Otamixaban
Otamixaban (INN) is an experimental injectable anticoagulant direct factor Xa inhibitor[1] that was investigated for the treatment for acute coronary syndrome. In 2013, Sanofi announced that it had ended development of the drug candidate after poor performance in a Phase III clinical trial.[2][3]
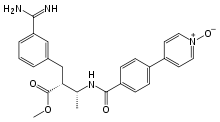 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C25H26N4O4 |
| Molar mass | 446.507 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| | |
References
- Guertin KR, Choi YM (2007). "The discovery of the Factor Xa inhibitor otamixaban: from lead identification to clinical development". Curr. Med. Chem. 14 (23): 2471–81. doi:10.2174/092986707782023659. PMID 17979700.
- "AstraZeneca, Sanofi Cut Programs". Chemical & Engineering News. American Chemical Society. 91 (23): 17. June 10, 2013.
Sanofi is ending development on two compounds, the anticancer compound iniparib and the anticoagulant otamixaban, both of which flunked Phase III studies.
- "Sanofi's Investigational Iniparib, Otamixaban Fail To Meet Goals, Ends Programs". RTT news. Retrieved 11 April 2014.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.