Terrien's marginal degeneration
| Terrien's marginal degeneration | |
|---|---|
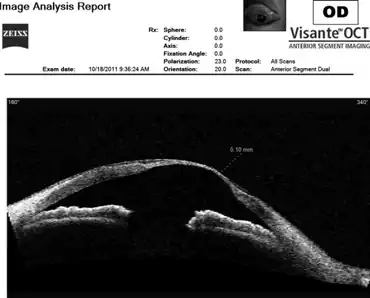 | |
| Anterior segment Visante optical coherence tomography scanning of right eye in this TMD individual showed that the thickness at the thinnest portion of cornea was 0.1 mm. | |
| Specialty | Ophthalmology |
Terrien marginal degeneration is a noninflammatory, unilateral or asymmetrically bilateral, slowly progressive thinning of the peripheral corneal stroma.[1][2]
Sign and symptoms
The clinical presentation of Terrien's marginal degeneration is consistent with progressive blurred vision.[3]
Cause
The cause of Terrien marginal degeneration is unknown, its prevalence is roughly equal between males and females, and it usually occurs in the second or third decade of life.[2]
Diagnosis
The diagnosis for this ocular condition is done via corneal topography ( photokeratoscopy or videokeratography)[3]
Treatments
Spectacles or RGP contact lenses can be used to manage the astigmatism. when the condition worsens, surgical correction may be required.[4]
References
- ↑ Risma, Justin. "Terrien Marginal Degeneration". EyeRounds Online Atlas of Ophthalmology. University of Iowa. Archived from the original on 2021-02-23. Retrieved 2022-03-22.
- 1 2 "Terrien marginal degeneration". American Academy of Ophthalmology. Archived from the original on 2015-02-06. Retrieved 2022-03-22.
- 1 2 "Terrien's Marginal Degeneration - EyeWiki". eyewiki.aao.org. Archived from the original on 14 February 2022. Retrieved 26 August 2022.
- ↑ Mihlstin, Melanie Lynn; Hwang, Frank S. "Terrien's Marginal Degeneration". EyeWiki. American Academy of Ophthalmology. Archived from the original on 2022-02-14. Retrieved 2022-03-22.
External links
| Classification |
|---|
This article is issued from Offline. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.