Iclazepam
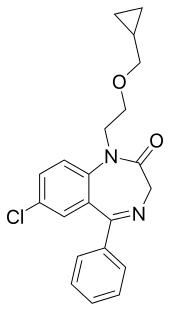
Iclazepam (Clazepam) is a drug which is a benzodiazepine derivative. It has sedative and anxiolytic effects similar to those produced by other benzodiazepine derivatives, and is around the same potency as chlordiazepoxide.
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C21H21ClN2O2 |
| Molar mass | 368.86 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Iclazepam is a derivative of nordazepam substituted with a cyclopropylmethoxyethyl group on the N1 nitrogen. Once in the body, iclazepam is quickly metabolised to nordazepam and its N-(2-hydroxyethyl) derivative, which are thought to be mainly responsible for its effects.[1]
See also
References
- Giudicelli JF, Berdeaux A, Idrissi N, Richer C (January 1978). "Clazepam: pharmacokinetics and effects on performance". British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology. 5 (1): 65–9. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2125.1978.tb01599.x. PMC 1429233. PMID 23135.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.