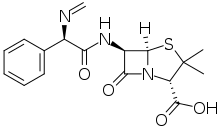
Metampicillin
Metampicillin (INN) is a penicillin antibiotic. It is prepared by the reaction of ampicillin with formaldehyde, and is hydrolysed in aqueous solution with the formation of ampicillin. Hydrolysis is rapid under acid conditions, e.g., in the stomach, less rapid in neutral media, and incomplete in solutions such as human serum.[1]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.026.696 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C17H19N3O4S |
| Molar mass | 361.42 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| | |
References
- Sutherland R, Elson S, Croydon EA (1972). "Metampicillin. Antibacterial activity and absorption and excretion in man". Chemotherapy. 17 (3): 145–60. doi:10.1159/000220849. PMID 4556172.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.