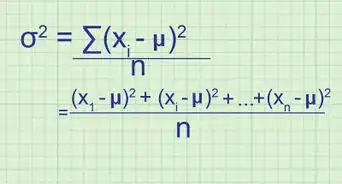wikiHow is a “wiki,” similar to Wikipedia, which means that many of our articles are co-written by multiple authors. To create this article, 30 people, some anonymous, worked to edit and improve it over time.
This article has been viewed 999,352 times.
Learn more...
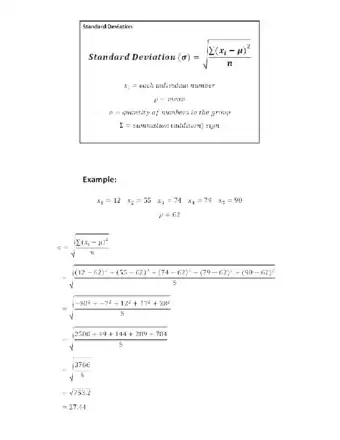
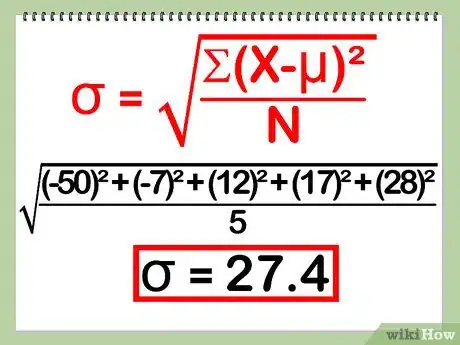
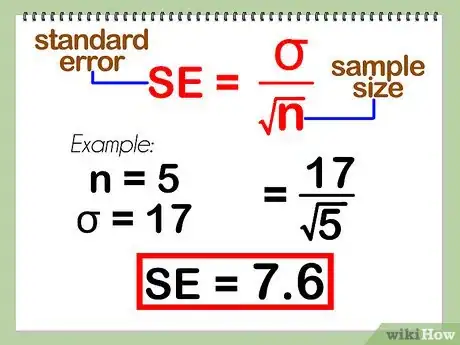
After collecting data, oftentimes the first thing you need to do is analyze it. This usually entails finding the mean, the standard deviation, and the standard error of the data. This article will show you how it's done.
Steps
Community Q&A
-
QuestionHow do you find the mean given number of observations?
 Community AnswerTo find the mean, add all the numbers together and divide by how many numbers there are. e.g to find the mean of 1,7,8,4,2: 1+7+8+4+2 = 22/5 = 4.4.
Community AnswerTo find the mean, add all the numbers together and divide by how many numbers there are. e.g to find the mean of 1,7,8,4,2: 1+7+8+4+2 = 22/5 = 4.4. -
QuestionThe standard error is calculated as 0.2 and the standard deviation of a sample is 5kg. Can it be said to be smaller or larger than the standard deviation?
 Community AnswerThe standard error (SE) must be smaller than the standard deviation (SD), because the SE is calculating by dividing the SD by something - i.e. making it smaller.
Community AnswerThe standard error (SE) must be smaller than the standard deviation (SD), because the SE is calculating by dividing the SD by something - i.e. making it smaller. -
QuestionHow can I find out the standard deviation of 50 samples?
 Community AnswerThe results of all your figures (number plus number plus number etc.) divided by quantity of samples 50 =SD.
Community AnswerThe results of all your figures (number plus number plus number etc.) divided by quantity of samples 50 =SD.
Warnings
- Check your math carefully. It is very easy to make mistakes or enter numbers incorrectly.⧼thumbs_response⧽
References
- ↑ https://www.radford.edu/~biol-web/stats/standarderrorcalc.pdf
- ↑ https://www.khanacademy.org/math/statistics-probability/summarizing-quantitative-data/variance-standard-deviation-population/a/calculating-standard-deviation-step-by-step
- ↑ https://sites.radford.edu/~biol-web/stats/standarderrorcalc.pdf
- ↑ https://handbook-5-1.cochrane.org/chapter_7/7_7_3_2_obtaining_standard_deviations_from_standard_errors_and.htm
About This Article
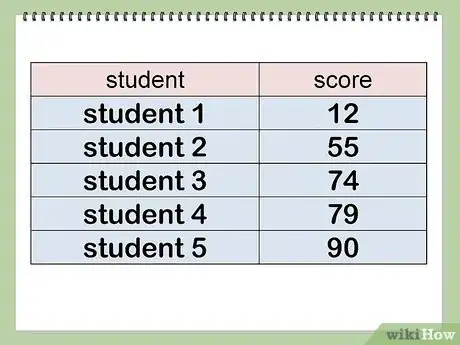
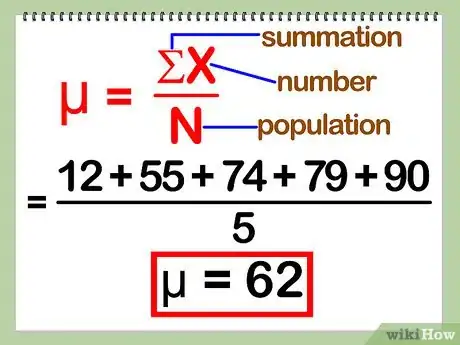
The mean is simply the average of a set of numbers. You can work it out by adding up all the numbers and dividing the total by the amount of numbers. For example, if you wanted to find the average test score of 3 students who scored 74, 79, and 90, you'd add the 3 numbers together to get 243, then divide it by 3 to get 81. The standard error represents how well the sample mean approximates the population mean. All you need to do is divide the standard deviation by the square root of the sample size. For instance, if you were sampling 5 students from a class of 50 and the 50 students had a standard deviation of 17, you'd divide 17 by the square root of 5 to get 7.6. For more tips, including how to calculate the standard deviation, read on!