Lassa fever
Lassa fever, also known as Lassa hemorrhagic fever (LHF), is a type of viral hemorrhagic fever caused by the Lassa virus.[1] Many of those infected by the virus do not develop symptoms.[1] When symptoms occur they typically include fever, weakness, headaches, vomiting, and muscle pains.[1] Less commonly there may be bleeding from the mouth or gastrointestinal tract.[1] The risk of death once infected is about one percent and frequently occurs within two weeks of the onset of symptoms.[1] Of those who survive, about a quarter have hearing loss, which improves within three months in about half of these cases.[1][3][4]
| Lassa fever | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Lassa hemorrhagic fever |
 | |
| Community education material for Lassa fever | |
| Specialty | Infectious disease |
| Symptoms | Fever, headaches, bleeding[1] |
| Complications | Partial or complete, temporary or permanent hearing loss[1] |
| Usual onset | 1–3 weeks following exposure[1] |
| Causes | Lassa virus[1] |
| Risk factors | Exposure to rodents in West Africa[1] |
| Diagnostic method | Laboratory testing[1] |
| Differential diagnosis | Ebola, malaria, typhoid fever[1] |
| Treatment | Supportive[1] |
| Prognosis | ~1% risk of death with treatment[1] |
| Frequency | 400,000 cases per year[2] |
| Deaths | 5,000 deaths per year[2] |
The disease is usually initially spread to people via contact with the urine or feces of an infected multimammate mouse.[1] Spread can then occur via direct contact between people.[1] Diagnosis based on symptoms is difficult.[1] Confirmation is by laboratory testing to detect the virus's RNA, antibodies for the virus, or the virus itself in cell culture.[1] Other conditions that may present similarly include Ebola, malaria, typhoid fever, and yellow fever.[1] The Lassa virus is a member of the Arenaviridae family of viruses.[1]
There is no vaccine.[5] Prevention requires isolating those who are infected and decreasing contact with the mice.[1] Other efforts to control the spread of disease include having a cat to hunt vermin, and storing food in sealed containers.[1] Treatment is directed at addressing dehydration and improving symptoms.[1] The antiviral medication ribavirin has been recommended,[1] but evidence to support its use is weak.[6][7]
Descriptions of the disease date from the 1950s.[1] The virus was first described in 1969 from a case in the town of Lassa, in Borno State, Nigeria.[1][8] Lassa fever is relatively common in West Africa including the countries of Nigeria, Liberia, Sierra Leone, Guinea, and Ghana.[1][2] There are about 300,000 to 500,000 cases which result in 5,000 deaths a year.[2][9]
Signs and symptoms
Onset of symptoms is typically 7 to 21 days after exposure.[10] In 80% of those who are infected few or no symptoms occur.[10][11] These mild symptoms may include fever, tiredness, weakness, and headache.[10] In 20% of people more severe symptoms such as bleeding gums, breathing problems, vomiting, chest pain, or dangerously low blood pressure may occur.[10] Long term complications may include hearing loss.[10] In those who are pregnant, miscarriage may occur in 95% of child-bearing women.[10] Lassa fever can be difficult to distinguish clinically from other viral hemorrhagic fevers, such as Ebola virus disease.[1] A combination of pharyngitis, pain behind the sternum, presence of excess protein in the urine and fever can indicate Lassa fever with higher specificity.[12][3]
In cases in which death occurs, this typically occurs within 14 days of onset.[10] About 1% of all Lassa virus infections result in death.[10] Approximately 15%-20% of those who have required hospitalization for Lassa fever die.[10] The risk of death is greater in those who are pregnant.[10] A "Swollen baby syndrome" may occur in newborns, infants and toddlers with pitting edema, abdominal distension and bleeding.[13]
Cause
Virology
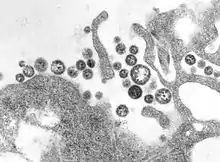
Lassa virus is a member of the Arenaviridae, a family of negative-sense, single-stranded RNA viruses.[14] Specifically it is an old world arenavirus, which is enveloped, single-stranded, and bi-segmented RNA. This virus has both a large and a small genome section, with four lineages identified to date: Josiah (Sierra Leone), GA391 (Nigeria), LP (Nigeria) and strain AV.[15]
Spread

Lassa virus commonly spreads to humans from other animals, specifically the Natal multimammate mouse or African rat, also called the Natal multimammate rat (Mastomys natalensis).[16] This is probably the most common mouse in equatorial Africa, common in human households and eaten as a delicacy in some areas.[16][17]
The multimammate mouse can quickly produce a large number of offspring, tends to colonize human settlements, increasing the risk of rodent-human contact, and is found throughout the west, central and eastern parts of the African continent.[18]
Once the mouse has become a carrier, it will excrete the virus throughout the rest of its lifetime through feces and urine creating ample opportunity for exposure.[18] The virus is probably transmitted by contact with the feces or urine of animals accessing grain stores in residences.[17] No study has proven presence in breast milk, but the high level of viremia suggests it may be possible.[13]
Individuals who are at a higher risk of contracting the infection are those who live in rural areas where Mastomys are discovered, and where sanitation is not prevalent. Infection typically occurs by direct or indirect exposure to animal excrement through the respiratory or gastrointestinal tracts. Inhalation of tiny particles of infectious material (aerosol) is believed to be the most significant means of exposure. It is possible to acquire the infection through broken skin or mucous membranes that are directly exposed to infectious material. Transmission from person to person has been established, presenting a disease risk for healthcare workers. The virus is present in urine for between three and nine weeks after infection, and it can be transmitted in semen for up to three months after becoming infected.[16][19][20]
Diagnosis
.jpg.webp)
A range of laboratory investigations are performed, where possible, to diagnose the disease and assess its course and complications. The confidence of a diagnosis can be compromised if laboratory tests are not available. One comprising factor is the number of febrile illnesses present in Africa, such as malaria or typhoid fever that could potentially exhibit similar symptoms, particularly for non-specific manifestations of Lassa fever.[14] In cases with abdominal pain, in countries where Lassa is common, Lassa fever is often misdiagnosed as appendicitis and intussusception which delays treatment with the antiviral ribavirin.[21] In West Africa, where Lassa is most common, it is difficult to diagnose due to the absence of proper equipment to perform testing.[22]
The FDA has yet to approve a widely validated laboratory test for Lassa, but there are tests that have been able to provide definitive proof of the presence of the LASV virus.[14] These tests include cell cultures, PCR, ELISA antigen assays, plaque neutralization assays, and immunofluorescence essays. However, immunofluorescence essays provide less definitive proof of Lassa infection.[14] An ELISA test for antigen and Immunoglobulin M antibodies give 88% sensitivity and 90% specificity for the presence of the infection. Other laboratory findings in Lassa fever include lymphocytopenia (low white blood cell count), thrombocytopenia (low platelets), and elevated aspartate transaminase levels in the blood. Lassa fever virus can also be found in cerebrospinal fluid.[23]
Prevention
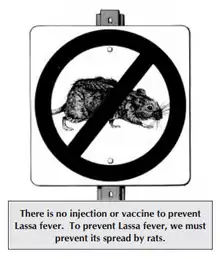
Control of the Mastomys rodent population is impractical, so measures focus on keeping rodents out of homes and food supplies, encouraging effective personal hygiene, storing grain and other foodstuffs in rodent-proof containers, and disposing of garbage far from the home to help sustain clean households.[24] Gloves, masks, laboratory coats, and goggles are advised while in contact with an infected person, to avoid contact with blood and body fluids.[25] These issues in many countries are monitored by a department of public health. In less developed countries, these types of organizations may not have the necessary means to effectively control outbreaks.[26]
Vaccine
There is no vaccine for humans as of 2019.[27] Researchers at the United States Army Medical Research Institute of Infectious Diseases facility had a promising vaccine candidate in 2002.[28] They have developed a replication-competent vaccine against Lassa virus based on recombinant vesicular stomatitis virus vectors expressing the Lassa virus glycoprotein. After a single intramuscular injection, test primates have survived lethal challenge, while showing no clinical symptoms.[29]
Treatment
Treatment is directed at addressing dehydration and improving symptoms.[1] All persons suspected of Lassa fever infection should be admitted to isolation facilities and their body fluids and excreta properly disposed of.
Medications
The antiviral medication ribavirin has been recommended,[1] but evidence to support its use is weak.[6] Some evidence has found that it may worsen outcomes in certain cases.[6] Fluid replacement, blood transfusions, and medication for low blood pressure may be required. Intravenous interferon therapy has also been used.
Pregnancy
When Lassa fever infects pregnant women late in their third trimester, inducing delivery is necessary for the mother to have a good chance of survival.[30] This is because the virus has an affinity for the placenta and other highly vascular tissues. The fetus has only a one in ten chance of survival no matter what course of action is taken; hence, the focus is always on saving the life of the mother.[31] Following delivery, women should receive the same treatment as other people with Lassa fever.
Prognosis
About 15–20% of hospitalized people with Lassa fever will die from the illness. The overall case fatality rate is estimated to be 1%, but during epidemics, mortality can climb as high as 50%. The mortality rate is greater than 80% when it occurs in pregnant women during their third trimester; fetal death also occurs in nearly all those cases. Abortion decreases the risk of death to the mother.[32] Some survivors experience lasting effects of the disease,[33] and can include partial or complete deafness.[1]
Because of treatment with ribavirin, fatality rates have declined.[34][35]
Epidemiology
There are about 300,000 to 500,000 cases which result in 5,000 deaths a year.[2][9] One estimate places [37] the number as high as 3 million cases per year.[18]
Estimates of Lassa fever are complicated by the lack of easy-available diagnosis, limited public health surveillance infrastructure, and high clustering of incidence near high intensity sampling.[14]
The infection affects females 1.2 times more than males. The age group predominantly infected is 21–30 years.[38]
Geography
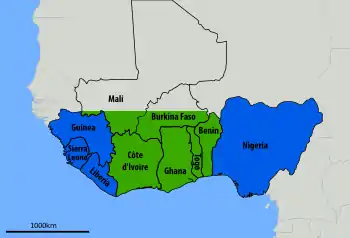
Lassa high risk areas are near the western and eastern extremes of West Africa. As of 2018, the Lassa belt includes Guinea, Nigeria, Sierra Leone and Liberia.[13] As of 2003, 10-16% of people in Sierra Leone and Liberia admitted to hospital had the virus.[16] The case fatality rate for those who are hospitalized for the disease is about 15-20%. Research showed a twofold increase risk of infection for those living in close proximity to someone with infection symptoms within the last year.
The high risk areas cannot be well defined by any known biogeographical or environmental breaks except for the multimammate rat, particularly Guinea (Kindia, Faranah and Nzérékoré regions), Liberia (mostly in Lofa, Bong, and Nimba counties), Nigeria (in about 10 of 36 states) and Sierra Leone (typically from Kenema and Kailahun districts). It is less common in the Central African Republic, Mali, Senegal and other nearby countries, and less common yet in Ghana and the Democratic Republic of the Congo. Benin had its first confirmed cases in 2014, and Togo had its first confirmed cases in 2016.[19]
As of 2013, the spread of Lassa outside of West Africa had been very limited. Twenty to thirty cases had been described in Europe, as being caused by importation through infected individuals.[18] These cases found outside of West Africa were found to have a high fatality risk because of the delay of diagnosis and treatment due to being unaware of the risk associated with the symptoms.[18] Imported cases have not manifested in larger epidemics outside of Africa due to a lack of human to human transmission in hospital settings. An exception had occurred in 2003 when a healthcare worker became infected before the person showed clear symptoms.[18]
2018 outbreak
An outbreak of Lassa fever occurred in Nigeria during 2018 and spread to 18 of the country's states; it was the largest outbreak of Lassa recorded.[39][40][41] On 25 February 2018, there were 1081 suspected cases and 90 reported deaths; 317 of the cases and 72 deaths were confirmed as Lassa which increased to a total of 431 reported cases in 2018.[42]
2019 outbreak
The total cases in Nigeria in 2019 was 810 with 167 deaths, the largest case fatality rate(23.3%) until then.[43][44]
2020 outbreak
The epidemic started from the second week of the January. By the tenth week the total number of cases has risen to 855 and deaths to 144, the case fatality rate of 16.8%.[44]
2021 Outbreak
On the 8th of December 2021, the Nigeria Centre for Disease Control (NCDC) was notified of the death of two persons from Lassa fever.[45]
2022 Outbreak
The epidemic took a new form, from 3 to 30 January 2022, 211 laboratory confirmed Lassa fever cases including 40 deaths (case fatality ratio: 19%) have been cumulatively reported in 14 of the 36 Nigerian states and the Federal Capital Territory across the country.[46] In total from January until March, 132 deaths have been reported with a case fatality rate (CFR) of 19.1% which is lower than the CFR for the same period in 2021 (21.0%).[47]
Liberia
Lassa fever is endemic in Liberia. From 1 January 2017 through 23 January 2018, 91 suspected cases were reported from six counties: Bong, Grand Bassa, Grand Kru, Lofa, Margibi, and Nimba. Thirty-three of these cases were laboratory confirmed, including 15 deaths (case fatality rate for confirmed cases = 45.4%).[48]
In February 2020, a total of 24 confirmed cases with nine associated deaths has been reported from nine health districts in six counties. Grand Bossa and Bong counties account for 20 of the confirmed cases.[49]
History
The disease was identified in Nigeria in 1969.[18] It is named after the town of Lassa, where it was discovered.[18]
A prominent expert in the disease, Aniru Conteh, died from the disease.[50]
Research
The Lassa virus is one of several viruses identified by WHO as a likely cause of a future epidemic. They therefore list it for urgent research and development to develop new diagnostic tests, vaccines, and medicines.[51][52]
In 2007, SIGA Technologies, studied a medication in guinea pig with Lassa fever.[53] Work on a vaccine is continuing, with multiple approaches showing positive results in animal trials.[54]
References
- "Lassa fever". WHO. March 2016. Archived from the original on 1 November 2016. Retrieved 2 November 2016.
- Ogbu O, Ajuluchukwu E, Uneke CJ (2007). "Lassa fever in West African sub-region: an overview". Journal of Vector Borne Diseases. 44 (1): 1–11. PMID 17378212.
Lassa fever is endemic in West Africa.
- "Lassa fever". www.who.int. Retrieved 29 April 2022.
- "Lassa Fever | CDC". www.cdc.gov. 4 March 2019. Retrieved 29 April 2022.
- Yun, N. E.; Walker, D. H. (2012). "Pathogenesis of Lassa Fever". Viruses. 4 (12): 2031–2048. doi:10.3390/v4102031. PMC 3497040. PMID 23202452.
- Eberhardt, KA; Mischlinger, J; Jordan, S; Groger, M; Günther, S; Ramharter, M (October 2019). "Ribavirin for the treatment of Lassa fever: A systematic review and meta-analysis". International Journal of Infectious Diseases. 87: 15–20. doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2019.07.015. PMID 31357056.
- Salam, Alex; Cheng, Vincent; Edwards, Tansy; Olliaro, Piero; Sterne, Jonathan; Horby, Peter (July 2021). "Time to reconsider the role of ribavirin in Lassa fever". PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases. 15 (7): e0009522. doi:10.1371/journal.pntd.0009522. PMC 8266111. PMID 34237063.
- Frame JD, Baldwin JM, Gocke DJ, Troup JM (1 July 1970). "Lassa fever, a new virus disease of man from West Africa. I. Clinical description and pathological findings". Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 19 (4): 670–6. doi:10.4269/ajtmh.1970.19.670. PMID 4246571.
- Houlihan, Catherine; Behrens, Ron (12 July 2017). "Lassa fever". BMJ. 358: j2986. doi:10.1136/bmj.j2986. PMID 28701331. S2CID 206916006.
- "Signs and Symptoms | Lassa Fever | CDC". www.cdc.gov. 6 March 2019. Retrieved 18 June 2019.
- Greenky D, Knust B, Dziuban EJ (May 2018). "What Pediatricians Should Know About Lassa Virus". JAMA Pediatrics. 172 (5): 407–408. doi:10.1001/jamapediatrics.2017.5223. PMC 5970952. PMID 29507948.
- McCormick JB, King IJ, Webb PA, Johnson KM, O'Sullivan R, Smith ES, Trippel S, Tong TC (March 1987). "A Case-Control Study of the Clinical Diagnosis and Course of Lassa Fever". The Journal of Infectious Diseases. 155 (3): 445–455. doi:10.1093/infdis/155.3.445. PMID 3805772.
- David Greenky; Barbara Knust; Eric J. Dziuban (2018). "What Pediatricians Should Know About Lassa Virus". JAMA Pediatrics. 172 (5): 407–408. doi:10.1001/jamapediatrics.2017.5223. PMC 5970952. PMID 29507948.
- Peterson, A. Townsend; Moses, Lina M.; Bausch, Daniel G. (8 August 2014). "Mapping Transmission Risk of Lassa Fever in West Africa: The Importance of Quality Control, Sampling Bias, and Error Weighting". PLOS ONE. 9 (8): e100711. Bibcode:2014PLoSO...9j0711P. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0100711. ISSN 1932-6203. PMC 4126660. PMID 25105746.
- Goeijenbier, Marco; Wagenaar, Jiri; Goris, Marga; Martina, Byron; Henttonen, Heikki; Vaheri, Antti; Reusken, Chantal; Hartskeerl, Rudy; Osterhaus, Albert (1 February 2013). "Rodent-borne hemorrhagic fevers: under-recognized, widely spread and preventable – epidemiology, diagnostics and treatment". Critical Reviews in Microbiology. 39 (1): 26–42. doi:10.3109/1040841X.2012.686481. ISSN 1040-841X. PMID 22670688. S2CID 31217913.
- Richmond, J. K.; Baglole, D. J. (2003). "Lassa fever: Epidemiology, clinical features, and social consequences". BMJ. 327 (7426): 1271–1275. doi:10.1136/bmj.327.7426.1271. PMC 286250. PMID 14644972.
- Werner, Dietrich, ed. (2004). Biological Resources and Migration. Springer. p. 363. ISBN 978-3-540-21470-0.
- Goeijenbier, Marco; Wagenaar, Jiri; Goris, Marga; Martina, Byron; Henttonen, Heikki; Vaheri, Antti; Reusken, Chantal; Hartskeerl, Rudy; Osterhaus, Albert; Van Gorp, Eric (7 June 2012). "Rodent-borne hemorrhagic fevers: under-recognized, widely spread and preventable – epidemiology, diagnostics and treatment". Critical Reviews in Microbiology. 39 (1): 26–42. doi:10.3109/1040841X.2012.686481. PMID 22670688. S2CID 31217913.
- Public Health England (5 September 2014). "Lassa fever: origins, reservoirs, transmission and guidelines". Archived from the original on 2 February 2016. Retrieved 1 April 2016.
- "Lassa fever". Media Centre Fact Sheet No 179. World Health Organization. Archived from the original on 5 June 2015. Retrieved 26 May 2015.
- Dongo, A. E.; Kesieme, E. B.; Iyamu, C. E.; Okokhere, P. O.; Akhuemokhan, O. C.; Akpede, G. O. (2013). "Lassa fever presenting as acute abdomen: a case series". Virology Journal. 10: 124. doi:10.1186/1743-422X-10-123. PMC 3639802. PMID 23597024.
- Asogun, D. A.; Adomeh, D. I.; Ehimuan, J.; Odia, I.; Hass, M.; Gabriel, M.; Olschläger, S.; Becker-Ziaja, B.; Folarin, O.; Phelan, E.; Ehiane, P. E.; Ifeh, V. E.; Uyigue, E. A.; Oladapo, Y. T.; Muoebonam, E. B.; Osunde, O.; Dongo, A.; Okokhere, P. O.; Okogbenin, S. A.; Momoh, M.; Alikah, S. O.; Akhuemokhan, O. C.; Imomeh, P.; Odike, M. A.; Gire, S.; Andersen, K.; Sabeti, P. C.; Happi, C. T.; Akpede, G. O.; Günther, S. (2012). Bausch, Daniel G (ed.). "Molecular Diagnostics for Lassa Fever at Irrua Specialist Teaching Hospital, Nigeria: Lessons Learnt from Two Years of Laboratory Operation". PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases. 6 (9): e1839. doi:10.1371/journal.pntd.0001839. PMC 3459880. PMID 23029594.
- Günther, S.; Weisner, B.; Roth, A.; Grewing, T.; Asper, M.; Drosten, C.; Emmerich, P.; Petersen, J.; Wilczek, M.; Schmitz, H. (2001). "Lassa Fever Encephalopathy: Lassa Virus in Cerebrospinal Fluid but Not in Serum". The Journal of Infectious Diseases. 184 (3): 345–349. doi:10.1086/322033. PMID 11443561.
- Ogbu O, Ajuluchukwu E, Uneke CJ (March 2007). "Lassa fever in West African sub-region: an overview". J Vector Borne Dis. 44 (1): 1–11. PMID 17378212.
- Weber DJ, Rutala WA, Fischer WA, Kanamori H, Sickbert-Bennett EE (May 2016). "Emerging infectious diseases: Focus on infection control issues for novel coronaviruses (Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome-CoV and Middle East Respiratory Syndrome-CoV), hemorrhagic fever viruses (Lassa and Ebola), and highly pathogenic avian influenza viruses, A(H5N1) and A(H7N9)". Am J Infect Control. 44 (5 Suppl): e91–e100. doi:10.1016/j.ajic.2015.11.018. PMC 7132650. PMID 27131142.
- "Driving and Public Health", Public Health, Oxford University Press, 23 November 2021, doi:10.1093/obo/9780199756797-0211, ISBN 978-0-19-975679-7, retrieved 23 April 2022
- "Lassa". Viral Hemorrhagic Fever Consortium. Retrieved 18 June 2019.
- Preston, Richard (2002). The demon in the freezer: a true story. New York: Random House. ISBN 978-0-375-50856-1.
- Geisbert TW, Jones S, Fritz EA, et al. (2005). "Development of a New Vaccine for the Prevention of Lassa Fever". PLOS Med. 2 (6): e183. doi:10.1371/journal.pmed.0020183. PMC 1160587. PMID 15971954.
- Price ME, Fisher-Hoch SP, Craven RB, McCormick JB (September 1988). "A prospective study of maternal and fetal outcome in acute Lassa fever infection during pregnancy". BMJ. 297 (6648): 584–7. doi:10.1136/bmj.297.6648.584. PMC 1834487. PMID 3139220.
- Samuel, Daso. "Lassa fever... What you need to know" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 25 June 2017. Retrieved 1 February 2017.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, "Lassa Fever, Signs and Symptoms" Archived 9 July 2017 at the Wayback Machine
- Emond, R. T.; Bannister, B.; Lloyd, G.; Southee, T. J.; Bowen, E. T. (1982). "A case of Lassa fever: Clinical and virological findings". British Medical Journal (Clinical Research Ed.). 285 (6347): 1001–1002. doi:10.1136/bmj.285.6347.1001. PMC 1500383. PMID 6812716.
- "Lassa fever". World Health Organization. Retrieved 11 September 2017.
- McCormick, J. B.; King, I. J.; Webb, P. A.; Scribner, C. L.; Craven, R. B.; Johnson, K. M.; Elliott, L. H.; Belmont-Williams, R. (2 January 1986). "Lassa fever. Effective therapy with ribavirin". The New England Journal of Medicine. 314 (1): 20–26. doi:10.1056/NEJM198601023140104. ISSN 0028-4793. PMID 3940312.
- "Outbreak Distribution Map of Lassa Fever". www.cdc.gov. CDC. 4 March 2019. Retrieved 27 April 2019.
- "Lassa Fever". Africa CDC. Retrieved 23 April 2022.
- Owoseye, Ayodamola (11 March 2020). "Lassa Fever: Nigeria's death toll reaches 144". Retrieved 13 March 2020.
- Maxmen, Amy (15 March 2018). "Deadly Lassa-fever outbreak tests Nigeria's revamped health agency". Nature. 555 (7697): 421–422. Bibcode:2018Natur.555..421M. doi:10.1038/d41586-018-03171-y. PMID 29565399.
- "On the frontlines of the fight against Lassa fever in Nigeria". World Health Organization. March 2018. Archived from the original on 18 March 2018.
- Beaubien, Jason (19 March 2018). "Nigeria Faces Mystifying Spike in Deadly Lassa Fever". NPR.
- "Lassa Fever – Nigeria". World Health Organization. 1 March 2018. Archived from the original on 1 March 2018.
- Edward-Ekpu, Uwagbale (8 March 2020). "Nigeria is already dealing with a deadlier viral outbreak than the coronavirus epidemic". Quartz Africa. Retrieved 13 March 2020.
- "Lassa fever situation report" (PDF). Nigeria Centre for Disease Control. March 2020.
- "Nigeria Centre for Disease Control". ncdc.gov.ng. Retrieved 23 April 2022.
- "Lassa Fever - Nigeria". www.who.int. Retrieved 23 April 2022.
- "NCDC Lassa fever Situation Report Epi Week 13: 28 March - 3 April, 2022 - Nigeria". ReliefWeb. Retrieved 23 April 2022.
- "WHO | Lassa Fever – Liberia". WHO. Archived from the original on 22 February 2018. Retrieved 13 March 2020.
- "Liberia reports increase in Lassa fever". Outbreak News Today. 4 February 2020. Retrieved 13 March 2020.
- Mellor, N. (1 May 2004). "Aniru Conteh". BMJ. 328 (7447): 1078.1. doi:10.1136/bmj.328.7447.1078. PMC 403863.
- Kieny, Marie-Paule. "After Ebola, a Blueprint Emerges to Jump-Start R&D". Scientific American Blog Network. Archived from the original on 20 December 2016. Retrieved 13 December 2016.
- "LIST OF PATHOGENS". World Health Organization. Archived from the original on 20 December 2016. Retrieved 13 December 2016.
- "SIGA Technologies says passes first hurdle with lassa fever..." Reuters. 15 May 2007. Retrieved 1 May 2019.
- "WHO Target Product Profiles for Lassa virus Vaccine" (PDF). World Health Organization. April 2017. Retrieved 11 September 2017.
Further reading
- Echioya, Deborah U.; Hass, Meike; Olshlager, Stephan; Becker-Ziaja, Beate; Chukwu, Christian O. Onyebuchi; Coker, Jide; Nasidi, Abdulsalam; Ogugua, Osi-Ogdu; Gunther, Stephan; Omilabu, Sunday A. (2010). "Lassa Fever, Nigeria, 2005-2008". Emerging Infectious Diseases. 6. 16 (6): 1040–41. doi:10.3201/eid1606.100080. PMC 3086228. PMID 20507773.
- Branco, Luis M.; Grove, Jessica N.; Boisen, Matt L.; Shaffer, Jeffrey G.; Goba, Augustine; Fullah, Mohammed; Momoh, Mambu; Grant, Donald S.; Garry, Robert F. (4 October 2011). "Emerging Trends in Lassa Fever: Redefining the Role of Immunoglobulin M and Inflammation in Diagnosing Acute Infection". Virology Journal. 8: 478. doi:10.1186/1743-422x-8-478. PMC 3223505. PMID 22023795.