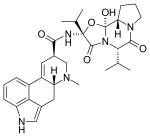
Ergocornine
Ergocornine is a crystalline ergopeptine and one of the ergot alkaloids separated from ergotoxine. It is also a dopamine receptor agonist.[1] It was discovered by Albert Hofmann, the Swiss chemist who created LSD.[2]
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.008.430 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C31H39N5O5 |
| Molar mass | 561.683 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
References
- Fuxe K, Corrodi H, Hökfelt T, Lidbrink P, Ungerstedt U (April 1974). "Ergocornine and 2-Br-alpha-ergocryptine. Evidence for prolonged dopamine receptor stimulation". Medical Biology. 52 (2): 121–32. PMID 4837435.
- Stoll A, Hoffmann A (1965). "Chapter 21: The Ergot Alkaloids". In Manske RH (ed.). Indole alkaloids. The alkaloids: chemistry and physiology. Vol. 8. New York: Academic Press. p. 759. ISBN 978-0-08-086532-4.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.