Halothane
Halothane, sold under the brand name Fluothane among others, is a general anaesthetic.[4] It can be used to induce or maintain anaesthesia.[4] One of its benefits is that it does not increase the production of saliva, which can be particularly useful in those who are difficult to intubate.[4] It is given by inhalation.[4]
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Fluothane |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | FDA Professional Drug Information |
| License data |
|
| Routes of administration | Inhalation |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Metabolism | Hepatic (CYP2E1[3]) |
| Excretion | Kidney, respiratory |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.005.270 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
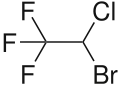
| Formula | C2HBrClF3 |
| Molar mass | 197.38 g·mol−1 |
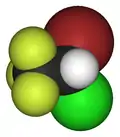
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Side effects include an irregular heartbeat, respiratory depression, and hepatotoxicity.[4] Like all volatile anesthetics, it should not be used in people with a personal or family history of malignant hyperthermia.[4] It appears to be safe in porphyria.[5] It is unclear whether use during pregnancy is harmful to the baby, and it is not generally recommended for use during a C-section.[6] Halothane is a chiral molecule that is used as a racemic mixture.[7]
Halothane was discovered in 1955.[8] It was approved for medical use in the United States in 1958.[2] It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines.[9][10] Its use in developed countries has been mostly replaced by newer anesthetic agents such as sevoflurane.[11] It is no longer commercially available in the United States.[6] Halothane also contributes to ozone depletion.[12][13]
Medical uses

It is a potent anesthetic with a minimum alveolar concentration (MAC) of 0.74%.[14] Its blood/gas partition coefficient of 2.4 makes it an agent with moderate induction and recovery time.[15] It is not a good analgesic and its muscle relaxation effect is moderate.[16]
Side effects
Side effects include irregular heartbeat, respiratory depression, and hepatotoxicity.[4] It appears to be safe in porphyria.[5] It is unclear whether use during pregnancy is harmful to the baby, and it is not generally recommended for use during a C-section.[6] In rare cases, repeated exposure to halothane in adults was noted to result in severe liver injury. This occurred in about one in 10,000 exposures. The resulting syndrome was referred to as halothane hepatitis, immunoallergic in origin,[17] and is thought to result from the metabolism of halothane to trifluoroacetic acid via oxidative reactions in the liver. About 20% of inhaled halothane is metabolized by the liver and these products are excreted in the urine. The hepatitis syndrome had a mortality rate of 30% to 70%. Concern for hepatitis resulted in a dramatic reduction in the use of halothane for adults and it was replaced in the 1980s by enflurane and isoflurane. By 2005, the most common volatile anesthetics used were isoflurane, sevoflurane, and desflurane. Since the risk of halothane hepatitis in children was substantially lower than in adults, halothane continued to be used in pediatrics in the 1990s as it was especially useful for inhalation induction of anesthesia. However, by 2000, sevoflurane, excellent for inhalation induction, had largely replaced the use of halothane in children.
Halothane sensitises the heart to catecholamines, so it is liable to cause cardiac arrhythmia, occasionally fatal, particularly if hypercapnia has been allowed to develop. This seems to be especially problematic in dental anesthesia.
Like all the potent inhalational anaesthetic agents, it is a potent trigger for malignant hyperthermia.[4] Similarly, in common with the other potent inhalational agents, it relaxes uterine smooth muscle and this may increase blood loss during delivery or termination of pregnancy.
Occupational safety
People can be exposed to halothane in the workplace by breathing it in as waste anaesthetic gas, skin contact, eye contact, or swallowing it. The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) has set a recommended exposure limit (REL) of 2 ppm (16.2 mg/m3) over 60 minutes.[18]
Pharmacology
The exact mechanism of the action of general anaesthetics has not been delineated.[19] Halothane activates GABAA and glycine receptors.[20][21] It also acts as an NMDA receptor antagonist,[21] inhibits nACh and voltage-gated sodium channels,[20][22] and activates 5-HT3 and twin-pore K+ channels.[20][23] It does not affect the AMPA or kainate receptors.[21]
Chemical and physical properties
| Boiling point: | 50.2 °C | (at 101.325 kPa) |
| Density: | 1.868 g/cm3 | (at 20 °C) |
| Molecular Weight: | 197.4 u | |
| Vapor pressure: | 244 mmHg (32kPa) | (at 20 °C) |
| 288 mmHg (38kPa) | (at 24 °C) | |
| MAC: | 0.75 | vol % |
| Blood:gas partition coefficient: | 2.3 | |
| Oil:gas partition coefficient: | 224 |
Chemically, halothane is an alkyl halide (not an ether like many other anesthetics).[3] The structure has one stereocenter, so (R)- and (S)-optical isomers occur.
Synthesis
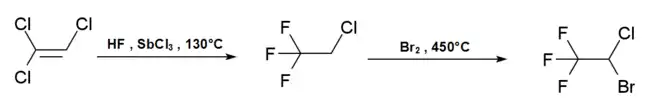
The commercial synthesis of halothane starts from trichloroethylene, which is reacted with hydrogen fluoride in the presence of antimony trichloride at 130 °C to form 2-chloro-1,1,1-trifluoroethane. This is then reacted with bromine at 450 °C to produce halothane.[24]
Related substances
Attempts to find anesthetics with less metabolism led to halogenated ethers such as enflurane and isoflurane. The incidence of hepatic reactions with these agents is lower. The exact degree of hepatotoxic potential of enflurane is debated, although it is minimally metabolized. Isoflurane is essentially not metabolized and reports of associated liver injury are quite rare. Small amounts of trifluoroacetic acid can be formed from both halothane and isoflurane metabolism and possibly accounts for cross sensitization of patients between these agents.
The main advantage of the more modern agents is lower blood solubility, resulting in faster induction of and recovery from anaesthesia.
History
Halothane was first synthesized by C. W. Suckling of Imperial Chemical Industries in 1951 at the ICI Widnes Laboratory and was first used clinically by M. Johnstone in Manchester in 1956. Initially, many pharmacologists and anesthesiologists had doubts about the safety and efficacy of the new drug. But halothane, which required specialist knowledge and technologies for safe administration, also afforded British anesthesiologists the opportunity to remake their speciality as a profession during a period, when the newly established National Health Service needed more specialist consultants.[25] In this context, halothane eventually became popular as a nonflammable general anesthetic replacing other volatile anesthetics such as trichloroethylene, diethyl ether and cyclopropane. In many parts of the world it has been largely replaced by newer agents since the 1980s but is still widely used in developing countries because of its lower cost.

Halothane was given to many millions of people worldwide from its introduction in 1956 through the 1980s.[26] Its properties include cardiac depression at high levels, cardiac sensitization to catecholamines such as norepinephrine, and potent bronchial relaxation. Its lack of airway irritation made it a common inhalation induction agent in pediatric anesthesia. Its use in developed countries has been mostly replaced by newer anesthetic agents such as sevoflurane.[27] It is not commercially available in the United States.[6]
Society and culture
Availability
It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines.[9][10] It is available as a volatile liquid, at 30, 50, 200, and 250 ml per container[28] but in many developed nations is not available having been displaced by newer agents.
It is the only inhalational anesthetic containing bromine, which makes it radiopaque. It is colorless and pleasant-smelling, but unstable in light. It is packaged in dark-colored bottles and contains 0.01% thymol as a stabilizing agent.
Ozone depletion
Halothane is an ozone depleting substance with an ODP of 1.56 and it is calculated to be responsible for 1% of total stratospheric ozone layer depletion.[12][13]
References
- "Halothane, USP". DailyMed. 18 September 2013. Retrieved 11 February 2022.
- "Fluothane: FDA-Approved Drugs". U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Retrieved 12 February 2022.
- "Halothane". DrugBank. DB01159.
- World Health Organization (2009). Stuart MC, Kouimtzi M, Hill SR (eds.). WHO Model Formulary 2008. World Health Organization. pp. 17–8. hdl:10665/44053. ISBN 9789241547659.
- James MF, Hift RJ (July 2000). "Porphyrias". British Journal of Anaesthesia. 85 (1): 143–53. doi:10.1093/bja/85.1.143. PMID 10928003.
- "Halothane - FDA prescribing information, side effects and uses". www.drugs.com. June 2005. Archived from the original on 21 December 2016. Retrieved 13 December 2016.
- Bricker S (17 June 2004). The Anaesthesia Science Viva Book. Cambridge University Press. p. 161. ISBN 9780521682480. Archived from the original on 10 September 2017 – via Google Books.
- Walker SR (2012). Trends and Changes in Drug Research and Development. Springer Science & Business Media. p. 109. ISBN 9789400926592. Archived from the original on 2017-09-10.
- World Health Organization (2019). World Health Organization model list of essential medicines: 21st list 2019. Geneva: World Health Organization. hdl:10665/325771. WHO/MVP/EMP/IAU/2019.06. License: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO.
- World Health Organization (2021). World Health Organization model list of essential medicines: 22nd list (2021). Geneva: World Health Organization. hdl:10665/345533. WHO/MHP/HPS/EML/2021.02.
- Yentis SM, Hirsch NP, Ip J (2013). Anaesthesia and Intensive Care A-Z: An Encyclopedia of Principles and Practice (5 ed.). Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 264. ISBN 9780702053757. Archived from the original on 2017-09-10.
- Kümmerer K (2013). Pharmaceuticals in the Environment: Sources, Fate, Effects and Risks. Springer Science & Business Media. p. 33. ISBN 9783662092590.
- Langbein T, Sonntag H, Trapp D, Hoffmann A, Malms W, Röth EP, et al. (January 1999). "Volatile anaesthetics and the atmosphere: atmospheric lifetimes and atmospheric effects of halothane, enflurane, isoflurane, desflurane and sevoflurane". British Journal of Anaesthesia. 82 (1): 66–73. doi:10.1093/bja/82.1.66. PMID 10325839.
- Lobo SA, Ojeda J, Dua A, Singh K, Lopez J (2022). "Minimum Alveolar Concentration". StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing. PMID 30422569. Retrieved 2022-08-09.
- Bezuidenhout E. "The blood–gas partition coefficient". Southern African Journal of Anaesthesia and Analgesia. 1 (3): 3. eISSN 2220-1173. ISSN 2220-1181. Archived from the original on 2022-08-08. Retrieved 2022-08-08 – via Charlotte Maxeke Johannesburg Academic Hospital.
- "Halothane". Anesthesia General. 2010-10-31. Archived from the original on 2011-02-16.
- Habibollahi P, Mahboobi N, Esmaeili S, Safari S, Dabbagh A, Alavian SM (2018-01-01). "Halothane". LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury [Internet]. NCBI Bookshelf. PMID 31643481. Retrieved 2021-01-27.
- "CDC - NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards - Halothane". www.cdc.gov. Archived from the original on 2015-12-08. Retrieved 2015-11-03.
- Perkins B (7 February 2005). "How does anesthesia work?". Scientific American. Retrieved 30 June 2016.
- Hemmings HC, Hopkins PM (2006). Foundations of Anesthesia: Basic Sciences for Clinical Practice. Elsevier Health Sciences. pp. 292–. ISBN 978-0-323-03707-5. Archived from the original on 2016-04-30.
- Barash P, Cullen BF, Stoelting RK, Cahalan M, Stock CM, Ortega R (7 February 2013). Clinical Anesthesia, 7e: Print + Ebook with Multimedia. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 116–. ISBN 978-1-4698-3027-8. Archived from the original on 17 June 2016.
- Schüttler J, Schwilden H (8 January 2008). Modern Anesthetics. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 70–. ISBN 978-3-540-74806-9. Archived from the original on 1 May 2016.
- Bowery NG (19 June 2006). Allosteric Receptor Modulation in Drug Targeting. CRC Press. pp. 143–. ISBN 978-1-4200-1618-5. Archived from the original on 10 May 2016.
- Suckling et al.,"PROCESS FOR THE PREPARATION OF 1,1,1-TRIFLUORO-2-BROMO-2-CHLOROETHANE", US patent 2921098, granted January 1960 , assigned to Imperial Chemical Industries
- Mueller LM (March 2021). "Medicating Anaesthesiology: Pharmaceutical Change, Specialisation and Healthcare Reform in Post-War Britain". Social History of Medicine. 34 (4): 1343–1365. doi:10.1093/shm/hkaa101.
- Niedermeyer E, da Silva FH (2005). Electroencephalography: Basic Principles, Clinical Applications, and Related Fields. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 1156. ISBN 978-0-7817-5126-1. Archived from the original on 2016-05-09.
- Yentis SM, Hirsch NP, Ip J (2013). Anaesthesia and Intensive Care A-Z: An Encyclopedia of Principles and Practice (5 ed.). Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 264. ISBN 9780702053757. Archived from the original on 2017-09-10.
- National formulary of India, 4th Ed. New Delhi, India, Indian Pharmacopoeia commission; 2011: 411
External links
- "Halothane". Drug Information Portal. U.S. National Library of Medicine.