Tick-borne disease
| Tick-borne disease | |
|---|---|
 | |
| A feeding tick | |
| Specialty | Infectious disease |
Tick-borne diseases, which afflict humans and other animals, are caused by infectious agents transmitted by tick bites.[1] They are caused by infection with a variety of pathogens, including rickettsia and other types of bacteria, viruses, and protozoa.[2] The economic impact of tick-borne diseases is considered to be substantial in humans,[3] and tick-borne diseases are estimated to affect ~80 % of cattle worldwide.[4]
As of 2020 18 tick-borne pathogens have been identified in the United States according to the Centers for Disease Control[5] and at least 27 are known globally.[6][7][8] New tick-borne diseases have been discovered in the 21st century, due in part to the use of molecular assays and next-generation sequencing.[9]
The occurrence of ticks and tick-borne illnesses in humans is increasing.[10] Tick populations are spreading into new areas, due in part to the warming temperatures of climate change.[6][11] Tick populations are also affected by changes in the populations of their hosts (e.g. deer, cattle, mice, lizards) and those hosts' predators (e.g. foxes). Diversity and availability of hosts and predators can be affected by deforestation and habitat fragmentation.[6]
Because individual ticks can harbor more than one disease-causing agent, patients can be infected with more than one pathogen at the same time, compounding the difficulty in diagnosis and treatment.[2] As the incidence of tick-borne illnesses increases and the geographic areas in which they are found expand, health workers increasingly must be able to distinguish the diverse, and often overlapping, clinical presentations of these diseases.[5]
Types

Bacterial
- Lyme disease or borreliosis
- Organism: Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato (bacterium)
- Vector: at least 15 species of ticks in the genus Ixodes, including deer tick (Ixodes scapularis (=I. dammini), I. pacificus, I. ricinus (Europe), I. persulcatus (Asia))[12]
- Endemic to: The Americas and Eurasia
- Symptoms: Fever, arthritis, neuroborreliosis, erythema migrans, cranial nerve palsy, carditis, fatigue, and influenza-like illness[13]
- Treatment: Antibiotics - amoxicillin in pregnant adults and children), (doxycycline in other adults[14]
- Relapsing fever (tick-borne relapsing fever, different from Lyme disease due to different Borrelia species and ticks)
- Organisms: Borrelia species such as B. hermsii, B. parkeri, B. duttoni, B. miyamotoi
- Vector: Ornithodoros species
- Regions : Primarily in Africa, Spain, Saudi Arabia, Asia in and certain areas of Canada and the western United States
- Symptoms: Relapsing fever typically presents as recurring high fevers, flu-like symptoms, headaches, and muscular pain, with less common symptoms including rigors, joint pain, altered mentation, cough, sore throat, painful urination, and rash[15]
- Treatment: Antibiotics are the treatment for relapsing fever, with doxycycline, tetracycline, or erythromycin being the treatment of choice.[16]
- Typhus Several diseases caused by Rickettsia bacteria (below)
- Rocky Mountain spotted fever
- Organism: Rickettsia rickettsii
- Vector: Wood tick (Dermacentor variabilis), D. andersoni
- Region (US): East, Southwest
- Vector: Amblyomma cajennense
- Region (Brazil): São Paulo, Rio de Janeiro, Minas Gerais.
- Symptoms:Fever, headache, altered mental status, myalgia, and rash
- Treatment: Antibiotic therapy, typically consisting of doxycycline or tetracycline
- Helvetica spotted fever
- Organism: Rickettsia helvetica
- Region(R. helvetica): Confirmed common in ticks in Sweden, Switzerland, France, and Laos[17]
- Vector/region(s)#1: Ixodes ricinus is the main European vector.[17]
- Symptoms: Most often small red spots, other symptoms are fever, muscle pain, headache and respiratory problems[17]
- Treatment: Broad-spectrum antibiotic therapy is needed, phenoxymethylpenicillin likely is sufficient.[17]
- Human granulocytic anaplasmosis (formerly human granulocytic ehrlichiosis or HGE)
- Organism: Anaplasma phagocytophilum (formerly Ehrlichia phagocytophilum or Ehrlichia equi)
- Vector: Lone star tick (Amblyomma americanum), I. scapularis
- Region (US): South Atlantic, South-central
- Bartonella: Bartonella transmission rates to humans via tick bite are not well established [18] but Bartonella is common in ticks. For example: 4.76% of 2100 ticks tested in a study in Germany [19]
- Tularemia
- Organism: Francisella tularensis, A. americanum
- Vector: D. variabilis, D. andersoni
- Region (US): Southeast, South-central, West, widespread
Viral
.png.webp)
- Tick-borne meningoencephalitis
- Organism: TBEV (FSME) virus, a flavivirus from family Flaviviridae
- Vector: deer tick (Ixodes scapularis), Ixodes ricinus (Europe), Ixodes persulcatus (Russia + Asia))
- Endemic to: Europe and northern Asia
- Powassan virus/deer tick virus[21][22]
- Organism: Powassan virus (POWV), a flavivirus from family Flaviviridae. Lineage 2 POWV is also known as deer tick virus (DTV)
- Vector: Ixodes cookei, Ix. scapularis, Ix. marxi, Ix. spinipalpusm, Dermacentor andersoni, and D. variabilis
- Endemic to: North America and eastern Russia
- Colorado tick fever
- Organism: Colorado tick fever virus (CTF), a coltivirus from the Reoviridae
- Vector: Dermacentor andersoni
- Region: US (West)
- Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever
- Organism: CCHF virus, a nairovirus, from the Bunyaviridae
- Vector: Hyalomma marginatum, Rhipicephalus bursa
- Region: Southern part of Asia, Northern Africa, Southern Europe
- Severe febrile illness[23]
- Organism: Heartland virus, a phlebovirus, from the Bunyaviridae
- Vector: Lone star tick (Amblyomma americanum)
- Region: Missouri and Tennessee, United States
- Severe febrile illness, headaches, coma in 1/3 patients[24]
- Organism: tentatively Alongshan virus, jingmenvirus group in the flavivirus family
- Vector: tick (likely Ixodes persulcatus, Ixodes ricinus), mosquitoes
- Region: Inner Mongolia but potentially more widespread
Protozoan
- Babesiosis
- Organism: Babesia microti, Theileria equi
- Vector: Ixodes scapularis (deer tick), I. pacificus (western black-legged tick)
- Region (US): Northeast, West Coast
- Cytauxzoonosis
- Organism: Cytauxzoon felis
- Vector: Amblyomma americanum (Lone star tick)
- Region (US): South, Southeast
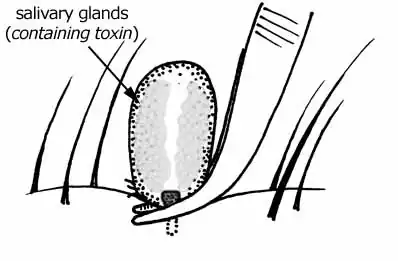
Toxin
- Tick paralysis
- Cause: Toxin
- Vector (US): Dermacentor andersoni (Rocky Mountain wood tick), D. variabilis (American dog tick or wood tick)
- Region (US): D. andersoni: East, D. variabilis: East, West coast
- Vector (Australia): Ixodes holocyclus (Australian paralysis tick)[25]
- Region (Australia): East
Allergies
- Alpha-gal allergy - Alpha-gal syndrome caused by immune reaction to the Alpha-gal sugar molecule introduced by ticks. The immune reaction can leave people with an allergy to red meat.
Risk assessment
For a person or pet to acquire a tick-borne disease requires that the individual gets bitten by a tick and that the tick feeds for a sufficient period of time. The feeding time required to transmit pathogens differs for different ticks and different pathogens. Transmission of the bacterium that causes Lyme disease is well understood to require a substantial feeding period.[26] In general, soft ticks (Argasidae) transmit pathogens within minutes of attachment because they feed more frequently, whereas hard ticks (Ixodidae) take hours or days, but the latter are more common and harder to remove.[27]
For an individual to acquire infection, the feeding tick must also be infected. Not all ticks are infected. In most places in the US, 30-50% of deer ticks will be infected with Borrelia burgdorferi (the agent of Lyme disease). Other pathogens are much more rare. Ticks can be tested for infection using a highly specific and sensitive qPCR procedure. Several commercial labs provide this service to individuals for a fee. The Laboratory of Medical Zoology (LMZ), a nonprofit lab at the University of Massachusetts, provides a comprehensive TickReport [28] for a variety of human pathogens and makes the data available to the public.[29] Those wishing to know the incidence of tick-borne diseases in their town or state can search the LMZ surveillance database.[29]
Prevention
Exposure
Ticks tend to be more active during warmer months, though this varies by geographic region and climate. Areas with woods, bushes, high grass, or leaf litter are likely to have more ticks. Those bitten commonly experience symptoms such as body aches, fever, fatigue, joint pain, or rashes. People can limit their exposure to tick bites by wearing light-colored clothing (including pants and long sleeves), using insect repellent with 20%–30% N,N-Diethyl-3-methylbenzamide (DEET), tucking their pants legs into their socks, checking for ticks frequently, and washing and drying their clothing (in a hot dryer).[30][31]
According to the World Health Organization, tick-to-animal transmission is difficult to prevent because animals do not show visible symptoms; the only effective prevention relies on killing ticks on the livestock production facility.[32]
Tick removal
Ticks should be removed as soon as safely possible once discovered. They can be removed either by grasping tweezers as close to the mouth as possible and pulling without rotation; some companies market grooved tools that rotate the hypostome to facilitate removal. Chemical methods to make the tick self-detach, or trying to pull the tick out with one’s fingers, are not efficient methods.[27]
Treatment
In general, specific laboratory tests are not available for rapid diagnosis of tick-borne diseases. Due to their seriousness, antibiotic treatment is often justified based on clinical presentation alone.
See also
- Arbovirus
- List of diseases spread by invertebrates
- List of insect-borne diseases
- Mosquito-borne disease
- Robovirus
- Tibovirus
- Ticks of domestic animals
References
- ↑ Wenner M (11 June 2021). "Let's Do a Tick Check - These pervasive bloodsuckers can give you more than just Lyme disease. Here's how to protect yourself. (Interactive)". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 19 June 2021. Retrieved 19 June 2021.
- 1 2 Kumar, Manish; Sharma, Aniket; Grover, Prashant (13 February 2019). "Triple Tick Attack". Cureus. 11 (2): e4064. doi:10.7759/cureus.4064. PMC 6464285. PMID 31016091.
- ↑ Mac, Stephen; da Silva, Sara R.; Sander, Beate (4 January 2019). "The economic burden of Lyme disease and the cost-effectiveness of Lyme disease interventions: A scoping review". PLOS ONE. 14 (1): e0210280. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0210280. ISSN 1932-6203. PMC 6319811. PMID 30608986.
- ↑ Rochlin, Ilia; Toledo, Alvaro (1 June 2020). "Emerging tick-borne pathogens of public health importance: a mini-review". Journal of Medical Microbiology. 69 (6): 781–791. doi:10.1099/jmm.0.001206. ISSN 0022-2615. PMC 7451033. PMID 32478654.
- 1 2 Tick-Borne Disease Working Group. 2020 Report to Congress (PDF). Washington, D.C.: U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. 2020. Archived (PDF) from the original on 24 January 2022. Retrieved 4 March 2022.
- 1 2 3 Chrobak, Ula (3 February 2022). "Lyme and other tick-borne diseases are on the rise. But why?". Knowable Magazine. doi:10.1146/knowable-020222-1. Archived from the original on 26 February 2022. Retrieved 4 March 2022.
- ↑ Paddock, Christopher D.; Lane, Robert S.; Staples, J. Erin; Labruna, Marcelo B. (21 September 2016). Changing paradigms for tick-borne diseases in the Americas. National Academies Press (US). Archived from the original on 20 January 2022. Retrieved 4 March 2022.
- ↑ Zhao, Guo-Ping; Wang, Yi-Xing; Fan, Zheng-Wei; Ji, Yang; Liu, Ming-jin; Zhang, Wen-Hui; Li, Xin-Lou; Zhou, Shi-Xia; Li, Hao; Liang, Song; Liu, Wei; Yang, Yang; Fang, Li-Qun (17 February 2021). "Mapping ticks and tick-borne pathogens in China". Nature Communications. 12 (1): 1075. doi:10.1038/s41467-021-21375-1. ISSN 2041-1723. PMC 7889899. PMID 33597544. Archived from the original on 6 May 2022. Retrieved 4 March 2022.
- ↑ Tokarz, Rafal; Lipkin, W. Ian (1 July 2021). "Discovery and Surveillance of Tick-Borne Pathogens". Journal of Medical Entomology. 58 (4): 1525–1535. doi:10.1093/jme/tjaa269. ISSN 0022-2585. PMC 8285023. PMID 33313662. Archived from the original on 6 May 2022. Retrieved 4 March 2022.
- ↑ "Lyme and Other Tickborne Diseases Increasing". Centers for Disease Control. 21 October 2021. Archived from the original on 4 March 2022. Retrieved 4 March 2022.
- ↑ Gilbert, Lucy (7 January 2021). "The Impacts of Climate Change on Ticks and Tick-Borne Disease Risk". Annual Review of Entomology. 66 (1): 373–388. doi:10.1146/annurev-ento-052720-094533. ISSN 0066-4170. PMID 33417823. S2CID 231300522. Archived from the original on 6 May 2022. Retrieved 4 March 2022.
- ↑ Wolcott KA, Margos G, Fingerle V, Becker NS (September 2021). "Host association of Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato: A review". Ticks and Tick-Borne Diseases. 12 (5): 101766. doi:10.1016/j.ttbdis.2021.101766. PMID 34161868.
- ↑ Mayo Clinic Staff. "Lyme disease: Symptoms". MayoClinic.com. Diseases and Conditions. Mayo Clinic. Archived from the original on 2017-10-13. Retrieved 2022-04-25.
- ↑ Mayo Clinic Staff. "Lyme disease: Treatments and drugs". MayoClinic.com. Diseases and Conditions. Mayo Clinic. Archived from the original on 2017-10-13. Retrieved 2022-04-25.
- ↑ Relapsing fever at eMedicine.
- ↑ Relapsing fever~treatment at eMedicine.
- 1 2 3 4 Lindblom A, Wallménius K, Nordberg M, Forsberg P, Eliasson I, Påhlson C, Nilsson K (March 2013). "Seroreactivity for spotted fever rickettsiae and co-infections with other tick-borne agents among habitants (sic) in central and southern Sweden". European Journal of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases. 32 (3): 317–323. doi:10.1007/s10096-012-1742-3. PMC 3569577. PMID 22961007.
- ↑ Ben Beard C, Nelson CA, Mead PS, Petersen LR (November 2012). "Bartonella spp. Bacteremia and rheumatic symptoms in patients from lyme disease-endemic region". Emerging Infectious Diseases. 18 (11): 1918–1919. doi:10.3201/eid1811.120675. PMC 3559143. PMID 23092626.
- ↑ Janecek E, Mietze A, Goethe R, Schnieder T, Strube C (October 2012). "Bartonella spp. infection rate and B. grahamii in ticks". Emerging Infectious Diseases. 18 (10): 1689–1690. doi:10.3201/eid1810.120390. PMC 3471628. PMID 23017501.
- ↑ Seo, Jun-Won; Kim, Dayoung; Yun, Nara; Kim, Dong-Min (23 June 2021). "Clinical Update of Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome". Viruses. 13 (7): 1213. doi:10.3390/v13071213. ISSN 1999-4915. Retrieved 19 January 2023.
- ↑ Dobler G (January 2010). "Zoonotic tick-borne flaviviruses". Veterinary Microbiology. Zoonoses: Advances and Perspectives. 140 (3–4): 221–228. doi:10.1016/j.vetmic.2009.08.024. PMID 19765917.
- ↑ "Powassan Virus | Powassan | CDC". www.cdc.gov. Archived from the original on 2017-06-16. Retrieved 2017-06-07.
- ↑ Pastula DM, Turabelidze G, Yates KF, Jones TF, Lambert AJ, Panella AJ, et al. (March 2014). "Notes from the field: Heartland virus disease - United States, 2012-2013". MMWR. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report. 63 (12): 270–271. PMC 5779346. PMID 24670929. Archived from the original on 2022-03-21. Retrieved 2022-04-25.
- ↑ "Chinese researchers highlight new tick-borne disease, Alongshan virus". CIDRAP - Center for Infectious Disease Research and Policy. Minneapolis, MN: University of Minnesota. May 29, 2019. Archived from the original on November 7, 2020. Retrieved April 25, 2022.
- ↑ "Ticks". medent.usyd.edu.au. Department of Entomology, University of Sydney and Westmead Hospital. November 7, 2003. Archived from the original on April 22, 2022. Retrieved April 25, 2022.
- ↑ "TickEncounter Resource Center". University of Rhode Island. Archived from the original on 2021-02-27. Retrieved 2022-04-25.
- 1 2 Pitches DW (August 2006). "Removal of ticks: a review of the literature". Euro Surveillance. 11 (8): E060817.4. doi:10.2807/esw.11.33.03027-en. PMID 16966784.
- ↑ "TickReport". Laboratory of Medical Zoology. University of Massachusetts. Archived from the original on 2022-04-05. Retrieved 2022-05-06.
- 1 2 "Tick-Borne Disease Network". Laboratory of Medical Zoology. University of Massachusetts. Archived from the original on 2022-04-05. Retrieved 2022-05-06.
- ↑ "Tick-Borne Diseases". cdc.gov. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health. Archived from the original on May 16, 2009. Retrieved May 21, 2009.
- ↑ Rahlenbeck S, Fingerle V, Doggett S (September 2016). "Prevention of tick-borne diseases: an overview". The British Journal of General Practice. 66 (650): 492–494. doi:10.3399/bjgp16X687013. PMC 5198687. PMID 27563139.
- ↑ "Crimean-Congo haemorrhagic fever". www.who.int. Archived from the original on 27 March 2022. Retrieved 13 September 2021.
External links
| Classification |
|
|---|---|
| External resources |
- Tick-Borne Diseases: Recommendations for Workers and Employers Archived 2022-03-01 at the Wayback Machine—National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health
- Tickborne Diseases Archived 2022-04-28 at the Wayback Machine—National Center for Infectious Diseases (CDC)
- Tickborne Disease Website Archived 2007-09-29 at the Wayback Machine—Massachusetts Department of Public Health
- Ixodes Scapularis—3D animation of Deer or Blacklegged Tick from US Army site
- Parasitic Insects, Mites and Ticks: Genera of Medical and Veterinary Importance Archived 2022-05-06 at the Wayback Machine Wikibooks