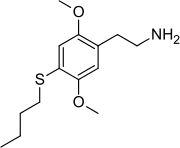
2C-T-19
2C-T-19 (2,5-dimethoxy-4-butylthiophenethylamine) is a psychedelic phenethylamine of the 2C family. It was first synthesized by Alexander Shulgin.
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
2-[4-(Butylsulfanyl)-2,5-dimethoxyphenyl]ethan-1-amine | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C14H23NO2S | |
| Molar mass | 269.40 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Dosage
In his book PiHKAL, Shulgin describes synthesis of the final intermediate of 2C-T-19 but did not bioassay the compound.[1]
Legality
Canada
As of October 31, 2016, 2C-T-19 is a controlled substance (Schedule III) in Canada.[2]
United States
In the United States, 2C-T-19 is not specifically scheduled, but possession and sales of 2C-T-19 could be prosecuted under the Federal Analog Act because of its structural similarities to 2C-T-7.
References
- 2C-T-21 Entry in PiHKAL, mentioning 2C-T-19
- Gazette, Government of Canada, Public Works and Government Services Canada, Public Services and Procurement Canada, Integrated Services Branch, Canada (4 May 2016). "Canada Gazette – Regulations Amending the Food and Drug Regulations (Part J — 2C-phenethylamines)". gazette.gc.ca.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.