Toxic and nutritional optic neuropathy
| Toxic and nutritional optic neuropathy | |
|---|---|
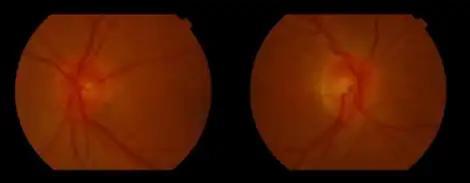 | |
| Bilateral hyperaemic optic discs seen in chloramphenicol-associated toxic optic neuropathy | |
Toxic and nutritional optic neuropathy is a group of medical disorders defined by visual impairment due to optic nerve damage secondary to a toxic substance and/or nutritional deficiency. The causes of these disorders are various, but they are linked by shared signs and symptoms, which this article will describe. In several of these disorders, both toxic and nutritional factors play a role, acting synergistically.
Signs and symptoms
Vision loss in toxic and nutritional optic neuropathy is bilateral, symmetric, painless, gradual, and progressive. Dyschromatopsia, a change in color vision, is often the first symptom. Some patients notice that certain colors, particularly red, are less bright or vivid; others have a general loss of color perception. Loss of visual acuity may start with a blur or haze at the point of fixation, followed by a progressive decline. The degree of vision loss can extend to total blindness, but a loss beyond 20/400 is rare, except in the case of methanol ingestion. Peripheral vision is usually spared since the pattern of loss typically involves a central or cecocentral scotoma, a visual field defect at or surrounding the point of fixation. This pattern can be revealed via visual field testing.
Upon examination, the pupils usually demonstrate a normal response to light and near stimulation. In those who are practically blind, the pupils will be dilated with a weak or absent response to light. The optic disc may appear normal, swollen, or hyperemic in early stages. With hyperemia, disc hemorrhages may also be present. Continued damage to the optic nerve results in the development of optic atrophy, classically seen as temporal pallor of the optic disc.
Cause
Toxic optic neuropathy
There are several causes of toxic optic neuropathy.[1] Among these are: ingestion of methanol (wood alcohol), ethylene glycol (automotive antifreeze), disulfiram (used to treat chronic alcoholism), halogenated hydroquinolones (amebicidal medications), ethambutol and isoniazid (tuberculosis treatment), and antibiotics such as linezolid and chloramphenicol as well as chloroquine and the related hydroxychloroquine (for lupus and rheumatoid arthritis) where it is known as chloroquine retinopathy. Tobacco is also a major cause of toxic optic neuropathy.
Nutritional optic neuropathy
The predominant cause of nutritional optic neuropathy is thought to be deficiency of B-complex vitamins, particularly thiamine[2] (vitamin B1), cyanocobalamin (vitamin B12) and recently copper.[3] Deficiency of pyridoxine (vitamin B6), niacin (vitamin B3), riboflavin (vitamin B2), and/or folic acid also seems to play a role. Those individuals who consume excessive amounts of alcohol and use tobacco are at greater risk because they tend to be malnourished. Those with pernicious anemia are also at risk due to an impaired ability to absorb vitamin B12 from the intestinal tract.
Pathophysiology
All of the above risk factors impact mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation. Thus, the toxic and nutritional optic neuropathies are actually acquired mitochondrial optic neuropathies. The clinical picture that they produce is akin to that of the congenital mitochondrial optic neuropathies, e.g., Leber's hereditary optic neuropathy and Kjer's optic neuropathy.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of toxic or nutritional optic neuropathy is usually established by a detailed medical history and careful eye examination. If the medical history clearly points to a cause, neuroimaging to rule out a compressive or infiltrative lesion is optional. However, if the medical history is atypical or does not clearly point to a cause, neuroimaging is required to rule out other causes and confirm the diagnosis. In most cases of suspected toxic or nutritional optic neuropathy that require neuroimaging, an MRI scan is obtained. Further testing, guided by the medical history and physical examination, can be performed to elucidate a specific toxin or nutritional deficiency as a cause of the optic neuropathy. Examples include blood testing for methanol levels or vitamin B12 levels.
Treatment
Treatment of toxic and nutritional optic neuropathy is dictated by the cause of the disorder.
- Toxic optic neuropathy is treated by identification and removal of the offending agent. Depending upon the individual affected, the nature of the agent, total exposure prior to removal, and degree of vision loss at the time of diagnosis, the prognosis is variable.
- Nutritional optic neuropathy is treated with improved nutrition. A well-balanced diet with plenty of protein and green leafy vegetables, vitamin supplementation (thiamine, vitamin B12, folic acid, multivitamins), and reduction of smoking and/or drinking are the mainstay of treatment. Again, prognosis is variable and dependent upon the affected individual, treatment compliance, and degree of vision loss at diagnosis.
In both toxic and nutritional neuropathy, vision generally recovers to normal over several days to weeks, though it may take months for full restoration and there is always the risk of permanent vision loss. Visual acuity usually recovers before color vision.
Epidemiology
In industrialized nations, toxic and nutritional optic neuropathy is relatively uncommon and is primarily associated with specific medications, occupational exposures, or tobacco and alcohol use disorder. However, in developing nations, nutritional optic neuropathy is much more common, especially in regions afflicted by famine. All genders and all races are equally affected, and all ages are susceptible.
References
- ↑ Neil R. Miller; William Fletcher Hoyt (2005). Walsh and Hoyt's clinical neuro-ophthalmology. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 447–. ISBN 978-0-7817-4811-7. Archived from the original on 24 July 2022. Retrieved 6 February 2011.
- ↑ Spinazzi, Marco; Angelini, Corrado; Patrini, Cesare (2010). "Subacute sensory ataxia and optic neuropathy with thiamine deficiency". Nature Reviews Neurology. 6 (5): 288–93. doi:10.1038/nrneurol.2010.16. PMID 20308997.
- ↑ Spinazzi, Marco; De Lazzari, Franca; Tavolato, Bruno; Angelini, Corrado; Manara, Renzo; Armani, Mario (2007). "Myelo-optico-neuropathy in copper deficiency occurring after partial gastrectomy". Journal of Neurology. 254 (8): 1012–7. doi:10.1007/s00415-006-0479-2. PMID 17415508.
Further reading
- Glaser, JS (1999). "Nutritional and toxic optic neuropathies". In Glaser, JS (ed.). Neuro-ophthalmology (3rd ed.). Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 181–6.
- Lessell, S (2000). "Nutritional deficiency and toxic optic neuropathies". In Albert, DM; Jakobiec, FA (eds.). Principles and Practice of Ophthalmology (2nd ed.). Philadelphia: W.B. Saunders Company. pp. 4169–76.
- Sadun, A. A (2002). "Mitochondrial optic neuropathies". Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry. 72 (4): 423–5. doi:10.1136/jnnp.72.4.423. PMC 1737836. PMID 11909893.
External links
| Classification | |
|---|---|
| External resources |
- eMedicine article Archived 2008-12-02 at the Wayback Machine