LAE-32
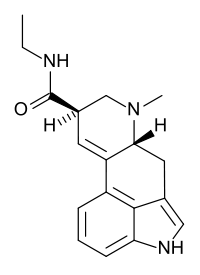
D-Lysergic acid ethylamide (LAE-32) is a derivative of ergine.[1][2] It is reported to have some LSD-like effects but is weaker and shorter lasting, with an active dose reported to be between 0.5 and 1.5 milligrams.
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | LAE; Lysergic acid ethylamide; d-Lysergic acid ethylamide; d-Ethyllysergamide, |
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Metabolism | Hepatic |
| Excretion | Renal |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider |
|
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C18H21N3O |
| Molar mass | 295.386 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
It was studied by the CIA as part of Project MKULTRA. Documents published by the CIA under the Freedom of Information Act suggest it causes "a schizophrenia-like condition" but it allows people with schizophrenia to remain indifferent to their disorder.
References
- "N-Ethyllysergamide". PubChem. U.S. National Library of Medicine. Retrieved 2022-11-16.
- Baquiran M, Al Khalili Y (2022). "Lysergic Acid Diethylamide Toxicity". StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing. PMID 31985997. Retrieved 2022-11-18.
| Lysergic acid derivatives |
|
|---|---|
| Psychedelic lysergamides |
|
| Clavines | |
| Other ergolines | |
| Natural sources |
Morning glory: Argyreia nervosa (Hawaiian Baby Woodrose), Ipomoea spp.(Morning Glory, Tlitliltzin, Badoh Negro), Rivea corymbosa (Coaxihuitl, Ololiúqui) |
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.