Infantile progressive bulbar palsy
| Infantile progressive bulbar palsy | |
|---|---|
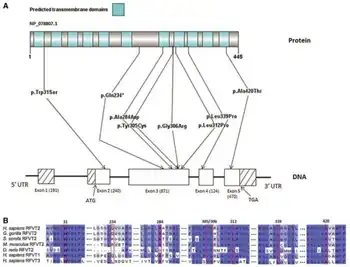 | |
| Mutations in SLC52A2 in Brown-Vialetto-Van Laere syndrome a) Predicted transmembrane domains in RFVT2 b)structural conservation of relevant amino acid residues in RFVT2 across species and in RFVT1 and RFVT3 | |
| Specialty | Neurology |
Infantile progressive bulbar palsy is a rare type of progressive bulbar palsy that occurs in children. The disease exists in both rapid and slow onsets, and involves inflammation of the gray matter of the bulb.[1]
Infantile PBP is a disease that manifests itself in two forms: Fazio–Londe syndrome (FL) and Brown–Vialetto–Van Laere syndrome (BVVL).[2]
References
- ↑ Wilson, John Eastman (1909). Diseases of the nervous system. Boericke & Runyon. p. 296. Retrieved 5 December 2017.
Infantile progressive bulbar palsy.
- ↑ Piña-Garza, J. Eric (2013). Fenichel's Clinical Pediatric Neurology E-Book: A Signs and Symptoms Approach. Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 328. ISBN 978-1455748129. Archived from the original on 18 July 2021. Retrieved 5 December 2017.
This article is issued from Offline. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.