Philippine languages
The Philippine languages or Philippinic are a proposed group by R. David Paul Zorc (1986) and Robert Blust (1991; 2005; 2019) that include all the languages of the Philippines and northern Sulawesi, Indonesia—except Sama–Bajaw (languages of the "Sea Gypsies") and a few languages of Palawan—and form a subfamily of Austronesian languages.[1][2][3][4] Although the Philippines is near the center of Austronesian expansion from Formosa, there is little linguistic diversity among the approximately 150 Philippine languages, suggesting that earlier diversity has been erased by the spread of the ancestor of the modern Philippine languages.[5][2]
| Philippine | |
|---|---|
| Philippine | |
| (proposed) | |
| Geographic distribution |
|
| Linguistic classification | Austronesian
|
| Proto-language | Proto-Philippine (disputed) |
| Subdivisions | |
| ISO 639-2 / 5 | phi |
| Glottolog | None |
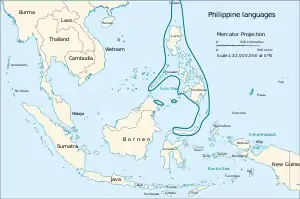 The Philippine languages, per Adelaar and Himmelmann (2005) | |
Classification
History and criticism
One of the first explicit classifications of a "Philippine" grouping based on genetic affiliation was in 1906 by Frank Blake, who placed them as a subdivision of the "Malay branch" within Malayo-Polynesian (MP), which at that time was considered as a family. Blake however encompasses every language within the geographic boundaries of the Philippine archipelago to be under a single group.[6] Formal arguments in support of a specific "Proto-Philippines" were followed by Matthew Charles in 1974, Teodoro Llamzon in 1966 and 1975, and Llamzon and Teresita Martin in 1976.[7][8][9][10] Blust (1991) two decades later updates this based on Zorc's (1986) inclusion of Yami, and the Sangiric, Minahasan, and Gorontalo groups.[6]
The genetic unity of a Philippines group has been rejected particularly by Lawrence Reid.[11] This arose with problems in reconstructing Philippine subgroups within MP (Pawley, 1999; Ross, 2005).[12][13] In a recent state-of-the art on the classification of Philippine languages, he provides multidisciplinary arguments on the field's methodological and theoretical shortcomings since Conant's description in the early 1900s. This includes Malayo-Polynesian archeology (Spriggs, 2003; 2007; 2011),[14][15][16] and Bayesian phylogenetic analyses (Gray et al., 2009)[17] substantiating the multiplicity of historical diffusion and divergence of languages across the archipelago.[18] He suggests that the primary branches under this widely acknowledged Philippine group should instead be promoted as primary branches under Malayo-Polynesian.[19] Malcolm Ross (2005) earlier also noted that the Batanic languages, constituting Yami, Itbayat, and Ivatan, should in fact be considered as a primary MP branch.[13] In an evaluation of the lexical innovations among the Philippine languages, Alexander Smith (2017) regards the evidence for a Philippine subgroup as weak, and concludes that "they may represent more than one primary subgroup or perhaps an innovation-defined linkage".[20] Chen et al. (2022) present further arguments for the Philippine languages being a convergence area rather than a unified phylogenetic subgroup.[21]
Internal classification
The Philippine group is proposed to have originated from Proto-Malayo-Polynesian and ultimately from Proto-Austronesian. There have been several proposals as to the composition within the group, but the most widely accepted groupings today is the consensus classifications by Blust (1991; 2005) and Reid (2017); however, both disagree on the existence of a Philippine group as a single genetic unit.
Zorc (1979)
An earlier classification by Zorc (1979) is presented below. From approximately north to south, a Philippine group according to his analysis of previous reconstructions are divided into two main subgroups, Northern or "Cordilleran" and Southern or "Sulic".[22] Note that the groupings herein no longer reflect widely accepted classifications or naming conventions today. For example South Extension nowadays reflects the widely established Central Luzon, and North Mangyan within Cordilleran is not supported by later reconstructions; the group containing Yami, Ivatan and Itbayat is called "Bashiic" in Zorc (1977) and remains generally accepted.[23]
- Northern Philippines or Cordilleran
- Pangasinica (includes Ilongot, Kallahan, Ibaloi, Pangasinan)
- Central Cordilleran (includes Isinai, Kalinga, Bontoc, Balangao, Ifugao)
- Ilokan (within Ilokano alone)
- Northern Cordilleran or Banagic (includes Ibanag, Isneg, Gaddang)
- Yami–Ivatan–Itbayatb
- South Extension (includes Sambal group, Kapampangan)
- Southern Philippines or Sulic
- Meso-Philippine
- South Mangyan (includes Hanunuo)
- Palawan
- Subanon (dialect cluster)
- Central Philippine (includes Tagalog, Bikol, Visayan, Mansakan)
- Manobo (includes Kagayanen, Western Bukidnon, Cotabato Manobo)
- Danao (includes Maranao, Maguindanao)
- Celebes Extension (includes Mongondow group)
- Meso-Philippine
Blust (1991; 2005)
From approximately north to south, the Philippine languages are divided into 12 subgroups (including unclassified languages):
- Batanic languages (4 languages between Batanes and Lanyu Island, Taiwan)
- Northern Luzon languages (40 languages, including Ilokano and Pangasinan)
- Central Luzon languages (5 languages, including Sambal and Kapampangan)
- Northern Mindoro languages (or North Mangyan; 3 languages)
- Greater Central Philippine languages
- Southern Mindoro languages (or South Mangyan; 3 languages)
- Central Philippine languages (40 languages, including Tagalog, Bikol languages and Visayan languages)
- Palawan languages (3 languages)
- Subanen languages (6 languages; sometimes considered one dialect cluster)
- Danao languages (3 languages; Iranun language, Maguindanao and Maranao)
- Manobo languages (15 languages)
- Gorontalo–Mongondow languages (9 languages of Gorontalo and North Sulawesi)
- Ati language
- Manide–Alabat
- Kalamian languages (2 languages of northern Palawan)
- South Mindanao languages (5 languages)
- Sangiric languages (4 languages of Sangir and Talaud Islands)
- Minahasan languages (5 languages of North Sulawesi)
- Unclassified
Formerly classified as one of the South Mindanao languages, the Klata language is now considered to be a primary branch of the Philippine languages by Zorc (2019).[24]
Vocabulary
Comparison chart between several selected Philippine languages spoken from north to south with Proto-Austronesian first for comparison.
| English | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | person | house | dog | coconut | day | new | we (incl.) | what | fire | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Proto-Austronesian | *əsa *isa | *duSa | *təlu | *Səpat | *lima | *Cau | *Rumaq | *asu | *niuR | *qaləjaw | *baqəRu | *i-kita | *n-anu | *Sapuy | |
| Batanic (Bashiic) | Yami (Tao) | ása | dóa (raroa) | tílo (tatlo) | apat (ápat) | lima | tao | vahay | chito | niyoy | araw | vayo | yaten | ango | apoy |
| Ivatan | asa | dadowa | tatdo | apat | lima | tao | vahay | chito | niyoy | araw | va-yo | yaten | ango | apoy | |
| Northern Luzon | Ilocano | maysa | dua | tallo | uppat | lima | tao | balay | aso | niog | aldaw | baro | sitayo | ania | apoy |
| Ibanag | tadday | dua | tallu | appa' | lima | tolay | balay | kitu | niuk | aggaw | bagu | sittam | anni | afi | |
| Gaddang | antet | addwa | tallo | appat | lima | tolay | balay | atu | ayog | aw | bawu | ikkanetam | sanenay | afuy | |
| Pangasinan | sakey | dua duara | talo talora | apat apatira | lima | too | abong | aso | niyog | ageo | balo | sikatayo | anto | pool | |
| Central Luzon | Kapampangan | métung | adwá | atlú | ápat | limá | táu | balé | ásu | ngúngut | aldó | báyu | ítámu | nánu | apî |
| Central Philippine | Tagalog | isa | dalawa | tatlo | apat | lima | tao | bahay | aso | niyog | araw | bago | tayo | ano | apoy |
| Central Bikol | sarô | duwa | tulo | apát | lima | tawo | harong | ayam idò | niyog | aldaw | bâgo | kitá | ano | kalayo | |
| Rinconada Bikol | əsad | darwā | tolō | əpat | lima | tawō | baləy | ayam | noyog | aldəw | bāgo | kitā | onō | kalayō | |
| Waray | usa sayo | duha | tulo | upat | lima | tawo | balay | ayam ido | lubi | adlaw | bag-o | kita | ano | kalayo | |
| Hiligaynon | isa | duha | tatlo | apat | lima | tawo | balay | ido | lubi | adlaw | bag-o | kita | ano | kalayo | |
| Bantoanon (Asi) | usa | ruha | tuyo | upat | lima | tawo | bayay | iro | nidog | adlaw | bag-o | kita | ni-o | kayado | |
| Romblomanon | isa | duha | tuyo | upat | lima | tawo | bayay | ayam | niyog | adlaw | bag-o | kita | ano | kalayo | |
| Onhan | isya | darwa | tatlo | ap-at | lima | tawo | balay | ayam | niyog | adlaw | bag-o | kita | ano | kalayo | |
| Karay-a | sara | darwa | tatlo | apat | lima | taho | balay | ayam | niyog | adlaw | bag-o | kita tatən | ano | kalayo | |
| Aklanon | isaea sambilog | daywa | tatlo | ap-at | lima | tawo | baeay | ayam | niyog | adlaw | bag-o | kita | ano | kaeayo | |
| Cebuano | usa | duha | tulo | upat | lima | tawo | balay | iro | lubi | adlaw | bag-o | kita | unsa | kalayo | |
| Tausug | isa hambuuk | duwa | tu | upat | lima | tau | bay | iru' | niyug | adlaw | ba-gu | kitaniyu | unu | kayu | |
| Danao | Maguindanao | isa | dua | telu | pat | lima | tau | walay | asu | niyug | gay | bagu | tanu | ngin | apuy |
| Mëranaw | isa | dowa | t'lo | phat | lima | taw | walay | aso | neyog | gawi'e | bago | tano | tonaa | apoy | |
| Iranun | isa | dua | telu | pa'at | lima | taw | walay | asu | niyug | gawi'i | bagu | tanu | antuna | apuy | |
| South Mindanao (Bilic) | Tboli | sotu | lewu | tlu | fat | lima | tau | gunu | ohu | lefo | kdaw | lomi | tekuy | tedu | ofih |
| Minahasan | Tombulu (Minahasa) | esa | zua rua | telu | epat | lima | tou | walé | asu | po'po' | endo | weru | kai kita | apa | api |
| Sangiric | Sangirese | sembau esa' | darua | tatelu | epa' | lima | tau | balé | kapuna' | bango' | elo | wuhu | kité | tawé | putung |
| Gorontalo–Mongondow | Gorontalo | tuwewu | duluwo | totolu | opato | limo | tawu | bele | 'apula | bongo | dulahu | bohu | 'ito | wolo | tulu |
| Mongondow | inta' | dua | tolu | opat | lima | intau | baloi | ungku' | bango' | singgai | mobagu | kita | onu, onda | tulu' | |
See also
- Languages of the Philippines
- List of regional languages of the Philippines
- Philippine Negrito languages
- Philippine literature
- Komisyon sa Wikang Filipino
- Visayan Academy of Arts and Letters
- Defunct language regulators
Notes
References
- Zorc, R. David Paul (1986). "The Genetic Relationships of Philippine Languages". In Geraghty, P.; Carrington, L.; Wurm, S. A. (eds.). FOCAL II: Papers from the Fourth International Conference on Austronesian Linguistics. Pacific Linguistics, Series C, No. 94. Canberra: The Australian National University. pp. 147–173. doi:10.15144/PL-C94.147. hdl:1885/252029. ISBN 0-85883-345-X.
- Blust, Robert (1991). "The Greater Central Philippines Hypothesis". Oceanic Linguistics. 30 (2): 73–129. doi:10.2307/3623084. JSTOR 3623084.
- Blust, Robert A. (2005). "The Linguistic Macrohistory of the Philippines". In Liao, Hsiu-Chuan; Rubino, Carl R.Galvez (eds.). Current Issues in Philippine Linguistics Pangaral Kay Lawrence A. Reid. Linguistic Society of the Philippines and SIL Philippines. pp. 31–68.
- Blust, Robert (2019). "The Resurrection of Proto-Philippines". Oceanic Linguistics. 58 (2): 153–256. doi:10.1353/ol.2019.0008. S2CID 216726665.
- Adelaar & Himmelmann (2005)
- Blust, Robert (1991). "The Greater Central Philippines Hypothesis". Oceanic Linguistics. 30 (2): 73–129. doi:10.2307/3623084. JSTOR 3623084.
- Llamzon, Teodoro A. (1975). "Proto-Philippine Phonology". Archipel. 9: 29–42. doi:10.3406/arch.1975.1214 – via Persée.
- Charles, Mathew (1974). "Problems in the Reconstruction of Proto-Philippine Phonology and the Subgrouping of the Philippine Languages". Oceanic Linguistics. 13 (1/2): 457–509. doi:10.2307/3622751. JSTOR 3622751.
- Llamzon, Teodoro (1966). "The Subgrouping of Philippine Languages". Philippine Sociological Review. 14 (3): 145–150. JSTOR 23892050.
- Llamzon, Teodoro; Martin, Teresita (1976). "A Subgrouping of 100 Philippine Languages" (PDF). South-East Asian Linguistic Studies. 2: 141–172.
- Reid, Lawrence (1982). "The Demise of Proto-Philippines" (PDF). In Amran Halim; Carrington, Lois; Stephen A. (eds.). Papers from the Third International Conference on Austronesian Linguistics. Pacific Linguistics, Series C, No. 75. Vol. 2: Tracking the Travellers. Canberra: Australian National University. pp. 201–216.
- Pawley, Andrew (1999). "Chasing Rainbows: Implications for the Rapid Dispersal of Austronesian Languages for Subgrouping and Reconstruction". In Zeitoun, Eilzabeth; Li, Paul Jen-kuei (eds.). Selected Papers from the Eighth International Conference on Austronesian Linguistics. Taipei: Academia Sinica. pp. 95–138.
- Ross, Malcolm (2005). "The Batanic Languages in Relation to the Early History of the Malayo-Polynesian Subgroup of Austronesian" (PDF). Journal of Austronesian Studies. 1 (2): 1–24.
- Spriggs, Matthew (2003). "Chronology of Neolithic Transition in Island Southeast Asia and The Western Pacific". The Review of Anthropology. 24: 57–80.
- Spriggs, Matthew (2007). "The Neolithic and Austronesian Expansion Within Island Southeast Asia and Into the Pacific". In Chiu, Scarlett; Sand, Christophe (eds.). From Southeast Asia to the Pacific: Archeological Perspectives on the Austronesian Expansion and the Lapita Cultural Complex. Taipei: Academia Sinica. pp. 104–140.
- Spriggs, Matthew (2011). "Archeology and Austronesian Expansion: Where Are We Now?" (PDF). Antiquity. 85 (328): 510–528. doi:10.1017/s0003598x00067910. S2CID 162491927.
- Gray, Russell; Drummond, Alexei; Greenhill, Simon (2009). "Language Phylogenies Reveal Expansion Pulses and Pauses in Pacific Settlement". Science. 323 (5913): 479–482. Bibcode:2009Sci...323..479G. doi:10.1126/science.1166858. PMID 19164742. S2CID 29838345.
- Reid, Lawrence (2017). Revisiting the Position of Philippine Languages in the Austronesian Family (PDF). The Br. Andrew Gonzalez FSC (BAG) Distinguished Professorial Chair Lecture, 2017, De La Salle University, Manila.
- Reid, Lawrence A. (2018). "Modeling the Linguistic Situation in the Philippines". In Kikusawa, Ritsuko; Reid, Lawrence A. (eds.). Let's Talk about Trees. doi:10.15021/00009006.
{{cite book}}:|journal=ignored (help) - Smith, Alexander D. (2017). "The Western Malayo-Polynesian Problem". Oceanic Linguistics. 56 (2): 435–490. doi:10.1353/ol.2017.0021. S2CID 149377092., p. 479
- Chen, Victoria, Kristina Gallego, Jonathan Kuo, Isaac Stead, & Benjamin van der Voorn. 2022. Contact or inheritance? New evidence on the Proto-Philippines debate. Presentation given at the 31st Annual Meeting of the Southeast Asian Linguistics Society (SEALS 31), University of Hawaiʻi at Mānoa, May 18–20, 2022. (slides)
- Zorc, R. David Paul (1979). "On the Development of Contrastive Word Accent: Pangasinan, a Case in Point". In Nguyen, Dang Liem (ed.). Southeast Asian Linguistic Studies, Vol. 3. Pacific Linguistics, Series C, No. 45. Canberra: The Australian National University. pp. 241–258. doi:10.15144/PL-C45.241. hdl:1885/253117. ISBN 0-85883-177-5.
- Zorc, David Paul (1977). The Bisayan Dialects of the Philippines: Subgrouping and Reconstruction. Pacific Linguistics, Series C, No. 44. Canberra: Australian National University. doi:10.15144/PL-C44. hdl:1885/146594. ISBN 0-85883-157-0 – via Archive.org.
- Zorc, R. David (2019). "Klata / Giangan: A New Southern Philippine Subgroup" (PDF). The Archive: Special Publication. 16: 33–51.
Works cited
- Adelaar, Alexander; Himmelmann, Nikolaus P., eds. (2005). The Austronesian Languages of Asia and Madagascar. London: Routledge.
Further reading
- Reid, Lawrence A. (2013). "Who Are the Philippine Negritos? Evidence from Language". Human Biology. 85 (1–3): 329–358. doi:10.3378/027.085.0316. PMID 24297232. S2CID 8341240.
- Wouk, Fay (Ed.); Ross, Malcolm (Ed.) (2002). Wouk, Fay; Ross, Malcolm (eds.). The History and Typology of Western Austronesian Voice Systems. doi:10.15144/PL-518. hdl:1885/146136. ISBN 0-85883-477-4.
{{cite book}}:|journal=ignored (help) - Zorc, R. David (1972). "Sealang Zorc Papers".