Charruan languages
The Charruan languages are a language family once spoken in Uruguay and the Argentine province of Entre Ríos. In 2005, a semi-speaker of the Chaná language, Blas Wilfredo Omar Jaime, was found in Entre Ríos Province, Argentina.[1]
| Charruan | |
|---|---|
| Ethnicity | Chaná people, Charrúa people, Guenoa people |
| Geographic distribution | Argentina (Entre Ríos Province) Brazil (formerly) Uruguay (formerly) |
| Linguistic classification | One of the world's primary language families
|
| Subdivisions | |
| Glottolog | char1238 |
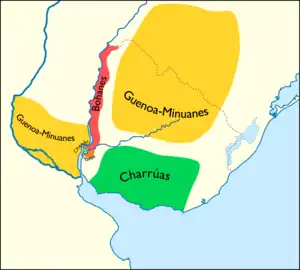 Pre-contact distribution of the Charruan languages | |
Internal coherence
Charruan may actually consist of two or three unrelated families according to Nikulin (2019).[2] Nikulin notes that many of the following languages share very few basic vocabulary items with each other.
- Chaná as spoken by Blas Wilfredo Omar Jaime
- Chaná of Larrañaga (1923)[3]
- Charrúa of Vilardebó (1842)
- Güenoa from a short 18th-century catechesis quoted by Lorenzo Hervás y Panduro[4]
Languages
Four languages are considered to definitively belong to the Charruan language family, basically Chañá (Lanték), Nbeuá, Charrúa and Guenoa.[5]
- Chaná
- Lanték Yañá (proper name of Chaná language)
- Yañá Nbeuá (the wrongly named "Mbeguá", "Beguá", "Chaná-Beguá", etc.)
- Yañá Ntimpúc (the wrongly named "Timbúes", "Chaná TImbúes", "Timbó", "Chaná timbó", etc.)
- Charrúa
- Güenoa
A number of unattested languages are also presumed to belong to the Charruan family:[5]
- Bohane – spoken near Maldonado, or Salto, in Uruguay
- Calchine – spoken in Santa Fe Province, Argentina, along the Salado River
- Caracañá – spoken along the Caracañá River, Santa Fe
- Chaná-Mbegua or Begua – spoken on the Paraná River between Crespo and Victoria
- Colastiné – spoken in Santa Fe Province near Colastiné
- Corondá – spoken in Coronda, Santa Fe Province
- Guaiquiaré – spoken in Entre Ríos on the Arroyo Guaiquiraré
- Mocoreta or Macurendá or Mocolete – spoken along the Mocoretá River in Entre Ríos Province
- Pairindi – spoken in Entre Ríos from Corrientes to the Feliciano River
- Timbu – spoken in Gaboto, Santa Fe Province
- Yaro – spoken in Uruguay between the Río Negro and the San Salvador River
Genetic relations
Jorge Suárez includes Charruan with Guaicuruan in a hypothetical Waikuru-Charrúa stock. Morris Swadesh includes Charruan along with Guaicuruan, Matacoan, and Mascoyan within his Macro-Mapuche stock. Both proposals appear to be obsolete.
Vocabulary comparison
The Charruan languages are poorly attested. However, sufficient vocabulary has been gathered for the languages to be compared:[5][6]
English Charrua Chaná Güenoa me m' mi-tí hum you m' mutí /em/ baté m we rampti/ am-ptí rambuí eye i-hou ocál ear i-mau / i-man timó mouth ej hek / obá hand guar nam foot / toe atit eté water hué atá sun dioi dog lohán agó white huok one yú u-gil / ngui yut two sam usan / amá three detí / datit detit / heít detit know sepé seker good / nice bilú oblí / oblé brother/sister inchalá nchalá friend huamá uamá why? / how? retám retanle* who? ua-reté past (suf.) ndau / nden edam
Lexical comparison from Nikulin (2019):[2]
gloss Chana (Jaime) Charrúa Chana (Larranaga 1923) Guenoa we ampti / am-, rampti rambui give ará da.jú sun dioi diói go nderé bajiná 'to walk' do thou empti em- / m- one gilí / güi yú ~ yu gil: ugil 'único' yut isa 'only one' who guareptí guárete sand lgorí han mouth uvá ej hek that huati / huat- white noá huóc good latár hear timotéc montéc come nderé na not reé =mén what r'eca 'what', r'epti retant 'how many?' two amá sam ~ sán san know seker, sekér see solá 'mirar' mountain to e woman adá ukái / kái 'female' I ytí / i- ~ y- all opá sleep utalá ando diabun 'vamos a dormir' foot vedé verá atit kill ña aú go nderé bajiná 'to walk' do stand reé utalá basquadé 'levantarse' mouth uvá ej hek hand nam guar moon aratá guidai water atá hué nose utí ibar eye ocál ijou ear timó imau head ta ~ ta ug vedé is hair moni itaj fire yogüín it dog agó samayoí two amá sam ~ sán san one gilí / güi yú ~ yu gil: ugil 'único' yut isa 'only one' person ëewuit edam who guareptí guárete die ña hallen name hapatam 'his name' we ampti / am-, rampti rambui what r'eca 'what', r'epti retant 'how many?' one gilí / güi yú ~ yu gil: ugil 'único' yut isa 'only one'
References
- La Nación, "Investigan los orígenes de una extraña lengua indígena". 2005-07-01.
- Nikulin, Andrey V. 2019. The classification of the languages of the South American Lowlands: State-of-the-art and challenges / Классификация языков востока Южной Америки. Illič-Svityč (Nostratic) Seminar / Ностратический семинар, Higher School of Economics, October 17, 2019.
- Larrañaga, Dámaso Antonio. 1923. Compendio del idioma de la nación chaná. In Escritos de D. Dámaso A. Larrañaga, tomo III, 163-174. Montevideo: Instituto Histórico y Geográfico del Uruguay, Imprenta Nacional.
- Hervás y Panduro, Lorenzo. 1787. Saggio Pratico delle lingue. (Idea dell'Universo, XXI.) Cesena: Gregorio Biasini all'Insengna di Pallade. 255pp.
- Loukotka, Čestmír (1968), Classification of South American Indian Languages, Los Angeles: UCLA Latin American Center
- This comparison table is a revision by Br. José Damián Torko Gómez, based on the J.C. Sábat Pébet and J.J. Figueira compilation of all terms known of the "Uruguayan" aboriginal languages. Source: https://www.estudioshistoricos-en.edu.uy/assets/080-boletín-histórico-nº-120---123---año-1969.pdf%5B%5D