Flaviviridae
| Flaviviridae | |
|---|---|
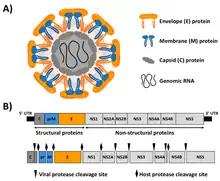 | |
| Zika virus virion structure and genome | |
| Virus classification | |
| (unranked): | Virus |
| Realm: | Riboviria |
| Kingdom: | Orthornavirae |
| Phylum: | Kitrinoviricota |
| Class: | Flasuviricetes |
| Order: | Amarillovirales |
| Family: | Flaviviridae |
| Genera | |
| |
Flaviviridae is a family of enveloped positive-strand RNA viruses which mainly infect mammals and birds.[1] They are primarily spread through arthropod vectors (mainly ticks and mosquitoes).[2] The family gets its name from the yellow fever virus; flavus is Latin for "yellow", and yellow fever in turn was named because of its propensity to cause jaundice in victims.[3] There are 89 species in the family divided among four genera.[2] Diseases associated with the group include: hepatitis (hepaciviruses), hemorrhagic syndromes, fatal mucosal disease (pestiviruses), hemorrhagic fever, encephalitis, and the birth defect microcephaly (flaviviruses).[4]
Structure
Virus particles are enveloped and spherical with icosahedral-like geometries that have pseudo T=3 symmetry. They are about 40–60 nm in diameter.[2][4]
Genome
Members of the family Flaviviridae have monopartite, linear, single-stranded RNA genomes of positive polarity, and 9.6 to 12.3 kilobase in total length. The 5'-termini of flaviviruses carry a methylated nucleotide cap, while other members of this family are uncapped and encode an internal ribosome entry site.
The genome encodes a single polyprotein with multiple transmembrane domains that is cleaved, by both host and viral proteases, into structural and non-structural proteins. Among the non-structural protein products (NS), the locations and sequences of NS3 and NS5, which contain motifs essential for polyprotein processing and RNA replication respectively, are relatively well conserved across the family and may be useful for phylogenetic analysis.
Life cycle
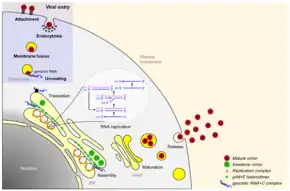
Viral replication is cytoplasmic. Entry into the host cell is achieved by attachment of the viral envelope protein E to host receptors, which mediates clathrin-mediated endocytosis. Replication follows the positive-stranded RNA virus replication model. Positive-stranded RNA virus transcription is the method of transcription. Translation takes place by viral initiation. The virus exits the host cell by budding. Humans and mammals serve as the natural hosts. The virus is transmitted via vectors (ticks and mosquitoes).[2][4]
| Genus | Host details | Tissue tropism | Entry details | Release details | Replication site | Assembly site | Transmission |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flavivirus | Humans; mammals; mosquitoes; ticks | Epithelium: skin; epithelium: kidney; epithelium: intestine; epithelium: testes | Clathrin-mediated endocytosis | Secretion | Cytoplasm | Cytoplasm | Zoonosis; arthropod bite |
| Hepacivirus | Humans | Epithelium: skin; epithelium: kidney; epithelium: intestine; epithelium: testes | Clathrin-mediated endocytosis | Secretion | Cytoplasm | Cytoplasm | Sex; blood |
| Pegivirus | Mammals | None | Clathrin-mediated endocytosis | Secretion | Cytoplasm | Cytoplasm | Unknown |
| Pestivirus | Mammals | None | Clathrin-mediated endocytosis | Secretion | Cytoplasm | Cytoplasm | Vertical: parental |
Taxonomy
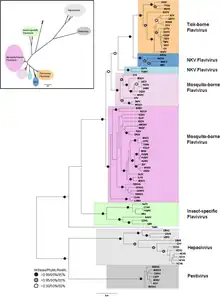
The family has four genera:[1][2]
- Genus Flavivirus (includes Dengue virus, Japanese encephalitis, Kyasanur Forest disease, Powassan virus, West Nile virus, Yellow fever virus, and Zika virus)
- Genus Hepacivirus (includes Hepacivirus C (hepatitis C virus) and Hepacivirus B (GB virus B))
- Genus Pegivirus (includes Pegivirus A (GB virus A), Pegivirus C (GB virus C), and Pegivirus B (GB virus D))
- Genus Pestivirus (includes Pestivirus A (bovine viral diarrhea virus 1) and Pestivirus C (classical swine fever virus, previously hog cholera virus)). Viruses in this genus infect nonhuman mammals.
- Unclassified
Other flaviviruses are known that have yet to be classified. These include Wenling shark virus.
Jingmenvirus is a group of unclassified viruses in the family which includes Alongshan virus, Guaico Culex virus, Jingmen tick virus and Mogiana tick virus. These viruses have a segmented genome of 4 or 5 pieces. Two of these segments are derived from flaviviruses.
A number of viruses may be related to the flaviviruses, but have features that are atypical of the flaviviruses. These include citrus Jingmen-like virus, soybean cyst nematode virus 5, Toxocara canis larva agent, Wuhan cricket virus, and possibly Gentian Kobu-sho-associated virus.
Clinical importance
Major diseases caused by members of the family Flaviviridae include:
References
- 1 2 Simmonds, P; Becher, P; Bukh, J; Gould, E; Meyers, G; Monath, T; Muerhoff, S; Pletnev, A; Rico-Hesse, R; Smith, D; Stapleton, J; ICTV Report Consortium (2017). "ICTV Virus Taxonomy Profile: Flaviviridae". Journal of General Virology. 98 (1): 2–3. doi:10.1099/jgv.0.000672. PMC 5370391. PMID 28218572.
- 1 2 3 4 5 "Flaviviridae". ICTV Online Report. Archived from the original on 2023-03-20. Retrieved 2022-12-20.
- ↑ "Flaviviridae". Microbe Wiki. Archived from the original on September 27, 2021. Retrieved July 22, 2008.
- 1 2 3 "Viral Zone". ExPASy. Archived from the original on 5 May 2017. Retrieved 15 June 2015.
External links
- ICTV Report: Flaviviridae Archived 2023-03-20 at the Wayback Machine
- Flaviviridae Genomes database search results from the Viral Bioinformatics Resource Center
- Viralzone: Flaviviridae Archived 2017-05-05 at the Wayback Machine
- Virus Pathogen Database and Analysis Resource (ViPR): Flaviviridae Archived 2019-09-19 at the Wayback Machine
- "Flaviviridae". NCBI Taxonomy Browser. 11050. Archived from the original on 2021-12-10. Retrieved 2022-12-20.