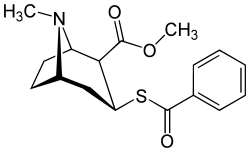
Benzoylthiomethylecgonine
Benzoylthiomethylecgonine is a cocaine analog which includes a sulfur in replacement of an oxygen on the single bonded benzoyl ester, resulting in lower electronegativity than the parent compound.[1]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Methyl 3β-(benzoylsulfanyl)tropane-2β-carboxylate | |
| Systematic IUPAC name
Methyl (1R,2S,3S,5S)-3-(Benzoylsulfanyl)-8-methyl-8-azabicyclo[3.2.1]octane-2-carboxylate | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C17H21NO3S | |
| Molar mass | 319.42 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
References
- Isomura, Shigeki; Hoffman, Timothy Z.; Wirsching, Peter; Janda, Kim D. (2002). "Synthesis, Properties, and Reactivity of Cocaine Benzoylthio Ester Possessing the Cocaine Absolute Configuration". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 124 (14): 3661–8. doi:10.1021/ja012376y. PMID 11929256.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.