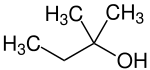
tert-Amyl alcohol
tert-Amyl alcohol (TAA) or 2-methylbutan-2-ol (2M2B), is a branched pentanol.
 | |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
2-Methylbutan-2-ol | |||
| Other names
2-Methyl-2-butanol tert-Amyl alcohol t-Amylol TAA tert-Pentyl alcohol 2-Methyl-2-butyl alcohol t-Pentylol Amylene hydrate Dimethylethylcarbinol | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol) |
|||
| 1361351 | |||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.827 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
| KEGG | |||
| MeSH | tert-amyl+alcohol | ||
PubChem CID |
|||
| RTECS number |
| ||
| UNII | |||
| UN number | 1105 | ||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C5H12O | |||
| Molar mass | 88.150 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | Colorless liquid | ||
| Odor | Camphorous | ||
| Density | 0.805 g/cm3[1] | ||
| Melting point | −9 °C; 16 °F; 264 K | ||
| Boiling point | 101 to 103 °C; 214 to 217 °F; 374 to 376 K | ||
| 120 g·dm−3 | |||
| Solubility | soluble in water, benzene, chloroform, diethylether and ethanol[2] | ||
| log P | 1.0950.5:1 volume ratio | ||
| Vapor pressure | 1.6 kPa (at 20 °C) | ||
| −7.09×10−5 cm3/mol | |||
Refractive index (nD) |
1.405 | ||
| Viscosity | 4.4740 mPa·s (at 298.15 K)[1] | ||
| Thermochemistry | |||
Std molar entropy (S⦵298) |
229.3 J K−1 mol−1 | ||
Std enthalpy of formation (ΔfH⦵298) |
−380.0 to −379.0 kJ mol−1 | ||
Std enthalpy of combustion (ΔcH⦵298) |
−3.3036 to −3.3026 MJ mol−1 | ||
| Hazards | |||
| GHS labelling: | |||
  | |||
| Danger | |||
| H225, H315, H332, H335 | |||
| P210, P261 | |||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |||
| Flash point | 19 °C (66 °F; 292 K) | ||
| 437 °C (819 °F; 710 K) | |||
| Explosive limits | 9% | ||
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | hazard.com | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |||
Historically TAA has been used an anesthetic[3] and more recently used as a recreational drug.[4] TAA is mostly a positive allosteric modulator for GABAA receptors in the same way as ethanol.[5] The psychotropic effects of TAA and ethanol are similar, though distinct. Impact on coordination and balance are proportionately more prominent with TAA, which is significantly more potent by weight than ethanol. It's appeal as an alternative to ethanol may stem from it's lack of a hangover (due to different metabolic pathways) and difficulty in detecting through standard drug testing.[6]
TAA is a colorless liquid with a burning flavor[7] and an unpleasant odor[8] similar to paraldehyde with a hint of camphor.[9] TAA remains as a liquid at room temperature making it a useful alternative solvent to tert-butyl alcohol.
Production
TAA is primarily made by the hydration of 2-methyl-2-butene in the presence of an acidic catalyst.[10][3] On the other hand, it could be product from acetone and acetylene by Favorskii reaction to give 2-Methylbut-3-yn-2-ol, then hydrogenation with Raney nickel catalyst to give Tert-Amyl alcohol.
Natural occurrence
Fusel alcohols like TAA are grain fermentation byproducts and therefore trace amounts of TAA are present in many alcoholic beverages.[11] Traces of TAA have been detected in other foods, like fried bacon,[12] cassava[13] and rooibos tea.[14] TAA is also present in rabbit milk and seems to play a role of pheromone inducing suckling in the newborn rabbit. [15]
History
From about 1880s to 1950s, TAA was used as an anesthetic with the contemporary name of amylene hydrate, but was rarely used solely because of the existence of more efficient drugs.[3] In the 1930s, TAA was mainly used as a solvent for the primary anesthetic tribromoethanol (TBE). Like chloroform, TBE is toxic for the liver, so the use of such solutions declined in the 1940s in humans. TBE-TAA-solutions remained in use as short-acting anesthetics for laboratory mice and rats. Such solutions are sometimes called Avertin, which was a brand name for the now discontinued TAA and TBE solution with a volume ratio of 0.5:1 made by the Winthrop Laboratories.[16] Nowadays TAA has found use as a recreational drug.[4]
Use and effects
Ingestion or inhalation of TAA causes euphoria, sedative, hypnotic, and anticonvulsant effects similar to ethanol.[17] When ingested, the effects of TAA may begin in about 30 minutes and can last up to 1–2 days.[18] 2–4 grams of TAA causes unconsciousness. About 100 g of ethanol induces a similar level of unconsciousness.[8]
Overdose and toxicity
The smallest known dose of TAA that has killed a person is 30 mL.[18]
An overdose produces symptoms similar to alcohol poisoning and is a medical emergency due to the sedative/depressant properties which manifest in overdose as potentially lethal respiratory depression. Sudden loss of consciousness, simultaneous respiratory and metabolic acidosis,[18] fast heartbeat, increased blood pressure, pupil constriction, coma, respiratory depression[19] and death may follow from an overdose. The oral LD50 in rats is 1 g/kg. The subcutaneous LD50 in mice is 2.1 g/kg.[20]
Metabolism
In rats, TAA is primarily metabolized via glucuronidation, as well as by oxidation to 2-methyl-2,3-butanediol. It is likely that the same path is followed in humans,[21] though older sources suggest TAA is excreted unchanged.[3]

The use of TAA cannot be detected with general ethanol tests or other ordinary drug tests. Its use can be detected from a blood or a urine sample by using gas chromatography–mass spectrometry for up to 48 hours after consumption.[19]
See also
References
- Lomte, S.B.; Bawa, M.J.; Lande, M.K.; Arbad, B.R. (2009). "Densities and Viscosities of Binary Liquid Mixtures of 2-Butanone with Branched Alcohols at (293.15 to 313.15) K". Journal of Chemical & Engineering Data. 54: 127–130. doi:10.1021/je800571y.
- Haynes, William M.; Lide, David R.; Bruno, Thomas J. (2014). "Section 3 - Physical Constants of Organic Compounds". CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 95th Edition (95th ed.). CRC Press. p. 362. ISBN 9781482208689. OCLC 908078665.
- Adriani, John (1962). The Chemistry and Physics of Anesthesia (2nd ed.). Illinois: Thomas Books. pp. 273–274. ISBN 9780398000110.
- Rusiecka, Izabela; Gągało, Iwona; Anand, Jacek Sein; Schetz, Daria; Waldman, Wojciech (October 2016). "Drinking "Vodka" or vodka – This is a question". Toxicology in Vitro. 36: 66–70. doi:10.1016/j.tiv.2016.07.009. ISSN 1879-3177. PMID 27448500.
- Martin, J (2004). "Influence of oxygenated fuel additives and their metabolites on γ-aminobutyric acidA (GABAA) receptor function in rat brain synaptoneurosomes". Toxicology Letters. 147 (3): 209–217. doi:10.1016/j.toxlet.2003.10.024. PMID 15104112.
- Syed, Alia N.; Leo, Raphael J. (2022-11-22). "Recreational 2-Methyl-2-Butanol Use: An Emerging Wave of Misuse of an Ethanol Substitute on the Horizon?". The Primary Care Companion for CNS Disorders. 24 (6): 44189. doi:10.4088/PCC.22cr03292. ISSN 2155-7780.
- O'Neil, Maryadele J., ed. (2006). The Merck index (14th ed.). Merck. p. 1232. ISBN 9780911910001. OCLC 70882070.
- Brandenberger, Hans; Maes, Robert A. A. (1997). Analytical Toxicology for Clinical, Forensic, and Pharmaceutical Chemists. Berlin: W. de Gruyter. pp. 400–401. ISBN 978-3110107319. OCLC 815506841.
- Yandell, D. W.; et al. (1888). "Amylene hydrate, a new hypnotic". The American Practitioner and News. 5: 88–98.
- Papa, Anthony J. (2004). "Amyl Alcohols". Kirk–Othmer Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology (5th ed.). Hoboken, N.J.: Wiley-Interscience. doi:10.1002/0471238961.0113251216011601.a01.pub2. ISBN 9780471238966.
- Gould, George M.; Scott, Richard J. E. (1919). The Practitioner's Medical Dictionary. P. Blakiston's. p. 50. Retrieved 2018-07-27.
- Ho, C.-T.; Lee, K.-N.; Jin, Q.-Z. (1983). "Isolation and identification of volatile flavor compounds in fried bacon". Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry. 31 (2): 336. doi:10.1021/jf00116a038. ISSN 0021-8561.
- Dougan, J.; Robinson, J. M.; Sumar, S.; Howard, G. E.; Coursey, D. G. (1983). "Some flavouring constituents of cassava and of processed cassava products". Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture. 34 (8): 874. doi:10.1002/jsfa.2740340816. ISSN 1097-0010.
- Habu, Tsutomu; Flath, Robert A.; Mon, T. Richard; Morton, Julia F. (1 March 1985). "Volatile components of Rooibos tea (Aspalathus linearis)". Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry. 33 (2): 249–254. doi:10.1021/jf00062a024. ISSN 0021-8561.
- Benoist, Schaal; Gérard, Coureaud; Langlois, Dominique; Giniès, Christian; Sémon, Etienne; Perrier, Guy (2003). "Chemical and behavioural characterization of the rabbit mammary pheromone". Nature.
- Meyer, Robert E.; Fish, Richard E. (November 2005). "A review of tribromoethanol anesthesia for production of genetically engineered mice and rats". Lab Animal. 34 (10): 47–52. doi:10.1038/laban1105-47. ISSN 0093-7355. PMID 16261153. S2CID 21759580.
- Lewis, Robert Alan (1998). Lewisʼ Dictionary of Toxicology. Boca Raton, Florida: CRC Press. pp. 45. ISBN 978-1566702232. OCLC 35269968.
- "2-METHYL-2-BUTANOL - National Library of Medicine HSDB Database". www.toxnet.nlm.nih.gov. Archived from the original on 2018-03-08. Retrieved 2018-04-08.
- Anand, Jacek Sein; Gieroń, Joanna; Lechowicz, Wojciech; Schetz, Daria; Kała, Maria; Waldman, Wojciech (September 2014). "Acute intoxication due to tert-amyl alcohol—a case report". Forensic Science International. 242: e31–e33. doi:10.1016/j.forsciint.2014.07.020. ISSN 1872-6283. PMID 25112153.
- Soehring, K.; Frey, H.H.; Endres, G. (1955). "Relations between constitution and effect of tertiary alcohols". Arzneimittel-Forschung. 5 (4): 161–165. PMID 14389140.
- Collins, A. S.; Sumner, S. C.; Borghoff, S. J.; Medinsky, M. A. (1999). "A physiological model for tert-amyl methyl ether and tert-amyl alcohol: Hypothesis testing of model structures". Toxicological Sciences. 49 (1): 15–28. doi:10.1093/toxsci/49.1.15. PMID 10367338.