AM-1220
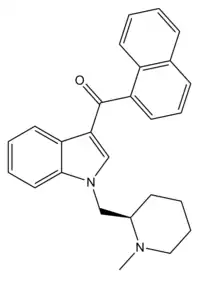
AM-1220 is a drug that acts as a potent and moderately selective agonist for the cannabinoid receptor CB1, with around 19 times selectivity for CB1 over the related CB2 receptor.[1] It was originally invented in the early 1990s by a team led by Thomas D'Ambra at Sterling Winthrop,[2] but has subsequently been researched by many others, most notably the team led by Alexandros Makriyannis at the University of Connecticut. The (piperidin-2-yl)methyl side chain of AM-1220 contains a stereocenter, so there are two enantiomers with quite different potency, the (R)-enantiomer having a Ki of 0.27 nM at CB1 while the (S)-enantiomer has a much weaker Ki of 217 nM.[3]
 | |
| Legal status | |
|---|---|
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII |
|
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C26H26N2O |
| Molar mass | 382.507 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Related compounds
A number of related compounds are known with similar potent cannabinoid activity, with modifications such as substitution of the indole ring at the 2- or 6-positions, the naphthoyl ring substituted at the 4-position or replaced by substituted benzoyl rings or other groups, or the 1-(N-methylpiperidin-2-ylmethyl) group replaced by similar heterocyclic groups such as N-methylpyrrolidin-2-ylmethyl or N-methylmorpholin-3-ylmethyl.[4][5][6] AM-1220 was first detected as an ingredient of synthetic cannabis smoking blends in 2010.[7]

Legal status
United States
in the United States of America all CB1 receptor agonists of the 3-(1-naphthoyl)indole class such as AM-1220 are Schedule I Controlled Substances under the Controlled Substances Act s.[8]
United Kingdom
it's illegal to supply, smuggle, distribute, transport, sell or trade the pharmaceutical drug under the Psychoactive Substances Act 2016 which was enforced on May26th 2016.
China
As of October 2015, AM-1220 is a controlled substance in China.[9]
References
- WO patent 200128557, Makriyannis A, Deng H, "Cannabimimetic indole derivatives", granted 2001-06-07
- US patent 5068234, D'Ambra TE, et al., "3-arylcarbonyl-1-(C-attached-N-heteryl)-1H-indoles", granted 1991-11-26
- D'ambra, T. (1996). "C-Attached aminoalkylindoles: potent cannabinoid mimetics". Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters. 6 (1): 17–22. doi:10.1016/0960-894X(95)00560-G.
- Deng H (2000). Design and synthesis of selective cannabinoid receptor ligands: Aminoalkylindole and other heterocyclic analogs (PhD. Dissertation). University of Connecticut. ProQuest 304624325.
- Willis PG, Pavlova OA, Chefer SI, Vaupel DB, Mukhin AG, Horti AG (September 2005). "Synthesis and structure-activity relationship of a novel series of aminoalkylindoles with potential for imaging the neuronal cannabinoid receptor by positron emission tomography". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 48 (18): 5813–22. doi:10.1021/jm0502743. PMID 16134948.
- US patent 7820144, Makriyannis A, et al., "Receptor selective cannabimimetic aminoalkylindoles", granted 2010-10-26
- Head Shop ‘Legal Highs’ Active Constituents Identification Chart (July - August 2010)
- : Schedules of controlled substances
- "关于印发《非药用类麻醉药品和精神药品列管办法》的通知" (in Chinese). China Food and Drug Administration. 27 September 2015. Archived from the original on 1 October 2015. Retrieved 1 October 2015.