for maintaining systems inside the body. It monitors many bodily functions including sleep, hunger, and thirst. It also involved with sleep and emotional activity.
- Amygdala: This section of the brain is also involved in emotions, specifically fear and anxiety. It is responsible for the survival instinct, also known as fight or flight.[6]
- Hippocampus: Responsible for the making and retaining of memories, the hippocampus plays and important role in learning, development and emotional behaviour. Simply stated, the hippocampus helps us to recall happy and traumatic events, make choices based on recalling past events, and perceive danger. It also aids in learning likes and dislikes, based on memories of places, people and events.
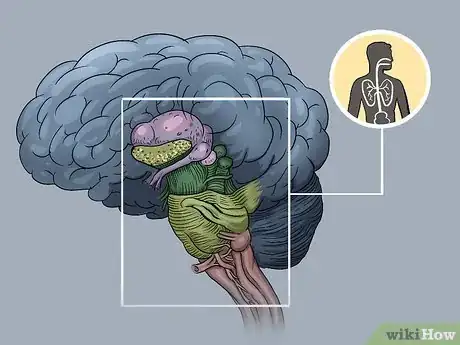
Understanding the Brain Stem
-
1Explore the role of this section: The brain stem is tasked with controlling the flow of messages between the brain and the rest of the body. Located below the limbic system, it supervises the function of consciousness, breathing, swallowing, as well as heart rate and blood pressure. It connects the spinal cord and the brain.
-
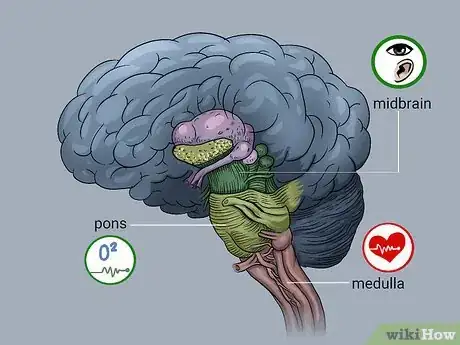
2Identify the parts of the brain stem. The brain stem is comprised of three parts: the midbrain, the pons, and the medulla (medulla oblongata).
- The midbrain (also called the mesencephalon) controls the functioning of hearing and vision as well as eye and body movement. This is also where involuntary actions such as digestion, heart rate and breathing rate takes place.
- The pons is located in the upper region of the brain stem and serves two main functions. First, it controls breathing rate, the amount of oxygen taken in along with the number of breaths per minute. Next, the pons controls communication within the brain, by sending messages to the cerebellum and cerebrum, for example. The pons is also an integral part of the body's hearing, taste, balance and posture, and regulating deep sleep.
- The medulla is positioned at the bottom of the brain stem. Its responsibilities include vital bodily functions, including heart rate, blood pressure and breathing. This area is involved in the body's natural reflexes and also involuntary actions including sneezing, coughing or vomiting.[7]
Expert Q&A
-
QuestionAre there some good habits to build, if you're hoping to reduce cognitive decline?
 Michael R. LewisMichael R. Lewis is a retired corporate executive, entrepreneur, and investment advisor in Texas. He has over 40 years of experience in business and finance, including as a Vice President for Blue Cross Blue Shield of Texas. He has a BBA in Industrial Management from the University of Texas at Austin.
Michael R. LewisMichael R. Lewis is a retired corporate executive, entrepreneur, and investment advisor in Texas. He has over 40 years of experience in business and finance, including as a Vice President for Blue Cross Blue Shield of Texas. He has a BBA in Industrial Management from the University of Texas at Austin.
Business Advisor Diet and exercise will always be number one and two, in no particular order. Eating healthy and getting your heart rate up a little bit every single day is good. It doesn't have to be going to the gym for two hours. It can be doing push-ups, sit-ups, or jumping jacks in your bedroom before you start your day. One of my favorite activities is taking a walk with a loved one or friends because it combines getting fresh air and social interaction while you get your heart rate up. One of the most important things that's been shown scientifically is the value of socialization on the quality and length of life. People who are more social live longer and live happier.
Diet and exercise will always be number one and two, in no particular order. Eating healthy and getting your heart rate up a little bit every single day is good. It doesn't have to be going to the gym for two hours. It can be doing push-ups, sit-ups, or jumping jacks in your bedroom before you start your day. One of my favorite activities is taking a walk with a loved one or friends because it combines getting fresh air and social interaction while you get your heart rate up. One of the most important things that's been shown scientifically is the value of socialization on the quality and length of life. People who are more social live longer and live happier.
References
- ↑ http://healthyliving.azcentral.com/four-main-parts-of-the-brain-12343937.html
- ↑ https://www.enkiverywell.com/parts-of-the-brain-and-their-functions.html
- ↑ https://www.healthline.com/human-body-maps/cerebellum
- ↑ By OpenStax College - Anatomy & Physiology, Connexions Web site. http://cnx.org/content/col11496/1.6/, Jun 19, 2013., CC BY 3.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=30148029
- ↑ https://www.thoughtco.com/thalamus-anatomy-373229
- ↑ https://howthebrainlearns.wordpress.com/2011/11/28/6-major-parts-of-the-brain-and-how-they-work/
- ↑ http://www.strokeeducation.info/brain/brainstem/