Oxacephem
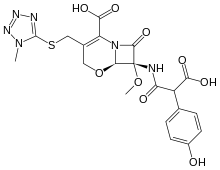
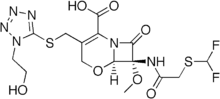
An oxacephem is a β-lactam molecule similar to a cephem, but with an oxygen substituted for the sulfur. They are synthetic compounds not seen in nature, generally used as β-lactam antibiotics. Examples include Latamoxef[1] and Flomoxef.[2][3]
References
- "Medscape.com". Retrieved 2008-12-29.
- Yazawa K, Mikami Y, Uno J, Otozai K, Arai T (December 1989). "In-vitro activity of flomoxef, a new oxacephem group antibiotic, against Nocardia in comparison with other cephalosporins". J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 24 (6): 921–5. doi:10.1093/jac/24.6.921. PMID 2621177.
- Cazzola M, Brancaccio V, De Giglio C, Paternò E, Matera MG, Rossi F (March 1993). "Flomoxef, a new oxacephem antibiotic, does not cause hemostatic defects". Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther Toxicol. 31 (3): 148–52. PMID 8468113.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.