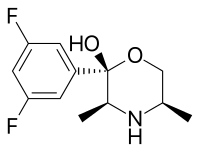
Manifaxine
Manifaxine (developmental code name GW-320,659) is a norepinephrine–dopamine reuptake inhibitor developed by GlaxoSmithKline through structural modification of radafaxine, an isomer of hydroxybupropion and one of the active metabolites of bupropion.[1] Manifaxine was researched for treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and obesity and was found to be safe, reasonably effective, and well-tolerated for both applications.[2][3] However, no results were reported following these initial trials and development was discontinued.[1]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | GW-320,659 |
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C12H15F2NO2 |
| Molar mass | 243.254 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Synthesis
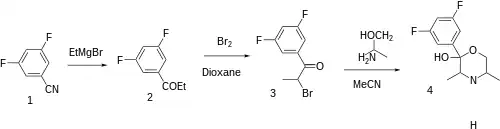
The Grignard reaction between 3,5-difluorobenzonitrile [64248-63-1] (1) and ethylmagnesium bromide gives 3,5-difluoropropiophenone [135306-45-5] (2). Halogenation with molecular bromine occurs at the alpha-keto position providing 2-bromo-3',5'-difluoropropiophenone [135306-46-6] (3). Intermolecular ring formation with DL-Alaninol (2-Aminopropanol) [6168-72-5] completed the synthesis of Manifaxine (4).
References
- "Manifaxine - AdisInsight".
- DeVeaugh-Geiss J, Conners CK, Sarkis EH, Winner PK, Ginsberg LD, Hemphill JM, et al. (August 2002). "GW320659 for the treatment of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder in children". Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry. 41 (8): 914–20. doi:10.1097/00004583-200208000-00009. PMID 12162627.
- Spraggs CF, Pillai SG, Dow D, Douglas C, McCarthy L, Manasco PK, et al. (December 2005). "Pharmacogenetics and obesity: common gene variants influence weight loss response of the norepinephrine/dopamine transporter inhibitor GW320659 in obese subjects". Pharmacogenetics and Genomics. 15 (12): 883–9. doi:10.1097/01213011-200512000-00006. PMID 16272960. S2CID 40809351.
- Kelley, J. L., Musso, D. L., Boswell, G. E., Soroko, F. E., Cooper, B. R. (1 January 1996). "(2 S ,3 S ,5 R )-2-(3,5-Difluorophenyl)-3,5- dimethyl-2-morpholinol: A Novel Antidepressant Agent and Selective Inhibitor of Norepinephrine Uptake". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 39 (2): 347–349. doi:10.1021/jm950630p. PMID 8558500.
- James Leroy Kelley, et al. EP0426416 (1991 to Wellcome Foundation Ltd).
- Frank Ivy Carroll, et al. US9562001 (2012 to Research Triangle Institute).
- Frank Ivy Carroll, et al. US20180215701 (Research Triangle Institute).