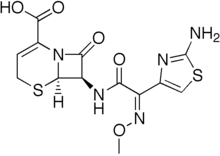
Ceftizoxime
Ceftizoxime is a third-generation cephalosporin available for parenteral administration.[1] Unlike other third-generation cephalosporins, the whole C-3 side chain in ceftizoxime has been removed to prevent deactivation by hydrolytic enzymes. It rather resembles cefotaxime in its properties, but is not subject to metabolism. It was removed from the US Market in 2007.
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Cefizox |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Consumer Drug Information |
| MedlinePlus | a684043 |
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.210.846 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C13H13N5O5S2 |
| Molar mass | 383.40 g·mol−1 |
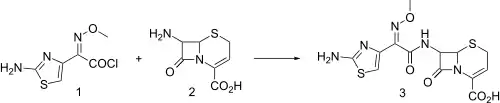
Synthesis
Injectable third generation cephalosporin antibiotic related to cefotaxime, q.v. Exhibits broad spectrum activity and resistance to β-lactamase hydrolysis.
References
- Aldridge KE (1990). "An update on the in vitro activity of ceftizoxime and other cephalosporin/cephamycin antimicrobial agents against clinically significant anaerobic bacteria". Clinical Therapeutics. 12 Suppl C: 3–12. PMID 2202509.
- DE 2810922, Takaya T, Hisashi T, Kiyoshi T, Toshiyuki C, "New cepham compounds and processes for the production thereof", issued 29 August 1985, assigned to Fujisawa
- US 4427674, Takaya T, Hisashi T, Kiyoshi T, Toshiyuki C, "Cephem compounds", issued 24 January 1984, assigned to Fujisawa
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.