Fluadinazolam
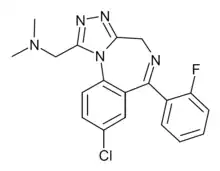
Fluadinazolam is a benzodiazepine derivative developed in 1973, with sedative and anxiolytic effects.[1] It is a derivative of the never commercially marketed benzodiazepine adinazolam and has similarly been sold as a designer drug.[2]
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C19H17ClFN5 |
| Molar mass | 369.83 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
References
- US 3957761, Gall M, Hester JB, "Process for the production of 1-aminomethyl-6-phenyl-4h-s-triazolo-[4,3-a][1]benzodiazepines and intermediates", issued 18 May 1976, assigned to Pharmacia and Upjohn
- Catalani V, Botha M, Corkery JM, Guirguis A, Vento A, Scherbaum N, Schifano F (July 2021). "The Psychonauts' Benzodiazepines; Quantitative Structure-Activity Relationship (QSAR) Analysis and Docking Prediction of Their Biological Activity". Pharmaceuticals. Basel, Switzerland. 14 (8): 720. doi:10.3390/ph14080720. PMC 8398354. PMID 34451817.
| Alcohols | |
|---|---|
| Barbiturates |
|
| Benzodiazepines |
|
| Carbamates | |
| Flavonoids | |
| Imidazoles | |
| Kava constituents |
|
| Monoureides |
|
| Neuroactive steroids |
|
| Nonbenzodiazepines | |
| Phenols | |
| Piperidinediones | |
| Pyrazolopyridines | |
| Quinazolinones | |
| Volatiles/gases |
|
| Others/unsorted |
|
See also: Receptor/signaling modulators • GABA receptor modulators • GABA metabolism/transport modulators | |
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.