Seoul
Seoul (/soʊl/; Korean: 서울; IPA: [sʌul] ⓘ; lit. 'Capital'), officially Seoul Special City, serves as the capital and South Korea's most extensive urban center. The broader Seoul metropolitan area, encompassing Gyeonggi province and Incheon metropolitan city, emerged as the world's fourth largest metropolitan economy in 2014, trailing only Tokyo, New York City, and Los Angeles, hosting more than half of South Korea's population. Although Seoul's population peaked at slightly over 10 million, it has gradually decreased since 2014, standing at approximately 9.97 million residents as of 2020. Seoul is the seat of the Korean government.
Seoul
서울 | |
|---|---|
| Seoul Special City 서울특별시 | |
Clockwise from top: Seongsan Bridge over the Han River; Gangnam District; Gyeongdong Market; Gyeongbokgung Palace; Cheonggyecheon; skyline at night; and Deoksugung | |
 Flag  Seal  Coat of arms | |
| Motto(s): "Seoul, my soul"[1] | |
| Anthem: none[2] | |
| Coordinates: 37°33′36″N 126°59′24″E | |
| Country | Republic of Korea |
| Area | Seoul Capital |
| Founded by | Gen. Yi Sŏng-gye |
| Districts | 25 districts |
| Government | |
| • Type | Mayor–council |
| • Body | Seoul Metropolitan Government Seoul Metropolitan Council |
| • Mayor | Oh Se-hoon (People Power) |
| • National Assembly | 49 |
| Area | |
| • Special city | 605.21 km2 (233.67 sq mi) |
| • Metro | 12,685 km2 (4,898 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 38 m (125 ft) |
| Highest elevation | 836.5 m (2,744.4 ft) |
| Lowest elevation | 0 m (0 ft) |
| Population (2Q 2023)[4] | |
| • Special city | 9,659,322 |
| • Rank | 1st |
| • Density | 16,000/km2 (41,000/sq mi) |
| • Metro | 26,037,000[5] |
| • Metro density | 2,053/km2 (5,320/sq mi) |
| • Demonym | Seoulite |
| • Dialect | Gyeonggi |
| Gross Regional Product (2020) | |
| • Total | KR₩444.5 trillion US$355.6 billion |
| Time zone | UTC+9 (Korean Standard Time) |
| ISO 3166 code | KR-11 |
| Bird | Korean magpie |
| Color | Seoul Red[7] |
| Flower | Forsythia |
| Font | Seoul fonts (Seoul Hangang and Seoul Namsan)[8] |
| Mascot | Haechi |
| Tree | Ginkgo |
| Seoul | |
| Hangul | |
|---|---|
| Revised Romanization | Seoul |
| McCune–Reischauer | Sŏul |
| Seoul Special City | |
| Hangul | |
| Hanja | |
| Revised Romanization | Seoul Teukbyeolsi |
| McCune–Reischauer | Sŏul T'ŭkpyŏlsi |
Seoul's history traces back to 18 BC when it was founded by the people of Baekje, one of the Three Kingdoms of Korea. During the Joseon dynasty, Seoul was officially designated as the capital, surrounded by the Fortress Wall of Seoul. In the early 20th century, Seoul was occupied by the Japanese Empire, temporarily renamed "Gyeongseong." The Korean War brought fierce battles, with Seoul changing hands four times and leaving the city mostly in ruins. Nevertheless, the city has since undergone significant reconstruction and rapid urbanization.
Seoul was rated Asia's most livable city, with the second-highest quality of life globally according to Arcadis in 2015 and a GDP per capita (PPP) of approximately $40,000. 15 Fortune Global 500 companies, including industry giants such as Samsung,[9] LG, and Hyundai, are headquartered in the Seoul Capital Area, which has major technology hubs, such as Gangnam and Digital Media City,[10]. Seoul is ranked seventh in the Global Power City Index and the Global Financial Centres Index, and is one of the five leading hosts of global conferences.[11] The city has also hosted major events such as the 1986 Asian Games, the 1988 Summer Olympics, and the 2010 G20 Seoul summit.
Seoul is geographically set in a mountainous and hilly terrain, with Bukhan Mountain positioned on its northern edge. Within the Seoul Capital Area lie five UNESCO World Heritage Sites: Changdeok Palace, Hwaseong Fortress, Jongmyo Shrine, Namhansanseong, and the Royal Tombs of the Joseon dynasty.[12] Furthermore, Seoul has witnessed a surge in modern architectural development, with iconic landmarks including the N Seoul Tower, the 63 Building, the Lotte World Tower, the Dongdaemun Design Plaza, Lotte World, the Trade Tower, COEX, IFC Seoul, and Parc1. Seoul was named the World Design Capital in 2010 and has served as the national hub for the music, entertainment, and cultural industries that have propelled K-pop and the Korean Wave to international prominence.
Toponomy
The city has been known in the past by the names Wiryeseong (위례성; 慰禮城, during the Baekje era), Bukhansangun (북한산군; 北漢山郡 during the Goguryeo era), Namcheon (남천; 南川,[13] during the Silla era), Hanyang (한양; 漢陽, during the Northern and Southern States period), Namgyeong(남경; 南京, during Goryeo era), Hanseong (한성; 漢城, during the Joseon era), and Keijō (京城) or Gyeongseong (경성; 京城) during Japanese rule.[14]
During Japan's annexation of Korea, Hanseong (漢城) was renamed Keijō (京城) by the Imperial authorities to prevent confusion with the Hanja '漢' (a transliteration of an ancient Korean word Han (한) meaning "great"), which also refers to Han people or the Han dynasty in Chinese and in Japanese is a term for "China".[15]
After World War II and the liberation of Korea, the city took its present name, which originated from the Korean word meaning "capital city", which is believed to have descended from an ancient word, Seorabeol (서라벌; 徐羅伐), which originally referred to Gyeongju, the capital of Silla.[16] Ancient Gyeongju was also known in documents by the Chinese-style name Geumseong (金城, literally "Gold Castle or City" or "Metal Castle or City"), but it is unclear whether the native Korean-style name Seorabeol had the same meaning as Geumseong.
Unlike most place names in Korea, "Seoul" has no corresponding Hanja (Chinese characters used in the Korean language). On 18 January 2005, the Seoul government changed its official name in Chinese characters from the historic Hancheng (simplified Chinese: 汉城; traditional Chinese: 漢城; pinyin: Hànchéng) to Shou'er (首尔; 首爾; Shǒu'ěr).[17][18]
History
Early history
Settlement of the Han River area, where present-day Seoul is located, began around 4000 BC.[19]
Seoul is first recorded as Wiryeseong, the capital of Baekje (founded in 18 BC) in the northeastern area of modern Seoul.[19] There are several city walls remaining in the area that date from this time. Pungnaptoseong, an earthen wall located southeast Seoul, is widely believed to have been at the main Wiryeseong site.[20] As the Three Kingdoms competed for this strategic region, control passed from Baekje to Goguryeo in the 5th century.[21]
However, according to Samguk Sagi, both Baekje and Silla described the land as frontier border of Baekje, not as the capital region.[22][23] Moreover, Jinheung Taewang Stele found at current day Bukhansan tells that the place was underdeveloped as of 6th century AD,[13] suggesting that the first capital Wiryeseong was not located in or nearby Seoul.
In July or August 553, Silla took the control of the region from Baekje, and the city became a part of newly established Sin Province (신주; 新州).[22][23] Sin (新) has both meaning of "New" and "Silla", thus literally means New Silla Province.
In November 555, Jinheung Taewang made royal visit to Bukhansan, and inspected the borderline.[24] In 557, Silla abolished Sin Province, and established Bukhansan Province (북한산주; 北漢山州).[25] The word Hanseong (한성; 漢城; lit. Han Fortress) appears on the stone wall of "Pyongyang Fortress", which was presumably built in the mid to late 6th century AD over period of 42 years, located in Pyongyang, while there is no evidence that Seoul had name Hanseong dating the three kingdoms and earlier period.[26][27][28][29][30]
In 568, Jinheung Taewang made another royal visit to the northern border, visited Hanseong, and stayed in Namcheon on his way back to the capital. During his stay, he set Jinheung Taewang Stele, abolished Bukhansan Province, and established Namcheon Province (남천주; 南川州; South River Province), appointing the city as the provincial capital.[13][31] Based on the naming system, the actual name of Han River during this time was likely Namcheon (Nam River) itself or should have the word ending with "cheon" (천; 川) not "gang" (강; 江) nor "su" (수; 水). In addition, "Bukhansan" Jinheung Stele clearly states that Silla had possession of Hanseong (modern day Pyongyang), thus Bukhansan has to be located north of Hanseong. Modern day Pyongyang was not Pyongyang, Taedong River was likely Han River, and Bukhansan was not Bukhansan during the three kingdoms period.[13][32] Moreover, Pyongyang was a common noun meaning capital used by Goguryeo and Goryeo dynasties, similar to Seoul.[33]
In 603, Goguryeo attacked Bukhansanseong (북한산성; 北漢山城; Bukhan Mountain Fortress), which Silla ended up winning.[34][35] In 604, Silla abolished Namcheon Province, and reestablished Bukhansan Province in order to strengthen the northern border. The city lost its provincial capital position and was put under Bukhansan Province once again.[36] This further proves that Bukhansan was located in the North of modern-day Pyongyang as changing the provincial name and objective would not be required if Bukhansan was located within Seoul.
In the 11th century Goryeo, which succeeded Unified Silla, built a summer palace in Seoul, which was referred to as the "Southern Capital". It was only from this period that Seoul became a larger settlement.[19]
Joseon

When Joseon replaced Goryeo, the capital was moved to Seoul (also known as Hanyang or Hanseong), where it remained until the fall of the dynasty. The Gyeongbok Palace, built in the 14th century, served as the royal residence until 1592. The other large palace, Changdeokgung, constructed in 1405, served as the main royal palace from 1611 to 1872.[19] After Joseon changed its name to the Korean Empire in 1897, Hwangseong also designated Seoul.
Originally, the city was entirely surrounded by a massive circular stone wall to provide its citizens security from wild animals, thieves and attacks. The city has grown beyond those walls and although the wall no longer stands (except along Bugaksan Mountain (북악산; 北岳山), north of the downtown area[37]), the gates remain near the downtown district of Seoul, including most notably Sungnyemun (commonly known as Namdaemun) and Heunginjimun (commonly known as Dongdaemun).[38] During the Joseon dynasty, the gates were opened and closed each day, accompanied by the ringing of large bells at the Bosingak belfry.[39] In the late 19th century, after hundreds of years of isolation, Seoul opened its gates to foreigners and began to modernize. Seoul became the first city in East Asia to introduce electricity in the royal palace, built by the Edison Illuminating Company[40] and a decade later Seoul also implemented electrical street lights.[41]
Much of the development was due to trade with foreign countries like France and the United States. For example, the Seoul Electric Company, Seoul Electric Trolley Company, and Seoul Fresh Spring Water Company were all joint Korean–U.S. owned enterprises.[42] In 1904, an American by the name of Angus Hamilton visited the city and said, "The streets of Seoul are magnificent, spacious, clean, admirably made and well-drained. The narrow, dirty lanes have been widened, gutters have been covered, roadways broadened. Seoul is within measurable distance of becoming the highest, most interesting and cleanest city in the East."[43]
Japanese annexation of Korea
After the annexation treaty in 1910, Japan annexed Korea and renamed the city Gyeongseong ("Kyongsong" in Korean and "Keijo" in Japanese). Japanese technology was imported, the city walls were removed, some of the gates demolished. Roads became paved and Western-style buildings were constructed. The city was liberated by U.S. forces at the end of World War II.[19]
Contemporary history
In 1945, the city was officially named Seoul, and was designated as a special city in 1949.[19]
During the Korean War, Seoul changed hands between the Soviet/Chinese-backed North Korean forces and the American-backed South Korean forces four times: falling to the North Koreans in the June 1950 First Battle of Seoul, recaptured by UN forces in the September 1950 Second Battle of Seoul, falling to a combined Chinese/North Korean force in the January 1951 Third Battle of Seoul, and finally being recaptured once more by UN forces in Operation Ripper during the spring of 1951.[44][45] The extensive fighting left the city heavily damaged after the war. The capital was temporarily relocated to Busan.[19] One estimate of the extensive damage states that after the war, at least 191,000 buildings, 55,000 houses, and 1,000 factories lay in ruins. In addition, a flood of refugees had entered Seoul during the war, swelling the population of the city and its metropolitan area to an estimated 1.5 million by 1955.[46]
Following the war, Seoul began to focus on reconstruction and modernization. As South Korea's economy started to grow rapidly from the 1960s, urbanization also accelerated and workers began to move to Seoul and other larger cities.[46] From the 1970s, the size of Seoul administrative area greatly expanded as it annexed a number of towns and villages from several surrounding counties.[47]
Until 1972, Seoul was claimed by North Korea as its de jure capital, being specified as such in Article 103 of the 1948 North Korean constitution.[48]
South Korea's 2019 population was estimated at 51.71 million, and according to the 2018 Population and Housing Census, 49.8% of the population resided in the Seoul metropolitan area. This was up by 0.7% from 49.1% in 2010, showing a distinct trend toward the concentration of the population in the capital.[49] Seoul has become the economic, political and cultural hub of the country,[19] with several Fortune Global 500 companies, including Samsung, SK Holdings, Hyundai, POSCO and LG Group headquartered there.[50]
Seoul was the host city of the 1986 Asian Games and 1988 Summer Olympics as well as one of the venues of the 2002 FIFA World Cup.
Geography

Seoul is in the northwest of South Korea. Seoul proper comprises 605.25 km2 (233.69 sq mi),[3] with a radius of approximately 15 km (9 mi), roughly bisected into northern and southern halves by the Han River. The river is no longer actively used for navigation, because its estuary is located at the borders of the two Koreas, with civilian entry barred. There are four main mountains in central Seoul: Bugaksan, Inwangsan, Naksan and Namsan. The Seoul Fortress Wall, which historically bounded the city, goes over these mountains. The city is bordered by eight mountains, as well as the more level lands of the Han River plain and western areas.
Climate
| Seoul | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Climate chart (explanation) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Seoul has a humid continental climate influenced by the monsoons (Köppen: Dwa). Being in the extreme East Asia, the climate can be described as humid subtropical (Cwa, by −3 °C or 26.6 °F isotherm) with great variation in temperature and precipitation throughout the year.[51][52] The suburbs of Seoul are generally cooler than the center of Seoul because of the urban heat island effect.[53] Summers are hot and humid, with the East Asian monsoon taking place from June until September. August, the hottest month, has average high and low temperatures of 32.6 and 23.4 °C (91 and 74 °F) with higher temperatures possible. Heat index values can surpass 40 °C (104.0 °F) at the height of summer. Winters are usually cold to freezing with average January high and low temperatures of 1.5 and −5.9 °C (34.7 and 21.4 °F), and are generally much drier than summers, with an average of 24.9 days of snow annually. Sometimes, temperatures drop dramatically to below −10 °C (14 °F), and on some occasions as low as −15 °C (5 °F) in the mid winter period of January and February. Temperatures below −20 °C (−4 °F) have been recorded.
| Climate data for Seoul (1991–2020 normals, extremes 1907–present) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 14.4 (57.9) |
18.7 (65.7) |
25.1 (77.2) |
29.8 (85.6) |
34.4 (93.9) |
37.2 (99.0) |
38.4 (101.1) |
39.6 (103.3) |
36.0 (96.8) |
30.1 (86.2) |
28.0 (82.4) |
17.7 (63.9) |
39.6 (103.3) |
| Average high °C (°F) | 2.1 (35.8) |
5.1 (41.2) |
11.0 (51.8) |
17.9 (64.2) |
23.6 (74.5) |
27.6 (81.7) |
29.0 (84.2) |
30.0 (86.0) |
26.2 (79.2) |
20.2 (68.4) |
11.9 (53.4) |
4.2 (39.6) |
17.4 (63.3) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | −2.0 (28.4) |
0.7 (33.3) |
6.1 (43.0) |
12.6 (54.7) |
18.2 (64.8) |
22.7 (72.9) |
25.3 (77.5) |
26.1 (79.0) |
21.6 (70.9) |
15.0 (59.0) |
7.5 (45.5) |
0.2 (32.4) |
12.8 (55.0) |
| Average low °C (°F) | −5.5 (22.1) |
−3.2 (26.2) |
1.9 (35.4) |
8.0 (46.4) |
13.5 (56.3) |
18.7 (65.7) |
22.3 (72.1) |
22.9 (73.2) |
17.7 (63.9) |
10.6 (51.1) |
3.5 (38.3) |
−3.4 (25.9) |
8.9 (48.0) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −22.5 (−8.5) |
−19.6 (−3.3) |
−15.3 (4.5) |
−9.4 (15.1) |
2.4 (36.3) |
7.0 (44.6) |
10.9 (51.6) |
13.5 (56.3) |
3.2 (37.8) |
−5.1 (22.8) |
−11.9 (10.6) |
−23.1 (−9.6) |
−23.1 (−9.6) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 16.8 (0.66) |
28.2 (1.11) |
36.9 (1.45) |
72.9 (2.87) |
103.6 (4.08) |
129.5 (5.10) |
414.4 (16.31) |
348.2 (13.71) |
141.5 (5.57) |
52.2 (2.06) |
51.1 (2.01) |
22.6 (0.89) |
1,417.9 (55.82) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.1 mm) | 6.1 | 5.8 | 7.0 | 8.4 | 8.6 | 9.9 | 16.3 | 14.7 | 9.1 | 6.1 | 8.8 | 7.8 | 108.6 |
| Average snowy days | 7.1 | 5.1 | 2.8 | 0.2 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 2.3 | 6.4 | 23.9 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 56.2 | 54.6 | 54.6 | 54.8 | 59.7 | 65.7 | 76.2 | 73.5 | 66.4 | 61.8 | 60.4 | 57.8 | 61.8 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 169.6 | 170.8 | 198.2 | 206.3 | 223.0 | 189.1 | 123.6 | 156.1 | 179.7 | 206.5 | 157.3 | 162.9 | 2,143.1 |
| Percent possible sunshine | 52.3 | 53.6 | 51.0 | 51.9 | 48.4 | 41.2 | 26.8 | 36.2 | 47.2 | 57.1 | 50.2 | 51.1 | 46.4 |
| Average ultraviolet index | 2 | 3 | 5 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 9 | 7 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 6 |
| Source 1: Korea Meteorological Administration (percent sunshine 1981–2010)[54][55][56] | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: Weather Atlas (UV),[57] Meteo Climat (record highs and lows)[58] | |||||||||||||
Air quality
.png.webp)
Air pollution is a major issue in Seoul.[61][62][63][64] According to the 2016 World Health Organization Global Urban Ambient Air Pollution Database,[65] the annual average PM2.5 concentration in 2014 was 24 micrograms per cubic meter (1.0×10−5 gr/cu ft), which is 2.4 times higher than that recommended by the WHO Air Quality Guidelines[66] for the annual mean PM2.5. The Seoul Metropolitan Government monitors and publicly shares real-time air quality data.[67]
Since the early 1960s, the Ministry of Environment has implemented a range of policies and air pollutant standards to improve and manage air quality for its people.[68] The "Special Act on the Improvement of Air Quality in the Seoul Metropolitan Area" was passed in December 2003. Its 1st Seoul Metropolitan Air Quality Improvement Plan (2005–2014) focused on improving the concentrations of PM10 and nitrogen dioxide by reducing emissions.[69] As a result, the annual average PM10 concentrations decreased from 70.0 μg/m3 in 2001 to 44.4 μg/m3 in 2011[70] and 46 μg/m3 in 2014.[65] As of 2014, the annual average PM10 concentration was still at least twice than that recommended by the WHO Air Quality Guidelines.[66] The 2nd Seoul Metropolitan Air Quality Improvement Plan (2015–2024) added PM2.5 and ozone to its list of managed pollutants.[71]
Asian dust, emissions from Seoul and in general from the rest of South Korea, as well as emissions from China, all contribute to Seoul's air quality.[62][72] A partnership between researchers in South Korea and the United States is conducting an international air quality field study in Korea (KORUS-AQ) to determine how much each source contributes.[73]
Besides air quality, greenhouse gas emissions represent hot issues in South Korea since the country is among top-10 strongest emitters in the world. Seoul is the strongest hotspot of greenhouse gas emissions in the country and according to satellite data, the persistent carbon dioxide anomaly over the city is one of the strongest in the world.[74]
Government
The Seoul Metropolitan Government is the local government for Seoul, and is responsible for the administration and provision of various services to the city, including correctional institutions, education, libraries, public safety, recreational facilities, sanitation, water supply, and welfare services. It is headed by a mayor and three vice mayors, and is divided into 25 autonomous districts and 522 administrative neighborhoods.[75][76]
Administrative districts

Seoul is divided into 25 gu (구; 區) (district).[77] The gu vary greatly in area (from 10 to 47 km2 or 3.9 to 18.1 sq mi) and population (from fewer than 140,000 to 630,000). Songpa has the most people, while Seocho has the largest area. The government of each gu handles many of the functions that are handled by city governments in other jurisdictions. Each gu is divided into "dong" (동; 洞) or neighborhoods. Some gu have only a few dong while others like Jongno District have a very large number of distinct neighborhoods. Gu of Seoul consist of 423 administrative dongs (행정동) in total.[77] Dong are also sub-divided into 13,787 tong (통; 統), which are further divided into 102,796 ban in total.
Demographics
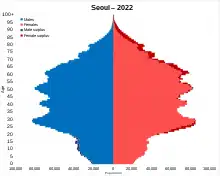
| Year | Pop. | ±% p.a. |
|---|---|---|
| 1950 | 1,021,000 | — |
| 1960 | 2,361,000 | +8.74% |
| 1970 | 5,312,000 | +8.45% |
| 1980 | 8,244,000 | +4.49% |
| 1990 | 10,518,000 | +2.47% |
| 2000 | 9,879,000 | −0.62% |
| 2010 | 9,796,000 | −0.08% |
| 2020 | 9,963,000 | +0.17% |
| source:[78] | ||
Seoul proper is noted for its population density, which is almost twice that of New York City and eight times greater than Rome. Its metropolitan area was the most densely populated among OECD countries in Asia in 2012, and second worldwide after that of Paris.[79] As of 2015, the population was 9.86 million,[80] in 2012, it was 10.44 million. As of 2021, the population is 9.59 million.[81][82] As of the end of June 2011, 10.29 million Republic of Korea citizens lived in the city. This was a 0.24% decrease from the end of 2010. The population of Seoul has been dropping since the early 1990s, the reasons being the high costs of living, urban sprawling to Gyeonggi region's satellite bed cities and an aging population.[80]
As of 2016, the number of foreigners living in Seoul was 404,037, 22.9% of the total foreign population in South Korea.[83] As of June 2011, 186,631 foreigners were Chinese citizens of Korean ancestry. This was an 8.84% increase from the end of 2010 and a 12.85% increase from June 2010. The next largest group was Chinese citizens who are not of Korean ethnicity; 29,901 of them resided in Seoul. The next highest group consisted of the 9,999 United States citizens who were not of Korean ancestry. The next highest group were Taiwanese citizens, at 8,717.[84]
The two major religions in Seoul are Christianity and Buddhism. Other religions include Muism (indigenous religion) and Confucianism. Seoul is home to one of the world's largest Christian congregations, Yoido Full Gospel Church, which has around 830,000 members.[85] According to the 2015 census, 10.8% of the population follows Buddhism and 35% follows Christianity (24.3% Protestantism and 10.7% Catholicism). 53.6% of the population is irreligious.[86]
Seoul is home to the world's largest modern university founded by a Buddhist Order, Dongguk University.[87] Native Seoulites tend to speak the Gyeonggi dialect of Korean.
Economy

Seoul is the business and financial hub of South Korea. Although it accounts for only 0.6 percent of the nation's land area, 48.3 percent of South Korea's bank deposits were held in Seoul in 2003,[88] and the city generated 23 percent of the country's GDP overall in 2012.[89] In 2008 the Worldwide Centers of Commerce Index ranked Seoul No.9.[90] The Global Financial Centres Index in 2015 listed Seoul as the 6th financially most competitive city in the world.[91] The Economist Intelligence Unit ranked Seoul 15th in the list of "Overall 2025 City Competitiveness" regarding future competitiveness of cities.[92]
Manufacturing
The traditional, labor-intensive manufacturing industries have been continuously replaced by information technology, electronics and assembly-type of industries;[93][94] however, food and beverage production, as well as printing and publishing remained among the core industries.[93] Major manufacturers are headquartered in the city, including Samsung, LG, Hyundai, Kia and SK. Notable food and beverage companies include Jinro, whose soju is the most sold alcoholic drink in the world, beating out Smirnoff vodka;[95] top selling beer producers Hite (merged with Jinro) and Oriental Brewery.[96] It also hosts food giants like Seoul Dairy Cooperative, Nongshim Group, Ottogi, CJ, Orion, Maeil Holdings, Namyang Dairy Products and Lotte.
Finance

Seoul hosts large concentration of headquarters of International companies and banks, including 15 companies on Fortune 500 list such as Samsung, LG and Hyundai.[97] Most bank headquarters and the Korea Exchange are located in Yeouido (Yeoui island),[93] which is often called "South Korea's Wall Street" and has been serving as the financial center of the city since the 1980s.[98] The Seoul international finance center & SIFC MALL, Hanhwa 63 building, the Hanhwa insurance company head office. Hanhwa is one of the three largest South Korean insurance companies, along with Samsung Life and Gangnam & Kyobo life insurance group.
Commerce

The largest wholesale and retail market in South Korea, the Dongdaemun Market, is located in Seoul.[99] Myeongdong is a shopping and entertainment area in downtown Seoul with mid- to high-end stores, fashion boutiques and international brand outlets.[100] The nearby Namdaemun Market, named after the Namdaemun Gate, is the oldest continually running market in Seoul.[101]
Insadong is the cultural art market of Seoul, where traditional and modern Korean artworks, such as paintings, sculptures and calligraphy are sold.[102] Hwanghak-dong Flea Market and Janganpyeong Antique Market also offer antique products.[103][104] Some shops for local designers have opened in Samcheong-dong, where numerous small art galleries are located. While Itaewon had catered mainly to foreign tourists and American soldiers based in the city, Koreans now comprise the majority of visitors to the area.[105] The Gangnam district is one of the most affluent areas in Seoul[105] and is noted for the fashionable and upscale Apgujeong-dong and Cheongdam-dong areas and the COEX Mall. Wholesale markets include Noryangjin Fisheries Wholesale Market and Garak Market.
The Yongsan Electronics Market is the largest electronics market in Asia. Electronics markets are Gangbyeon station metro line 2 Techno mart, ENTER6 MALL & Shindorim station Technomart mall complex.[106] Times Square is one of Seoul's largest shopping malls, and contains the world's largest permanent 35 mm cinema screen, the CGV Starium.[107]
Korea World Trade Center Complex, which comprises COEX mall, congress center, 3 Inter-continental hotels, Business tower (Asem tower), Residence hotel, Casino and City airport terminal was established in 1988 in time for the Seoul Olympics. The 2nd World trade trade center is being planned at Seoul Olympic stadium complex as MICE HUB by Seoul city. Ex-Kepco head office building was purchased by Hyundai motor group with 9billion USD to build 115-storey Hyundai GBC & hotel complex until 2021. Now ex-kepco 25-storey building is under demolition.
Technology
Seoul has been described as the world's "most wired city",[108] ranked first in technology readiness by PwC's Cities of Opportunity report.[109] Seoul has a very technologically advanced infrastructure.[110][111]
Seoul is among the world leaders in Internet connectivity, being the capital of South Korea, which has the world's highest fiber-optic broadband penetration and highest global average internet speeds of 26.1 Mbit/s.[112][113] Since 2015, Seoul has provided free Wi-Fi access in outdoor spaces through a 47.7 billion won ($44 million) project with Internet access at 10,430 parks, streets and other public places.[114] Internet speeds in some apartment buildings reach up to 52.5Gbit/s with assistance from Nokia, and though the average standard consists of 100 Mbit/s services, providers nationwide are rapidly rolling out 1Gbit/s connections at the equivalent of US$20 per month.[115] In addition, the city is served by the KTX high-speed rail and the Seoul Subway, which provides 4G LTE, Wi-Fi, and DMB inside subway cars. 5G will be introduced commercially in March 2019 in Seoul.
Architecture
_2011%EB%85%84_11%EC%9B%94_%EB%8C%80%ED%95%9C%EB%AF%BC%EA%B5%AD_%EC%84%9C%EC%9A%B8%ED%8A%B9%EB%B3%84%EC%8B%9C_%EB%AA%85%EC%86%8C_(Seoul_best_attractions)_10.jpg.webp)
The traditional heart of Seoul is the old Joseon dynasty city, now the downtown area, where most palaces, government offices, corporate headquarters, hotels, and traditional markets are located. Cheonggyecheon, a stream that runs from west to east through the valley before emptying into the Han River, was for many years covered with concrete, but was recently restored by an urban revival project in 2005.[116] Jongno street, meaning "Bell Street", has been a principal street and one of the earliest commercial streets of the city,[117][118] on which one can find Bosingak, a pavilion containing a large bell. The bell signaled the different times of the day and controlled the four major gates to the city. North of downtown is Bukhan Mountain, and to the south is the smaller Namsan. Further south are the old suburbs, Yongsan District and Mapo District. Across the Han River are the newer and wealthier areas of Gangnam District, Seocho District and surrounding neighborhoods.
Historical architecture

Seoul has many historical and cultural landmarks. In Amsa-dong Prehistoric Settlement Site, Gangdong District, neolithic remains were excavated and accidentally discovered by a flood in 1925.[119]
Urban and civil planning was a key concept when Seoul was first designed to serve as a capital in the late 14th century. The Joseon dynasty built the "Five Grand Palaces" in Seoul—Changdeokgung, Changgyeonggung, Deoksugung, Gyeongbokgung and Gyeonghuigung—all of which are located in the Jongno and Jung Districts. Among them, Changdeokgung was added to the UNESCO World Heritage List in 1997 as an "outstanding example of Far Eastern palace architecture and garden design". The main palace, Gyeongbokgung, underwent a large-scale restoration project.[120] The palaces are considered exemplary architecture of the Joseon period. Beside the palaces, Unhyeongung is known for being the royal residence of Regent Daewongun, the father of Emperor Gojong at the end of the Joseon Dynasty.
Seoul has been surrounded by walls that were built to regulate visitors from other regions and protect the city in case of an invasion. Pungnap Toseong is a flat earthen wall built at the edge of the Han River, which is widely believed to be the site of Wiryeseong. Mongchon Toseong is another earthen wall built during the Baekje period that is now located inside the Olympic Park.[20] The Fortress Wall of Seoul was built early in the Joseon dynasty for protection of the city. After many centuries of destruction and rebuilding, about 2⁄3 of the wall remains, as well as six of the original eight gates. These gates include the south gate Namdaemun and the east gate Dongdaemun. Namdaemun was the oldest wooden gate until a 2008 arson attack, and was re-opened after complete restoration in 2013.[121] Located near the gates are the traditional markets and largest shopping center, Namdaemun Market and Dongdaemun Market.
Modern architecture
Various high-rise office buildings and residential buildings, like the Gangnam Finance Center, the Tower Palace, Namsan Seoul Tower, and the Lotte World Tower, dominate the city's skyline. The tallest building is Lotte World Tower, reaching a height of 555m. It opened to the public in April 2017. It is also the 6th highest building in the world.
The World Trade Center Seoul, located in Gangnam District, hosts various expositions and conferences. Also in Gangnam District is the COEX Mall, a large indoor shopping and entertainment complex. Downstream from Gangnam District is Yeouido, an island that is home to the National Assembly, major broadcasting studios, and a number of large office buildings, as well as the Korea Finance Building and the Yoido Full Gospel Church. The Olympic Stadium, Olympic Park, and Lotte World are located in Songpa District, on the south side of the Han River, upstream from Gangnam District. Three new modern landmarks of Seoul are Dongdaemun Design Plaza & Park, designed by Zaha Hadid, the new wave-shaped Seoul City Hall, by Yoo Kerl of iArc, and the Lotte World Tower, the 6th tallest building in the world designed by Kohn Pedersen Fox.
In 2010 Seoul was designated the World Design Capital for the year.[122]
Culture
Museums
Seoul is home to 115 museums,[123] including four national and nine official municipal museums. The National Museum of Korea has a collection of 220,000 artifacts.[124] The National Folk Museum is located on the grounds of Gyeongbokgung and focuses on the daily life of historical Koreans.[125] Bukchon Hanok Village and Namsangol Hanok Village are old residential districts consisting of hanok (traditional Korean houses).[126][127]
The War Memorial covers the history of wars that Korea has been involved with, especially the Korean War.[128][129] Seodaemun Prison is a former prison built during the Japanese occupation, and is used as a historic museum.[130]
The Seoul Museum of Art, Leeum, Samsung Museum of Art, and Ilmin Museum of Art are art museums in the city.
Religious monuments
The city has buildings related to a number of religions. The Wongudan altar has been used since the Three Kingdoms Period. There are also a number of Confucian shrines, such as Jongmyo, Sajikdan, Munmyo, and Dongmyo. For Buddhism, Jogyesa is the headquarters of the Jogye Order of Korean Buddhism. Hwagyesa and Bongeunsa are also major Buddhist temples in Seoul.
The Myeongdong Cathedral is a landmark of the Myeongdong, Jung District. Yakhyeon Catholic Church is the first Gothic church to be built in Korea. Yoido Full Gospel Church is a Pentecostal church affiliated with the Assemblies of God on Yeouido in Seoul. The St. Nicholas Cathedral, but sometimes called bald church, is the only Byzantine-style church in Seoul.
Festivals
In October 2012, KBS Hall in Seoul hosted major international music festivals – First ABU TV and Radio Song Festivals within frameworks of Asia-Pacific Broadcasting Union 49th General Assembly.[131][132] Hi! Seoul Festival is a seasonal cultural festival held four times a year every spring, summer, autumn, and winter in Seoul, South Korea since 2003. It is based on the "Seoul Citizens' Day" held on every October since 1994 to commemorate the 600 years history of Seoul as the capital of the country. The festival is arranged under the Seoul Metropolitan Government. As of 2012, Seoul has hosted Ultra Music Festival Korea, an annual dance music festival that takes place on the 2nd weekend of June.[133]
Parks

Seoul has a large quantity of parks. One of the most famous parks is Namsan Park, which offers recreational hiking and views of the downtown Seoul skyline, especially via its N Seoul Tower. Seoul Olympic Park, located in Songpa District and built to host the 1988 Summer Olympics, is the largest park. The areas near the stream Tancheon are popular for exercise. Cheonggyecheon also has spaces for recreation. In 2017 the Seoullo 7017 Skypark opened, spanning diagonally overtop Seoul Station.
There are also many parks along the Han River, such as Ichon Hangang Park, Yeouido Hangang Park, Mangwon Hangang Park, Nanji Hangang Park, Banpo Hangang Park, Ttukseom Hangang Park and Jamsil Hangang Park. The Seoul National Capital Area also contains a green belt aimed at preventing the city from sprawling out into neighboring Gyeonggi Province. These areas are frequently sought after by people looking to escape from urban life on weekends and during vacations.
Media
Seoul is home of the major South Korean networks KBS, SBS, and MBC. The city is also home to the major South Korean newspapers Chosun Ilbo, Donga Ilbo, Joongang Ilbo, and Hankook Ilbo.
Sports

Seoul is a major center of South Korean sports, and has the largest number of professional sports teams and facilities in the country.
In the history of South Korea's major professional sports league championships, which include the K League, KBO League, KBL, and V-League, Seoul had multiple championship winners during the same season twice; in 1990, when Lucky-Goldstar FC (currently FC Seoul) won the 1990 K League and the LG Twins won the 1990 KBO League, and in 2016, when FC Seoul won the 2016 K League Classic and the Doosan Bears won the 2016 KBO League.[134]
International competition
Seoul hosted the 1986 Asian Games, also known as Asiad, 1988 Olympic Games, and Paralympic Games. It also served as one of the host cities of the 2002 FIFA World Cup. Seoul World Cup Stadium hosted the opening ceremony and first game of the tournament.
Taekwondo is South Korea's national sport and Seoul is the location of the Kukkiwon, the world headquarters of taekwondo, as well as the World Taekwondo Federation.
Football
Seoul's most well-known football club is FC Seoul.
- Men's football
| Tier | League | Club | Home stadium |
|---|---|---|---|
| Top | K League 1 | FC Seoul | Seoul World Cup Stadium |
| 2nd | K League 2 | Seoul E-Land | Mokdong Stadium |
| 4th | K4 League | Seoul Jungnang FC | Jungnang Public Ground |
| Seoul Nowon United | Nowon Madeul Stadium |
- Women's football
| Tier | League | Club | Home stadium |
|---|---|---|---|
| Top | WK League | Seoul City WFC | Seoul World Cup Auxiliary Stadium |
Baseball
| League | Club | Home stadium |
|---|---|---|
| KBO League | ||
| LG Twins | Jamsil Baseball Stadium | |
| Doosan Bears | ||
| Kiwoom Heroes | Gocheok Sky Dome | |
Basketball
| League | Club | Home stadium |
|---|---|---|
| KBL | ||
| Seoul SK Knights | Jamsil Students' Gymnasium | |
| Seoul Samsung Thunders | Jamsil Arena | |
Volleyball
| League | Division | Club | Home stadium |
|---|---|---|---|
| V-League | |||
| Men | Seoul Woori Card Woori Won | Jangchung Arena | |
| Women | GS Caltex Seoul KIXX | ||
Handball
- Seoul City
Transportation
Seoul has a well developed transportation network. Its system dates back to the era of the Korean Empire, when the first streetcar lines were laid and a railroad linking Seoul and Incheon was completed.[135] Seoul's most important streetcar line ran along Jongno until it was replaced by Line 1 of the subway system in the early 1970s. Other notable streets in downtown Seoul include Euljiro, Teheranno, Sejongno, Chungmuro, Yulgongno, and Toegyero. There are nine major subway lines stretching for more than 250 km (155 mi), with one additional line planned. As of 2010, 25% of the population has a commute time of an hour or longer.
Bus

Seoul's bus system is operated by the Seoul Metropolitan Government (S.M.G.), with four primary bus configurations available servicing most of the city. Seoul has many large intercity/express bus terminals. These buses connect Seoul with cities throughout South Korea. The Seoul Express Bus Terminal, Central City Terminal and Seoul Nambu Terminal are located in the district of Seocho District. In addition, East Seoul Bus Terminal in Gwangjin District and Sangbong Terminal in Jungnang District handles traffics mainly from Gangwon and Chungcheong provinces.
Urban rail
Seoul has a comprehensive urban railway network of 21 rapid transit, light metro and commuter lines that interconnects every district of the city and the surrounding areas of Incheon, Gyeonggi province, western Gangwon province, and northern Chungnam province. With more than 8 million passengers per day, the subway is one of the busiest subway systems in the world and the largest in the world, with a total track length of 940 km (580 mi). In addition, in order to cope with the various modes of transport, Seoul's metropolitan government employs several mathematicians to coordinate the subway, bus, and traffic schedules into one timetable. The various lines are run by Korail, Seoul Metro, NeoTrans Co. Ltd., AREX, and Seoul Metro Line 9 Corporation.
Train
Seoul is connected to every major city in South Korea by rail. Most major South Korean cities are linked via the KTX high-speed train, which has a normal operation speed of more than 300 km/h (186 mph). The Mugunghwa and Saemaeul trains also stop at all major stations. Major railroad stations include:
- Seoul Station, Yongsan District: Gyeongbu line (KTX/ITX-Saemaeul/Nuriro/Mugunghwa-ho)
- Yongsan station, Yongsan District: Honam line (KTX/ITX-Saemaeul/Nuriro/Mugunghwa), Jeolla/Janghang lines (Saemaul/Mugunghwa)
- Yeongdeungpo station, Yeongdeungpo District: Gyeongbu/Honam/Janghang lines (KTX/ITX-Saemaeul/Saemaul/Nuriro/Mugunghwa)
- Cheongnyangni station, Dongdaemun District: Gyeongchun/Jungang/Yeongdong/Taebaek lines (ITX-Cheongchun/ITX-Saemaeul/Mugunghwa)
- Suseo station (HSR), Gangnam District: Suseo HSR (SRT)
Airports
Seoul is served by two international airports, Incheon International Airport and Gimpo International Airport.
Gimpo International Airport opened in 1939 as an airfield for the Japanese Imperial Army and opened for civil aircraft in 1957. Since the opening of Incheon International, Gimpo International handles domestic flights along with some short haul international flights to Tokyo Haneda, Osaka Kansai, Taipei Songshan, Shanghai Hongqiao, and Beijing Capital although flights to Osaka Kansai and Beijing Capital also operate from Incheon International.
Incheon International Airport opened in March 2001 in Yeongjong island. It is now responsible for major international flights. Incheon International Airport is Asia's eighth busiest airport in terms of passengers, the world's fourth busiest airport by cargo traffic, and the world's eighth busiest airport in terms of international passengers in 2014. In 2016, 57,765,397 passengers used the airport. Incheon International Airport opened terminal 2 on 18 January 2018.
Incheon and Gimpo are linked to Seoul by expressway, and to each other by the AREX to Seoul Station. Intercity bus services are available to various destinations around the country.
Cycling
Cycling is becoming increasingly popular in Seoul and in the entire country. Both banks of the Han River have cycling paths that run all the way across the city along the river. In addition, Seoul introduced in 2015 a bicycle-sharing system named Ddareungi (and named Seoul Bike in English).[136]
Education
Universities

Seoul is home to the majority of South Korea's most prestigious universities, including Seoul National University, Yonsei University, Korea University.
Seoul ranked 2nd on the QS Best Student Cities 2023.[137]
Secondary education
Compulsory education lasts from grade 1–9 (six years of elementary school and 3 years of middle school).[138] Students spend six years in elementary school, three years in middle school, and three years in high school. Secondary schools generally require students to wear uniforms. There is an exit exam for graduating from high school and many students proceeding to the university level are required to take the College Scholastic Ability Test that is held every November. Although there is a test for non-high school graduates, called school qualification exam, most Koreans take the test.
Seoul is home to various specialized schools, including three science high schools, and six foreign language High Schools. Seoul Metropolitan Office of Education comprises 235 College-Preparatory High Schools, 80 Vocational Schools, 377 Middle Schools, and 33 Special Education Schools as of 2009.
International relations
Seoul is a member of the Asian Network of Major Cities 21 and the C40 Cities Climate Leadership Group. In addition, Seoul hosts many embassies of countries it has diplomatic ties with.
Sister cities
References
- ""Seoul, my soul" selected as the city's new slogan". Seoul Metropolitan Government. 5 April 2023. Archived from the original on 7 May 2023. Retrieved 11 May 2023.
- "서울시 사이트에 서울 시가인 서울의 찬가가 없습니다". Seoul Metropolitan Government. Archived from the original on 22 September 2021. Retrieved 22 September 2021.
- "Seoul Statistics (Land Area)". Seoul Metropolitan Government. Archived from the original on 19 October 2013. Retrieved 24 March 2010.
- "City Overview (Population)". Seoul Metropolitan Government. Archived from the original on 26 November 2021. Retrieved 26 November 2021.
- Seoul Capital Area
- "2021년 지역소득(잠정)".
- "Color". Archived from the original on 11 May 2012. Retrieved 8 April 2012.
- "Seoul's symbols". Seoul Metropolitan Government. Archived from the original on 19 August 2016. Retrieved 3 August 2016.
- "Samsung Electronics". Fortune. Archived from the original on 24 October 2014. Retrieved 24 October 2014.
- "Tech capitals of the world". The Age. Melbourne. 15 June 2009. Archived from the original on 12 September 2009. Retrieved 7 August 2013.
- Union of International Associations (UIA) International Meetings Statistics for the Year 2011 Archived 3 July 2014 at the Wayback Machine. Joel Fischer.
- "Lists: Republic of Korea". UNESCO. Archived from the original on 25 December 2019. Retrieved 26 December 2019.
- "Monument on Bukhansan Mountain Commemorating the Border Inspection by King Jinheung of Silla". National Institute of Korean History. Archived from the original on 22 January 2023. Retrieved 22 January 2023.
- Yu, Woo-ik; Lee, Chan (6 November 2019). "Seoul". Encyclopædia Britannica. Archived from the original on 9 June 2015. Retrieved 4 July 2020.
The city was popularly called Seoul in Korean during both the Chosŏn (Yi) dynasty (1392–1910) and the period of Japanese rule (1910–45), although the official names in those periods were Hansŏng (Hanseong) and Kyŏngsŏng (Gyeongseong), respectively.
- Kim, Dong Hoon (22 March 2017). Eclipsed Cinema: The Film Culture of Colonial Korea. ISBN 9781474421829. Archived from the original on 14 July 2022. Retrieved 21 November 2020.
- "Yahoo holiday travel guide". Uk.holidaysguide.yahoo.com. Archived from the original on 7 January 2007.
- 서울특별시표기 首爾로...중국, 곧 정식 사용키로 :: 네이버 뉴스 (in Korean). News.naver.com. 23 October 2005. Archived from the original on 25 January 2016. Retrieved 10 February 2012.
- Characters, Good. "Chinese Naming Crisis Danger Opportunity Summer 2006 – Good Characters". goodcharacters.com. Archived from the original on 30 September 2018. Retrieved 18 November 2018.
- "Seoul". Encyclopædia Britannica. Archived from the original on 22 February 2014. Retrieved 7 February 2014.
- "Pungnap-toseong (Earthen Ramparts)". Seoul Metropolitan Government. Archived from the original on 22 February 2014. Retrieved 7 February 2014.
- Tennant (12 November 2012). History Of Korea. Routledge. ISBN 9781136166983. Archived from the original on 10 October 2020.
- "Samguk Sagi Silla Jinheung 19". National Institute of Korean History. Archived from the original on 22 January 2023. Retrieved 22 January 2023.
- "Samguk Sagi Baekje Seong 19". National Institute of Korean History. Archived from the original on 22 January 2023. Retrieved 22 January 2023.
- "Samguk Sagi Silla Jinheung 24". National Institute of Korean History. Archived from the original on 22 January 2023. Retrieved 22 January 2023.
- "Samguk Sagi Silla Jinheung 28". National Institute of Korean History. Archived from the original on 22 January 2023. Retrieved 22 January 2023.
- "Pyongyang Fortress Stone 1". National Institute of Korean History. Archived from the original on 22 January 2023. Retrieved 22 January 2023.
- "Pyongyang Fortress Stone 2". National Institute of Korean History. Archived from the original on 22 January 2023. Retrieved 22 January 2023.
- "Pyongyang Fortress Stone 3". National Institute of Korean History. Archived from the original on 22 January 2023. Retrieved 22 January 2023.
- "Pyongyang Fortress Stone 4". National Institute of Korean History. Archived from the original on 22 January 2023. Retrieved 22 January 2023.
- "Pyongyang Fortress Stone 6". National Institute of Korean History. Archived from the original on 22 January 2023. Retrieved 22 January 2023.
- "Samguk Sagi Silla Jinheung 45". National Institute of Korean History. Archived from the original on 22 January 2023. Retrieved 22 January 2023.
- ""고구려 수도 평양은 북한땅에 없었다"". 신동아 (in Korean). 22 January 2013. Archived from the original on 22 January 2023. Retrieved 22 January 2023.
- "고대 평양은 지금의 평양이 아니다". K스피릿 (in Korean). 11 July 2016. Archived from the original on 22 January 2023. Retrieved 22 January 2023.
- "Samguk Sagi Silla Jinpyeong 30". National Institute of Korean History. Archived from the original on 22 January 2023. Retrieved 22 January 2023.
- "Samguk Sagi Goguryeo Yeongyang 15". National Institute of Korean History. Archived from the original on 22 January 2023. Retrieved 22 January 2023.
- "Samguk Sagi Silla Jinpyeong 32". National Institute of Korean History. Archived from the original on 22 January 2023. Retrieved 22 January 2023.
- "Bugaksan Mountain". Korea Tourism Organization. Archived from the original on 22 February 2014. Retrieved 7 February 2014.
- "Seoul City Wall". UNESCO. Archived from the original on 31 December 2019. Retrieved 7 February 2014.
- "Bosingak Belfry". Korea Tourism Organization. Archived from the original on 22 February 2014. Retrieved 7 February 2014.
- Nam Moon Hyon. "Early History of Electrical Engineering in Korea: Edison and First Electric Lighting in the Kingdom of Corea" (PDF). Promoting the History of EE Jan 23–26, 2000. Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers. Archived (PDF) from the original on 22 February 2014. Retrieved 7 February 2014.
- Kyung Moon Hwang (2010). A History of Korea. Palgrave Macmillan. p. 142. ISBN 9780230364523. Archived from the original on 25 January 2016. Retrieved 9 November 2015.
- Young-Iob Chung (2006). Korea under Siege, 1876–1945 : Capital Formation and Economic Transformation. Oxford University Press. p. 70. ISBN 9780198039662.
- Bruce Cumings (2005). Korea's Place in the Sun: A Modern History. W. W. Norton & Company. ISBN 9780393347531. Archived from the original on 30 September 2022. Retrieved 21 November 2020.
- "The Korean War Chronology | U.S. Army Center of Military History". history.army.mil. Archived from the original on 9 September 2023. Retrieved 6 September 2023.
- "CHAPTER XXVI: The Capture of Seoul". history.army.mil. Archived from the original on 7 February 2023. Retrieved 6 September 2023.
- Stephen Hamnett, Dean Forbes, ed. (2012). Planning Asian Cities: Risks and Resilience. Routledge. p. 159. ISBN 9781136639272. Archived from the original on 25 January 2016. Retrieved 9 November 2015.
- "Urban Planning of Seoul" (PDF). Seoul Metropolitan Government. 2009. Archived from the original on 25 January 2016. Retrieved 7 February 2014.
- "Constitution of the Democratic People's Republic of Korea" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 14 September 2016. Retrieved 20 January 2017.
- "Korean Cultural Centre India New Delhi". Korean Cultural Centre India New Delhi. Archived from the original on 20 July 2020. Retrieved 31 October 2021.
- "GLOBAL 500". CNNMoney. 23 July 2012. Archived from the original on 19 November 2018. Retrieved 7 February 2014.
- "Seoul, South Korea Köppen Climate Classification (Weatherbase)". Weatherbase. Archived from the original on 10 October 2020. Retrieved 9 June 2019.
- Peterson, Adam (31 October 2018), English: Data sources: Köppen types calculated from data from WorldClim.org, archived from the original on 10 October 2020, retrieved 9 June 2019
- Lee, Sang-Hyun; Baik, Jong-Jin (1 March 2010). "Statistical and dynamical characteristics of the urban heat island intensity in Seoul". Theoretical and Applied Climatology. 100 (1–2): 227–237. Bibcode:2010ThApC.100..227L. doi:10.1007/s00704-009-0247-1. S2CID 120641921. Archived from the original on 10 October 2020. Retrieved 18 November 2018.
- "Climatological Normals of Korea (1991 ~ 2020)" (PDF) (in Korean). Korea Meteorological Administration. Archived from the original (PDF) on 29 January 2022. Retrieved 31 January 2022.
- 순위값 - 구역별조회 (in Korean). Korea Meteorological Administration. Retrieved 2 October 2021.
- "Climatological Normals of Korea" (PDF). Korea Meteorological Administration. 2011. p. 499 and 649. Archived from the original (PDF) on 7 December 2016. Retrieved 8 December 2016.
- "Seoul, South Korea - Detailed climate information and monthly weather forecast". Weather Atlas. Yu Media Group. Retrieved 9 July 2019.
- "Station Seoul" (in French). Meteo Climat. Retrieved 10 October 2018.
- "South Korea near bottom of world survey of air quality". The Korea Herald. 16 May 2016. Archived from the original on 2 April 2017. Retrieved 4 May 2017.
South Korea ranked 173rd out of 180 countries in terms of air quality, the Environmental Performance Index 2016 rankings showed Monday. ... A report said that 1.3 billion people exposed to poor air quality lived in East Asian countries, with more than 50 percent of the populations in South Korea and China exposed to dangerous levels of fine dust.
- "South Korea | Environmental Performance Index – Development". epi.yale.edu. Archived from the original on 7 May 2017. Retrieved 4 May 2017.
- Lee, Hyun-jeong. "Korea Wrestles with Growing Health Threat from Fined Dust" Archived 9 April 2017 at the Wayback Machine. Korea Herald. 23 March 2015. Retrieved 8 April 2017.
- Hu, Elise. "Korea's Air Is Dirty, But It's Not All Close-Neighbor China's Fault" Archived 9 August 2018 at the Wayback Machine. NPR. 3 June 2016. Retrieved 8 April 2017.
- "Seoul's smelly gingko problem". BBC News. 12 October 2015. Archived from the original on 17 February 2019. Retrieved 16 February 2019.
- "[Feature] South Korea's odor pollution problem". 3 October 2018. Archived from the original on 17 February 2019. Retrieved 16 February 2019.
- Global Urban Ambient Air Pollution Database. Archived 19 April 2019 at the Wayback Machine World Health Organization. May 2016. Retrieved 8 April 2017.
- WHO Air Quality Guidelines. Archived 23 April 2018 at the Wayback Machine World Health Organization. September 2016. Retrieved 8 April 2017.
- Air Quality Information. Archived 10 April 2017 at the Wayback Machine Seoul Metropolitan Government. Retrieved 8 April 2017.
- Yu-Jin Choi; Woon-Soo Kim (25 June 2015). "Changes in Seoul's Air Quality Control Policy". Seoul Solution. Archived from the original on 6 September 2017. Retrieved 12 April 2017.
- 1st Seoul Metropolitan Air Quality Improvement Plan. Archived 27 April 2017 at the Wayback Machine Ministry of Environment, Republic of Korea. Retrieved 21 April 2017.
- Kim, Honghyok; Kim, Hyomi; Lee, Jong-Tae (2015). "Effects of ambient air particles on mortality in Seoul: Have the effects changed over time?". Environmental Research. 140: 684–690. Bibcode:2015ER....140..684K. doi:10.1016/j.envres.2015.05.029. PMID 26079317.
- 2nd Seoul Metropolitan Air Quality Improvement Plan. Archived 26 April 2017 at the Wayback Machine Ministry of Environment, Republic of Korea. Retrieved 21 April 2017.
- Chung, Anna. "Korea's policy towards pollution and fine particle: a sense of urgency" Archived 2017-04-27 at the Wayback Machine. Korea Analysis. v2. June 2014. Retrieved 21 April 2017.
- Zastrow, Mark (6 May 2016). "NASA jet gets a sniff of pollution over South Korea". Nature. doi:10.1038/nature.2016.19875. S2CID 130657973. Archived from the original on 26 April 2017. Retrieved 26 April 2017.
- Labzovskii, Lev; Jeong, Su-Jong; Parazoo, Nicholas C. (2019). "Working towards confident spaceborne monitoring of carbon emissions from cities using Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2". Remote Sensing of Environment. 233. 111359. Bibcode:2019RSEnv.23311359L. doi:10.1016/j.rse.2019.111359. S2CID 202176909.
- "서울특별시청 Seoul Metropolitan Government" (in Korean). Doosan Encyclopedia. Archived from the original on 22 January 2013. Retrieved 7 May 2008.
- "Organization Chart". Official site of Seoul Metropolitan Government. Archived from the original on 8 May 2008. Retrieved 7 May 2008.
- "Administrative Districts". Seoul Metropolitan Government. Archived from the original on 10 August 2011. Retrieved 8 February 2014.
- "World Urbanization Prospects". Archived from the original on 19 January 2020. Retrieved 20 February 2020.
- "Regional population density: Asia and Oceania, 2012: Inhabitants per square kilometre, TL3 regions". OECD Regions at a Glance 2013. 2013. doi:10.1787/reg_glance-2013-graph37-en. Archived from the original on 21 February 2014. Retrieved 11 February 2014.
- "Seoul's Population Drops Below 10 Million for First Time in 25 Years". Chosun Ilbo. 14 February 2014. Archived from the original on 4 March 2014. Retrieved 16 February 2014.
- "32년 만에 '1000만 서울 시대' 막 내렸다..." 한국일보 (in Korean). 3 March 2021. Archived from the original on 17 April 2021. Retrieved 17 April 2021.
- "Seoul Statistics (Population)". Seoul Metropolitan Government. Archived from the original on 19 October 2013. Retrieved 3 March 2013.
- "1.76 million foreigners live in South Korea; 3.4% of population". 17 November 2017. Archived from the original on 21 December 2017. Retrieved 20 December 2017.
- "Korean Chinese account for nearly 70% of foreigners in Seoul". The Korea Times. 11 September 2011. Archived from the original on 19 January 2012. Retrieved 11 February 2014.
- "South Korean mega-churches. For God and country". Economist. 15 October 2011. Archived from the original on 15 January 2018. Retrieved 11 February 2014.
- "2015 Census – Religion Results" (in Korean). KOSIS KOrean Statistical Information Service. Archived from the original on 26 February 2021. Retrieved 10 March 2021.
- "Dongguk University". Archived from the original on 15 September 2018.
- Yim, Seok-hui. "Geographical Features of Social Polarization in Seoul, South Korea" (PDF). In Mizuuchi, Toshio (ed.). Representing Local Places and Raising Voices from Below. Osaka City University. p. 34. Archived (PDF) from the original on 23 April 2016. Retrieved 19 April 2016.
- Industrial Policy and Territorial Development: Lessons from Korea. OECD Development Center. 16 May 2012. p. 58. ISBN 9789264173897.
- "Worldwide Centers of Commerce Index" (PDF). MasterCard. Archived from the original (PDF) on 24 June 2008. Retrieved 13 February 2014.
- "The Global Financial Centres Index 12" (PDF). Z/Yen Group. 2012. Archived from the original (PDF) on 23 March 2014. Retrieved 11 February 2014.
- "Hot Spots 2025: Benchmarking the Future Competitiveness of Cities" (PDF). The Economist Intelligence Unit. 2013. Archived (PDF) from the original on 9 January 2014. Retrieved 13 February 2014.
- "Seoul: Economy". Encyclopædia Britannica. Archived from the original on 22 February 2014. Retrieved 13 February 2014.
- "The primacy of Seoul and the capital region". United Nations University. Archived from the original on 4 November 2014. Retrieved 13 February 2014.
- "It's official: Jinro soju is the world's best-selling liquor". CNNTravel. 12 June 2012. Archived from the original on 21 February 2014. Retrieved 29 April 2013.
- "Fiery food, boring beer". The Economist. 24 November 2012. Archived from the original on 1 July 2017. Retrieved 24 April 2013.
- "Global : Cities". CNN. Archived from the original on 29 May 2010. Retrieved 3 August 2020.
- "Neon shines brightly during the bustle on Yeouido stock street". Korea JoongAng Daily. 5 January 2010. Archived from the original on 17 May 2014. Retrieved 13 February 2014.
- "Dongdaemun Market". Visit Seoul. Archived from the original on 22 February 2014. Retrieved 11 February 2014.
- "Myeong-dong". Korea Tourism Organization. Archived from the original on 15 February 2014. Retrieved 11 February 2014.
- 서울공식여행가이드. Visit Seoul Net. Archived from the original on 14 February 2016. Retrieved 16 May 2018.
- "Insa-dong". Korea Tourism Organization. Archived from the original on 16 January 2014. Retrieved 11 February 2014.
- "Hwanghak-dong Flea Market". Korea Tourism Organization. Archived from the original on February 22, 2014. Retrieved February 12, 2014.
- "Antique Markets". Seoul Matropolitan Government. Archived from the original on 8 October 2010. Retrieved 12 February 2014.
- "Itaewon: Going Gangnam Style?". The Korea Times. 14 February 2013. Archived from the original on 4 March 2016. Retrieved 12 February 2014.
- "Yongsan Electronics Market, Asia's largest IT shopping mall". KBS World. 1 March 2011. Archived from the original on 21 February 2014. Retrieved 12 February 2014.
- "Largest Permanent 35mm Cinema Screen". Guinnessworldrecords.com. 18 August 2009. Archived from the original on 16 January 2013. Retrieved 7 August 2013.
- "50 reasons why Seoul is world's greatest city". 12 July 2017. Archived from the original on 22 October 2014. Retrieved 24 October 2014.
- PricewaterhouseCoopers. "Cities of Opportunity" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 20 May 2014. Retrieved 20 May 2014.
- "KOREA: Future is now for Korean info-tech". AsiaMedia. Regents of the University of California. 14 June 2005. Archived from the original on 16 December 2008.
- "Tech capitals of the world – Technology". The Age. Melbourne, Australia. 18 June 2007. Archived from the original on 12 September 2009. Retrieved 18 June 2009.
- akamai's [state of the internet] Q4 2016 report (PDF) (Report). Akamai Technologies. Archived (PDF) from the original on 13 May 2018. Retrieved 18 December 2017.
- "Hi Seoul, SOUL OF ASIA – Seoul Located In the Center of Asian Metropolises". English.seoul.go.kr. Archived from the original on 10 July 2012. Retrieved 7 August 2013.
- Wifi in All Public Areas Archived 17 June 2011 at the Wayback Machine
- CJ헬로비전-에러페이지. Archived from the original on 20 December 2017. Retrieved 18 December 2017.
- "Seoul's Cheonggyecheon Stream symbolizes Korea's past, present and tomorrow". Korea.net. Archived from the original on 22 February 2014. Retrieved 12 February 2014.
- Vinayak Bharne, ed. (2013). The Emerging Asian City: Concomitant Urbanities and Urbanisms. Routledge. p. 59. ISBN 9780415525978. Archived from the original on 25 January 2016. Retrieved 9 November 2015.
- Andrei Lankov (24 June 2010). "Jongno walk". The Korea Times. Archived from the original on 1 October 2015. Retrieved 12 February 2014.
- "Amsa-dong Prehistoric Settlement Site". Korea Tourism Organization. Archived from the original on 22 February 2014. Retrieved 12 February 2014.
- "About the Palace". Gyeongbokgung Palace. Archived from the original on 14 June 2008. Retrieved 12 February 2014.
- "Sungnyemun to open to great fanfare after more than five years of renovation". The Korea Herald. 30 April 2013. Archived from the original on 30 April 2013. Retrieved 1 May 2013.
- "The Seoul of World Design". Bloomberg Businessweek. 27 February 2008. Archived from the original on 18 April 2014. Retrieved 12 February 2014.
- "Status of Museum". Seoul Metropolitan Government. Archived from the original on 11 September 2014. Retrieved 18 September 2014.
- "Seoul's best museums". CNN. 27 October 2011. Archived from the original on 16 September 2014. Retrieved 2 June 2013.
- "National Folk Museum of Korea". Korea Tourism Organization. Archived from the original on 16 July 2014. Retrieved 18 September 2014.
- "Namsangol Hanok Village". Korea Tourism Organization. Archived from the original on 12 October 2014. Retrieved 18 September 2014.
- "Bukchon Hanok Village". Korea Tourism Organization. Archived from the original on 15 September 2014. Retrieved 18 September 2014.
- Veale, Jennifer. "Seoul: 10 Things to Do". Time. Time magazine. Archived from the original on 27 September 2014. Retrieved 18 September 2014.
- "The War Memorial of Korea". Korea Tourism Organization. Archived from the original on 14 February 2015. Retrieved 18 September 2014.
- "Seodaemun Prison History Museum". Korea Tourism Organization. Archived from the original on 4 June 2014. Retrieved 18 September 2014.
- "ABU TV and Radio Song Festivals 2012". ESCKAZ.com. Archived from the original on 10 April 2014. Retrieved 17 August 2012.
- "ABU GA Seoul 2012". Asia-Pacific Broadcasting Union. Archived from the original on 3 March 2013. Retrieved 17 August 2012.
- "Ultra Korea – June 8, 9, 10 2018". Ultra Korea. Archived from the original on 6 September 2015. Retrieved 31 December 2014.
- 2016 프로야구와 프로축구는 모두'서울의 봄' (in Korean). Medeaus Ilbo. 7 November 2016. Archived from the original on 9 November 2016. Retrieved 7 November 2016.
- "The subway's past and present". Archived from the original on 18 February 2023.
- "Expanded Operation of Seoul Bike "Ddareungi"". 18 March 2016. Archived from the original on 5 April 2019.
- "QS Best Student Cities 2023". Quacquarelli Symonds Limited. 29 June 2022. Archived from the original on 7 July 2022. Retrieved 20 July 2022.
- 의무교육(무상의무교육). Archived from the original on 10 October 2020. Retrieved 13 October 2017.
- "Sister & Friendship Cities -". Official Website of the Seoul Metropolitan Government. Archived from the original on 30 September 2022. Retrieved 30 September 2022.
- "Exchange Cities of Seoul Metropolitan Council". Seoul Metropolitan Council. Archived from the original on 7 September 2022. Retrieved 7 September 2022.
External links
 The dictionary definition of Seoul at Wiktionary
The dictionary definition of Seoul at Wiktionary Media related to Seoul (category) at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Seoul (category) at Wikimedia Commons Quotations related to Seoul at Wikiquote
Quotations related to Seoul at Wikiquote Seoul travel guide from Wikivoyage
Seoul travel guide from Wikivoyage
Official sites
- Official website (in English)
- Seoul Information & Communication Plaza website (in Korean)
Tourism and living information
- i Tour Seoul – The Official Seoul Tourism Guide Site
_(cropped).jpg.webp)
_%EC%82%AC%EB%B3%B8_-1S6O1452.jpg.webp)


.jpg.webp)
.jpg.webp)





.jpg.webp)





