Pinguecula
| Pinguecula | |
|---|---|
 | |
| pinguecula | |
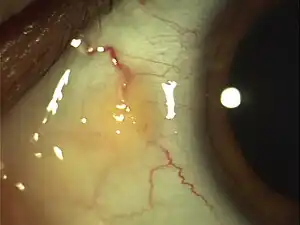
A pinguecula is a common type of conjunctival stromal degeneration in the eye. It appears as an elevated yellow-white plaque in the bulbar conjunctiva near the limbus.[1] Calcification may also seen occasionally.[1]
Signs and symptoms
It is seen as a yellow-[2]white deposit on the conjunctiva adjacent to the limbus (the junction between the cornea and sclera). (It is to be distinguished clinically from a pterygium, which is a wedge shaped area of fibrosis that may grow onto the cornea.) A pinguecula usually does not cause any symptoms. It is most common in tropical climates and there is a direct correlation with UV exposure.
Histologically, there is degeneration of the collagen fibers of the conjunctival stroma with thinning of the overlying epithelium and occasionally calcification.[2] Actinic exposure of the thin conjunctival tissue is thought to cause fibroblasts to produce more elastin fibers, which are more twisted than normal elastin fibers and may lead to the degradation of the collagen fibers.[3] Alternatively, it has been postulated that the sub-epithelial collagen fibers undergo degradation and assume the qualities of elastic tissue while fragmenting and twisting in a different configuration from their normal state.[4]
It is thought that the high reflectivity of the solid white scleral tissue underlying the conjunctival tissue may result in additional UV exposure to the back side of the tissue.[5] The side of the nose also reflects sunlight on to the conjunctiva. As a result, pingueculae tend to occur more often on the nasal side of the eye. While most pingueculae are found in people over the age of 40, they are not uncommon in 20- and 30-year-old adults who spend significant time in the sun.
The surface of the conjunctival tissue overlying a pinguecula interferes with the normal spreading of the tear film. The tear ferning test reveals abnormalities of the mucous component of the tear film, making it useful as a predictor of a person's tolerance of hydrophilic soft contact lenses.[6] Contact lens intolerance can also result from the elevation of the peripheral edge of the contact lens if it overlies a pinguecula.
The plural form of pinguecula is pingueculae. Pinguecula is derived from the Latin word "pinguis" for fat or grease.[7]
Associated conditions
A pinguecula is one of the differential diagnoses for a limbal nodule. It may have an increased prevalence in Gaucher's disease.
Etiology
The exact etiology is unknown, but it may be associated with aging and excessive exposure to UV light.[8]
Diagnosis
.png.webp)
Diagnosis of pinguecula is usually done by an eye care professional during routine eye examination using slit lamp. Conjunctival biopsy may be advised if malignancy is suspected.[9]
Treatment
Pingueculae may enlarge slowly over time, but are a benign condition, usually requiring no treatment.[1] Artificial tears may help to relieve discomfort, if it occurs.[1] If cosmesis is a concern, or if there is discomfort in contact lens use, surgical excision may be done.[9] Occasionally, a pinguecula may become inflamed, a condition called pingueculitis. The cause of pingueculitis is unknown and there are no known infectious agents associated with it. If an inflamed pinguecula is causing discomfort or cosmetic concerns, it may be treated with short course of topical steroid.[1] Laser photocoagulation may also be used to remove pinguecula.[9]
See also
- Peripheral light focusing
- Pterygium (conjunctiva)
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 John F., Salmon (2020). "Conjunctiva". Kanski's clinical ophthalmology : a systematic approach (9th ed.). Edinburgh: Elsevier. ISBN 978-0-7020-7713-5. OCLC 1131846767.
- 1 2 Bowling, Brad (2015-03-24). Kanski's Clinical Ophthalmology E-Book: A Systematic Approach. Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 162. ISBN 9780702055744. Archived from the original on 2022-07-29. Retrieved 2022-04-20.
- ↑ Weedon, David (2010). Weedon's Skin Pathology. ISBN 978-0-7020-3485-5.
- ↑ Sutphin, John (ed.). 2007-2008 Basic and Clinical Science Course Section 8: External Disease and Cornea. American Academy Ophthalmology. p. 365. ISBN 1-56055-814-8.
- ↑ Kisling, David (2010-06-26). "Eye Growth & Bumps Often Pinguecula". Archived from the original on 2018-02-05. Retrieved 2018-02-21.
- ↑ Ravazzoni L, Ghini C, Macri A, Rolando M (1998). "Forecasting of hydrophilic contact lens tolerance by means of tear ferning test". Clinical and Experimental Ophthalmology. 236 (5): 354–358. doi:10.1007/s004170050090. PMID 9602319. S2CID 9448528.
- ↑ "pingu-, pingue-, pingui-". English-Word Information. Senior Scribe Publications. Archived from the original on 2018-02-21. Retrieved 2018-02-21.
- ↑ Myron, Yanoff; Jay S., Duker (2019). "Cornea and ocular surface diseases". Ophthalmology (5th ed.). Edinburgh: Elsevier. p. 206. ISBN 978-0-323-52821-4. OCLC 1051774434.
- 1 2 3 "Pinguecula - EyeWiki". eyewiki.aao.org. Archived from the original on 2020-07-11. Retrieved 2022-04-20.
External links
| Classification | |
|---|---|
| External resources |