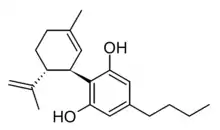
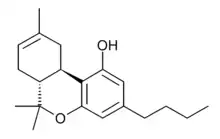
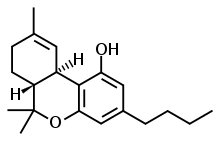
Tetrahydrocannabutol
Δ9-Tetrahydrocannabutol (tetrahydrocannabinol-C4, THC-C4, Δ9-THCB, (C4)-Δ9-THC, butyl-THC) is a phytocannabinoid found in cannabis that is a homologue of tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), the main active component of Cannabis.[1] Structurally, they are only different by the pentyl side chain being replaced by a butyl side chain.
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C20H28O2 |
| Molar mass | 300.442 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Pharmacology
Δ9-THCB, showed an affinity for the human CB1 (Ki = 15 nM) and CB2 receptors (Ki = 51 nM) comparable to that of Δ9-THC.[1] The formalin test in vivo was performed on Δ9-THCB in order to reveal possible analgesic and anti-inflammatory properties.[1] The tetrad test in mice showed a partial agonistic activity of Δ9-THCB toward the CB1 receptor.[1] THCB has rarely been isolated from cannabis samples,[1][2] but appears to be less commonly present than THC or THCV. It is metabolized in a similar manner to THC.[3]
In an analysis by the University of Rhode Island on phytocannabinoids it was found that THC-Butyl had the highest 3C-like protease inhibitor activity against COVID-19 out of all the phytocannabinoids tested within that study but not as high as the antiviral drug GC376 (81% THCB vs 100% GC376). [4]
Chemistry
Similarly to THC, it has 7 double bond isomers and 30 stereoisomers.[5] The Δ8 isomer is known as a synthetic cannabinoid under the code name JWH-130,[6] and the ring-opened analogue cannibidibutol is also known.[7] THC-Butyl can be synthesized from 4-Butylresorcinol.
Legality
THCB is not scheduled internationally under the Convention on Psychotropic Substances, but may be controlled under analogue law in some individual jurisdictions as a homologue of THC.
See also
References
- Linciano P, Citti C, Luongo L, Belardo C, Maione S, Vandelli MA, et al. (January 2020). "Isolation of a High-Affinity Cannabinoid for the Human CB1 Receptor from a Medicinal Cannabis sativa Variety: Δ9-Tetrahydrocannabutol, the Butyl Homologue of Δ9-Tetrahydrocannabinol". Journal of Natural Products. 83 (1): 88–98. doi:10.1021/acs.jnatprod.9b00876. PMID 31891265. S2CID 209519659.
- Harvey DJ (April 1976). "Characterization of the butyl homologues of delta1-tetrahydrocannabinol, cannabinol and cannabidiol in samples of cannabis by combined gas chromatography and mass spectrometry". The Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology. 28 (4): 280–285. doi:10.1111/j.2042-7158.1976.tb04153.x. PMID 6715. S2CID 32734030.
- Brown NK, Harvey DJ (April 1988). "In vivo metabolism of the n-butyl-homologues of delta 9-tetrahydrocannabinol and delta 8-tetrahydrocannabinol by the mouse". Xenobiotica; the Fate of Foreign Compounds in Biological Systems. 18 (4): 417–427. doi:10.3109/00498258809041678. PMID 2840781.
- Liu C, Puopolo T, Li H, Cai A, Seeram NP, Ma H (September 2022). "Identification of SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease Inhibitors from a Library of Minor Cannabinoids by Biochemical Inhibition Assay and Surface Plasmon Resonance Characterized Binding Affinity". Molecules. 27 (18): 6127. doi:10.3390/molecules27186127. PMC 9502466. PMID 36144858.
- "Verschil THC Olie, CBD olie, wietolie, hennepolie en cannabisolie?". Dutch-Headshop.com. Retrieved 19 November 2016.
- Bow EW, Rimoldi JM (2016). "The Structure-Function Relationships of Classical Cannabinoids: CB1/CB2 Modulation". Perspectives in Medicinal Chemistry. 8: 17–39. doi:10.4137/PMC.S32171. PMC 4927043. PMID 27398024.
- Hanuš LO, Meyer SM, Muñoz E, Taglialatela-Scafati O, Appendino G (November 2016). "Phytocannabinoids: a unified critical inventory". Natural Product Reports. 33 (12): 1357–1392. doi:10.1039/c6np00074f. PMID 27722705.