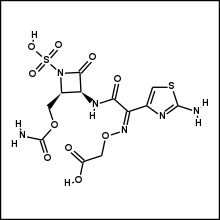
Carumonam
Carumonam (INN) is a monobactam antibiotic.[1] It is very resistant to beta-lactamases, which means that it is more difficult for bacteria to break down using β-lactamase enzymes.[2]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Amasulin |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C12H14N6O10S2 |
| Molar mass | 466.40 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| | |
References
- McNulty CA, Garden GM, Ashby J, Wise R (September 1985). "Pharmacokinetics and tissue penetration of carumonam, a new synthetic monobactam". Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy. 28 (3): 425–7. doi:10.1128/aac.28.3.425. PMC 180266. PMID 4073864.
- PubChem. "Carumonam". pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. Retrieved 2021-12-08.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.