This article was co-authored by wikiHow staff writer, Jack Lloyd. Jack Lloyd is a Technology Writer and Editor for wikiHow. He has over two years of experience writing and editing technology-related articles. He is technology enthusiast and an English teacher.
The wikiHow Tech Team also followed the article's instructions and verified that they work.
This article has been viewed 2,926,835 times.
Learn more...
This wikiHow teaches you how to write and save a basic batch file on a Windows computer. A batch file contains a series of DOS (Windows language) commands, and is commonly written to automate frequently performed tasks such as moving files. You shouldn't have to download any fancy editors to create a batch file—the Windows-standard Notepad program is more than sufficient.
Steps
Learning Batch Basics
-
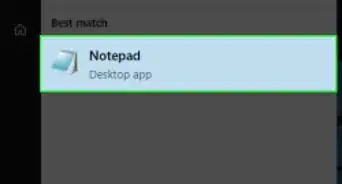
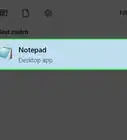
1Open Notepad. Notepad allows you to create code as a text file and then save it when you're done as a batch file. You can open Notepad by opening Start , typing in Notepad, and clicking the blue Notepad app icon at the top of the menu.
- Notepad is commonly used to convert text files into batch files, but you can write your batch file's text virtually anywhere.
-
2Learn some basic batch commands. Batch files run a series of DOS commands, so the commands that you can use are similar to DOS commands. Some of the more important ones include:
- ECHO - Displays text on the screen
- @ECHO OFF - Hides the text that is normally output
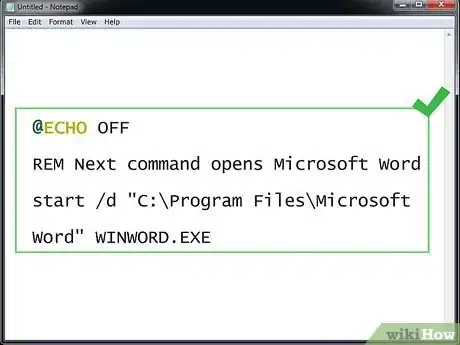
- START - Run a file with its default application
- REM - Inserts a comment line in the program
- MKDIR/RMDIR - Create and remove directories
- DEL - Deletes a file or files
- COPY - Copy a file or files
- XCOPY - Allows you to copy files with extra options
- FOR/IN/DO - This command lets you specify files.
- TITLE- Edit the title of the window. [1]
Advertisement -
3Write a program to create a directory. One of the easiest ways to learn how to create batch files is to focus on doing basic tasks first. For example, you can use a batch file to quickly create multiple directories:[2]
MKDIR c:\example1 MKDIR c:\example2
-
4Write the code to make a basic backup program. Batch files are great for running multiple commands, especially if you configure it to be able to run multiple times. With the XCOPY command, you can make a batch file that copies files from select folders to a backup folder, only overwriting files that have been updated since the last copy:
@ECHO OFF XCOPY c:\original c:\backupfolder /m /e /y
- This copies over files from the folder "original" to the folder "backupfolder". You can replace these with the paths to the folders you want. /m specifies that only updated files will be copied, /e specifies that all subdirectories in the listed directory will be copied, and /y keeps the confirmation message appearing every time a file is overwritten.
-
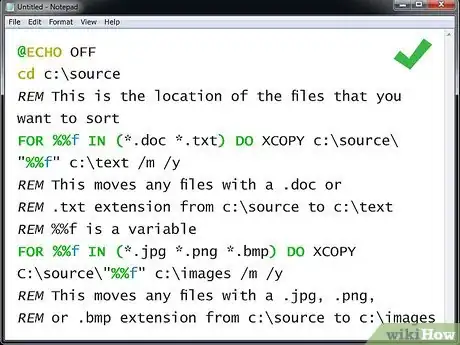
5Write a more advanced backup program. While simply copying the files from one folder to another is nice, what if you want to do a little sorting at the same time? That's where the FOR/IN/DO command comes in. You can use that command to tell a file where to go depending on the extension:
@ECHO OFF cd c:\source REM This is the location of the files that you want to sort FOR %%f IN (*.doc *.txt) DO XCOPY c:\source\"%%f" c:\text /m /y REM This moves any files with a .doc or REM .txt extension from c:\source to c:\text REM %%f is a variable FOR %%f IN (*.jpg *.png *.bmp) DO XCOPY C:\source\"%%f" c:\images /m /y REM This moves any files with a .jpg, .png, REM or .bmp extension from c:\source to c:\images
-
6Display some text. If you want to know what is happening in your batch file but don't want to see all the commands, you could program the batch file to print some text that explains what the batch file does. You can print text with ECHO. For example:
@ECHO OFF MKDIR c:\example1 ECHO Created directory example1
- You can change the color of the output with COLOR bf, where b is the background and f is the foreground color, both a hexadecimal number. Following colors are possible:
Number Color Number Color 0 black
8
dark grey
1 dark blue
9
blue
2 dark green
a
green
3 dark turquoise
b
turquoise
4 dark red
c
red
5 dark magenta
d
magenta
6 dark yellow
e
yellow
7 light grey
f
white
- For example, red text on a dark green background would be displayed with
COLOR 2c - You need run the batch file from the command line to see the text, because else the window will close too fast to actually read the text you printed.
- You can change the color of the output with COLOR bf, where b is the background and f is the foreground color, both a hexadecimal number. Following colors are possible:
-
7Experiment with different batch commands. If you want inspiration, you can check out the sample batch text at the end of this article.
Saving the Batch File
-
1Finish entering your batch file's text. Once you've completed and proofread your batch file, you can proceed with saving it as an executable file.
-
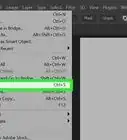
2Click File. It's in the top-left corner of the Notepad window. A drop-down menu will appear.
-
3Click Save As…. This option is in the File drop-down menu. Clicking it prompts the Save As window to open.
-
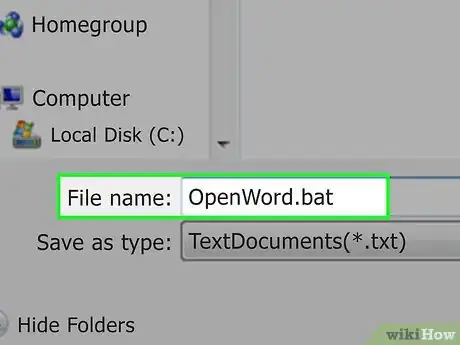
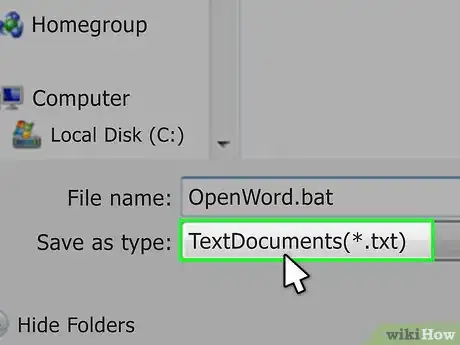
4Enter a name and the ".bat" extension. In the "File name" text box, type in whatever you want to name your program followed by .bat.
- For a program named "Backup", for example, you'd type in Backup.bat here.
-
5Click the "Save as type" drop-down box. You'll find it near the bottom of the Save As window. A drop-down menu will appear.
-
6Click All Files. It's in the drop-down menu. This will allow your file to be saved as whatever its extension is (in this case, ".bat").
-
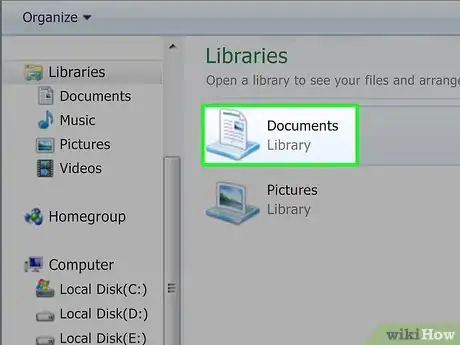
7Select a save location. Click a folder on the left side of the window (e.g., Desktop) to do so.
-
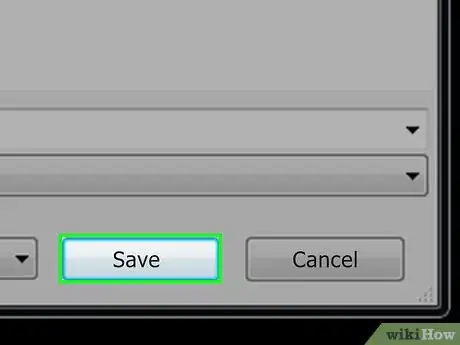
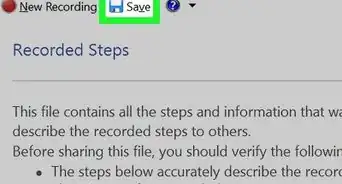
8Click Save. It's in the bottom-right corner of the Save As window. The window will close.
-
9Close your Notepad file. It will be saved as a batch file in your selected location.
-
10Edit the batch file's contents. At any time, you can right-click your batch file and click Edit in the resulting drop-down menu. This will open the batch file as a Notepad document; at this point, you can make any changes and then save the file by pressing Ctrl+S.
- The changes will immediately be reflected when you run the batch file.
Sample Batch File
Community Q&A
-
QuestionHow can I run multiple batch files?
 Community AnswerOpen multiple files at once. But if you really wanted to, you can open other batch files within a batch file as such: start "c:\Users\Xx_balzeitmichael_xX\Documents" random.bat.
Community AnswerOpen multiple files at once. But if you really wanted to, you can open other batch files within a batch file as such: start "c:\Users\Xx_balzeitmichael_xX\Documents" random.bat. -
QuestionHow do I open images using a batch file?
 David LangrCommunity AnswerYou can do so by typing the following command: start "C:\Path\picture.jpg".
David LangrCommunity AnswerYou can do so by typing the following command: start "C:\Path\picture.jpg". -
QuestionHow do I create a batch file?
 Arsalan KazmiCommunity AnswerEnter the code in Notepad and then go to File > Save As, click File Type, set it to All Files, then in the Name box, enter name.bat, where 'name' is the name of your batch file.
Arsalan KazmiCommunity AnswerEnter the code in Notepad and then go to File > Save As, click File Type, set it to All Files, then in the Name box, enter name.bat, where 'name' is the name of your batch file.
Warnings
- Depending on the commands you use, batch files can be dangerous. Make sure that none of your code runs the risk of performing an undesirable task (e.g., deleting files or crashing your computer).⧼thumbs_response⧽
References
About This Article
1. Learn basic batch commands.
2. Open Notepad.
3. Write your program.
4. Go to File > Save As.
5. Type a name for the file that ends with ".bat"
6. Select All Files from the "Save as type" menu.
7. Click Save.