EDMA
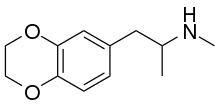
3,4-Ethylenedioxy-N-methylamphetamine (EDMA) is an entactogen drug of the methamphetamine class.[1][2] It is an analogue of MDMA where the methylenedioxy ring has been replaced by an ethylenedioxy ring.[1][2] EDMA was first synthesized by Alexander Shulgin.[1] In his book PiHKAL, the dosage is listed as 150–250 mg, and the duration listed as 3–5 hours.[1] According to Shulgin, EDMA produces a bare threshold consisting of paresthesia, nystagmus, and hypnogogic imagery, with few to no other effects.[1] Scientific research has demonstrated that EDMA acts as a non-neurotoxic serotonin releasing agent with moderately diminished potency relative to MDMA, and with negligible effects on dopamine release.[2]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C12H17NO2 |
| Molar mass | 207.273 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
References
- Ann Shulgin; Alexander Shulgin (1991). Pihkal: A Chemical Love Story. Transform Press. ISBN 0-9630096-0-5.
- McKenna DJ, Guan XM, Shulgin AT (March 1991). "3,4-Methylenedioxyamphetamine (MDA) analogues exhibit differential effects on synaptosomal release of 3H-dopamine and 3H-5-hydroxytryptamine". Pharmacology Biochemistry and Behavior. 38 (3): 505–12. doi:10.1016/0091-3057(91)90005-M. PMID 1829838. S2CID 2740262.
External links
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.