This article was co-authored by wikiHow staff writer, Jack Lloyd. Jack Lloyd is a Technology Writer and Editor for wikiHow. He has over two years of experience writing and editing technology-related articles. He is technology enthusiast and an English teacher.
The wikiHow Tech Team also followed the article's instructions and verified that they work.
This article has been viewed 740,428 times.
Learn more...
Whether you're writing Python code on your Windows PC or just want to use existing Python scripts, it'll be helpful to learn how to run code from the Command Prompt. Running Python code is easy—you'll just need to have Python installed. This wikiHow article will walk you through opening a Python file from Command Prompt, and teach you how to fix the common "python is not recognized as an internal or external command" error.
Steps
Finding the Python File Path
-
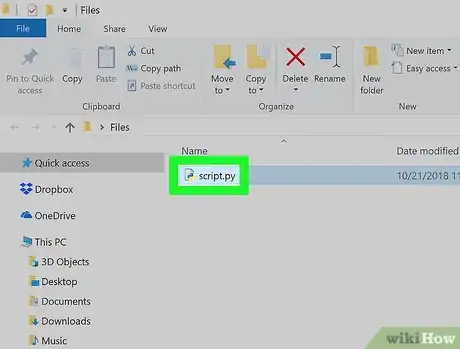
1Go to the Python file's location. Find the Python file that you want to open in Command Prompt.
- If you already know the folder path to the Python file you want to open, skip ahead to opening the file in Command Prompt.
-
2Select the Python file. Click once the Python file for which you want to see the folder path.Advertisement
-
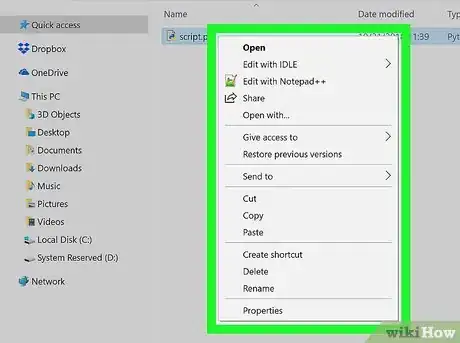
3Right-click the Python file. Doing so prompts a drop-down menu to appear.
-
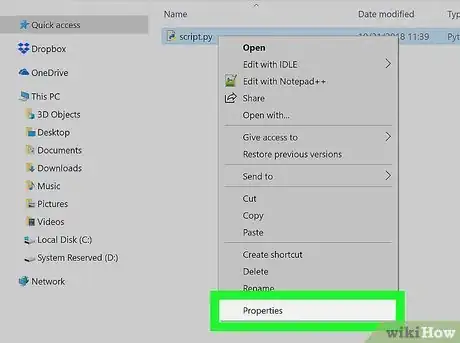
4Click Properties. It's in the drop-down menu. The properties window will open.
-
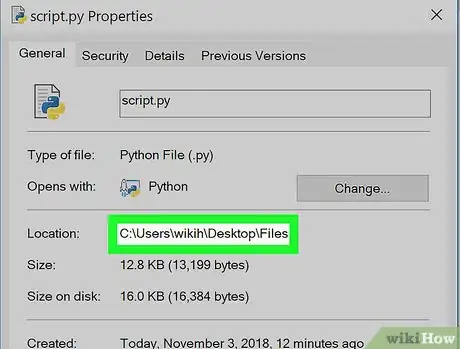
5Note the "Location" value. The folder address (or "path") to the right of the "Location" heading is what you'll need to enter into Command Prompt when switching to the directory in which your Python file is stored.
- You can copy the location by highlighting it (click and drag your mouse across the "Location" value) and then pressing Ctrl+C.
Running a Python File
-
1
-
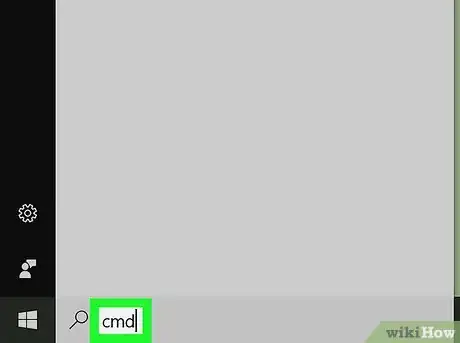
2Search for Command Prompt. Type in cmd to do so.
-
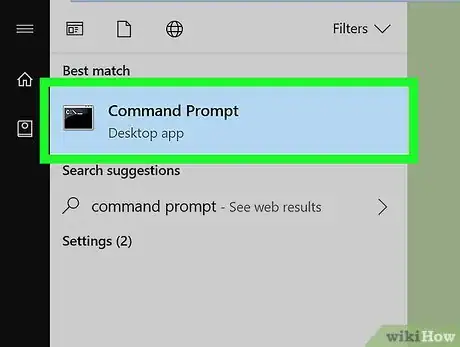
3Click Command Prompt. It's at the top of the Start menu. Doing so will open Command Prompt.
-
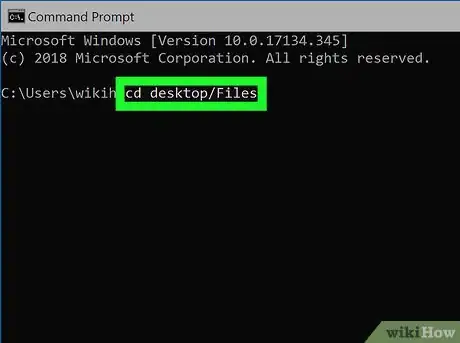
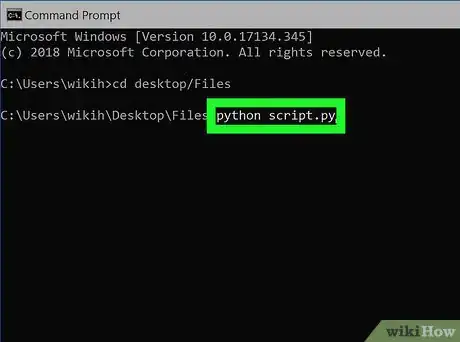
4Switch to your Python file's directory. Type cd and a space, then type in the "Location" address for your Python file and press ↵ Enter.
- For example, to open a Python file in a folder named "Files" on your Desktop, you would enter cd desktop/Files here.
- If you copied the path to the file, you can type in cd and a space and then press Ctrl+V to paste in the path.
-
5Enter the "python" command and your file's name. Type in python file.py where file is your Python file's name.
- For example, if your Python file is named "script", you would type in python script.py here.
- If your Python file has one or more spaces in its name, you'll place quotation marks around the file name and extension (e.g., python "my script.py").
-
6Press ↵ Enter. Doing so runs your command and opens your Python file via your computer's installed Python program.
- If you encounter an error that says
'python' is not recognized as an internal or external commandafter pressing Enter, you'll need to add Python to the PATH list before retrying this part.
- If you encounter an error that says
Adding Python to the PATH List
-
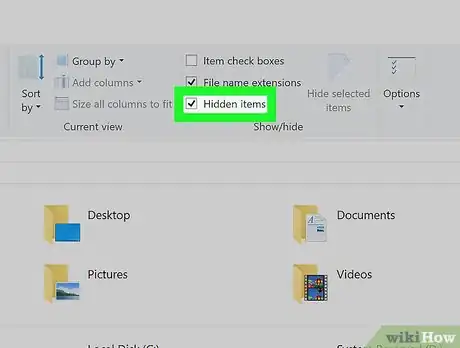
1Enable viewing for hidden folders. Since one of the folders that contains your Python installation folder is most likely hidden, you'll have to unhide it before proceeding:
- Open File Explorer .
- Click the View tab.
- Check the "Hidden items" box.
-
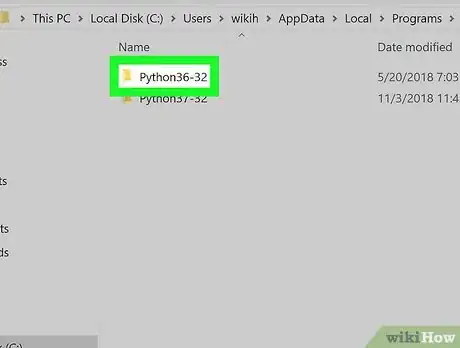
2Navigate to your Python folder. In some cases, the Python path is "C:\Python27"; however, if you've installed the most recent version of Python using the default settings, it's tucked away in a hidden folder. You can copy the proper file path by doing the following:
- Click This PC on the left side of the File Explorer.
- Double-click your hard drive in the "Devices and drives" section.
- Scroll down and double-click the "Users" folder.
- Double-click the folder with your username on it.
- Scroll down and double-click "AppData".
- Double-click "Local".
- Scroll down and double-click "Programs".
- Double-click the "Python" folder.
- Double-click the Python folder with your preferred version number (e.g., "Python36").
-
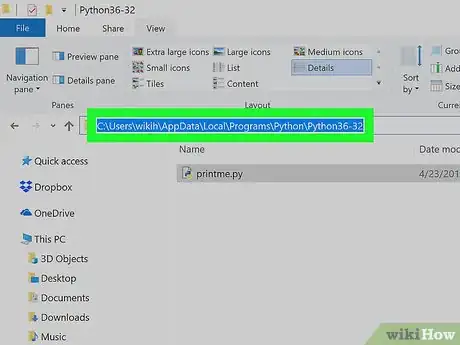
3Copy the path to the Python folder. Click once the address bar at the top of the File Explorer to highlight its contents, then press Ctrl+C to copy the highlighted address.
-
4
-
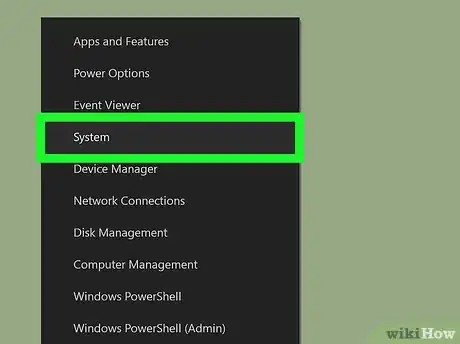
5Click System. It's in the pop-up menu. A new window will open.
-
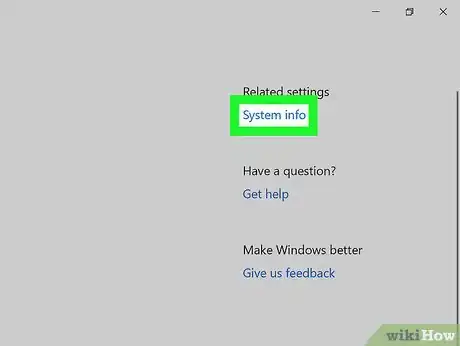
6Click System info. This is a link in the upper-right corner of the window. Doing so opens the System Information window.
-
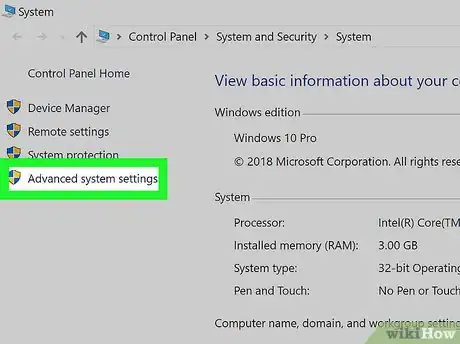
7Click the Advanced system settings link. You'll see this in the upper-left side of the System Information window. Yet another window will pop up.
-
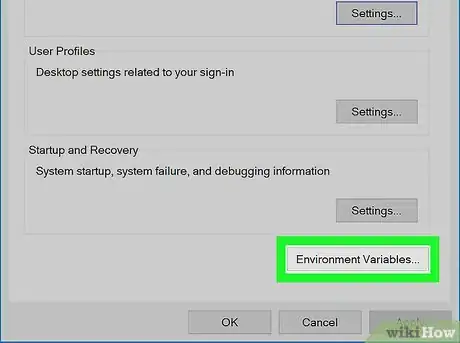
8Click Environment Variables…. It's in the bottom-right corner of the pop-up window.
-
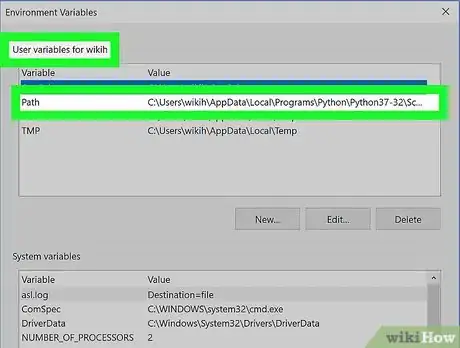
9Find the "Path" heading in the "User variables" pane. This window is at the top of the Environment Variables window.
- You may have to scroll up or down with your mouse cursor hovering over the "User variables" pane to find the "Path" variable.
-
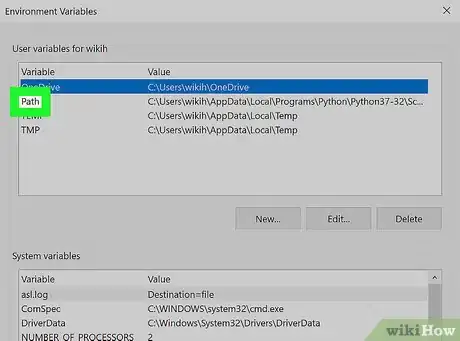
10Double-click the "Path" heading. Doing so opens a pop-up window.
-
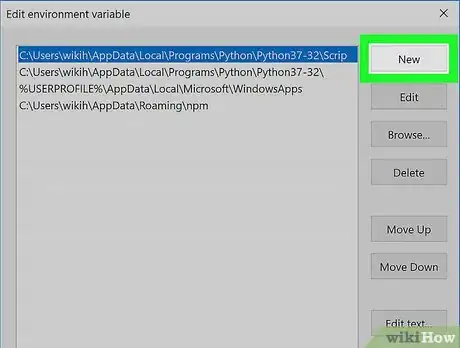
11Click New. It's on the right side of the window. A text field will open in the middle of the window.
-
12Paste in your copied path. Press Ctrl+V to do so. Your copied path will appear in the text field in the middle of the window.
-
13Click OK on the three open windows. This will save your changes and close the "Path" window, the "Environmental Variables" window, and the "System Properties" window.
Community Q&A
-
QuestionI want to create a shortcut that executes the utility "ptpython," running in the cmd prompt. The shortcut I have points to the directory containing "ptpython.exe" file but it does not execute it.
 Community AnswerIt sounds like ptpython.exe is a command-line utility, meaning it will only start if you execute it from a DOS window - you can't create a shortcut for it directly. You can probably create a shortcut to cmd.exe, though (the DOS window) and pass it the ptpython.exe file as a parameter. Something like "cmd.exe /c ptpython.exe" should work, or if this disappears in the end, try with /k (instead of /c).
Community AnswerIt sounds like ptpython.exe is a command-line utility, meaning it will only start if you execute it from a DOS window - you can't create a shortcut for it directly. You can probably create a shortcut to cmd.exe, though (the DOS window) and pass it the ptpython.exe file as a parameter. Something like "cmd.exe /c ptpython.exe" should work, or if this disappears in the end, try with /k (instead of /c). -
QuestionDoes this work on Windows 7?
 ArroganceTop AnswererYes. The directions to access the environment variables would be slightly different, as there is no "Power User" menu in Windows 7. Instead: 1. Press the Windows key and R to open the Run dialog. 2. Enter "sysdm.cpl". 3. Click the "Advanced" tab of the System Properties Window. 4. Click the "Environmental variables". Most everything else would work as described even on Windows 95 (if there's a version of Python for Windows 95).
ArroganceTop AnswererYes. The directions to access the environment variables would be slightly different, as there is no "Power User" menu in Windows 7. Instead: 1. Press the Windows key and R to open the Run dialog. 2. Enter "sysdm.cpl". 3. Click the "Advanced" tab of the System Properties Window. 4. Click the "Environmental variables". Most everything else would work as described even on Windows 95 (if there's a version of Python for Windows 95). -
QuestionAfter opening the Command Prompt and navigation to the directory in which the py file exists and opening Python, not able to run the file using python file_name.py. It says that the syntax is wrong.
 ArroganceTop AnswererThat sounds like a problem with the file you're trying to run. Make sure you are using the right version of Python for it (version 2 or 3, usually).
ArroganceTop AnswererThat sounds like a problem with the file you're trying to run. Make sure you are using the right version of Python for it (version 2 or 3, usually).