Betalipothrixvirus
Betalipothrixvirus is a genus of viruses in the family Lipothrixviridae. Archaea serve as natural hosts. The genus contains six species.[1][2]
| Betalipothrixvirus | |
|---|---|
| Virus classification | |
| (unranked): | Virus |
| Realm: | Adnaviria |
| Kingdom: | Zilligvirae |
| Phylum: | Taleaviricota |
| Class: | Tokiviricetes |
| Order: | Ligamenvirales |
| Family: | Lipothrixviridae |
| Genus: | Betalipothrixvirus |
Taxonomy
The following six species are assigned to the genus:[2]
- Acidianus filamentous virus 3
- Acidianus filamentous virus 6
- Acidianus filamentous virus 7
- Acidianus filamentous virus 8
- Acidianus filamentous virus 9
- Sulfolobus islandicus filamentous virus
Structure
Viruses in Betalipothrixvirus are enveloped, with rod-shaped geometries. The diameter is around 24 nm, with a length of 2000 nm. Genomes are linear, around 40.5kb in length. The genome has 67 open reading frames.[1]
| Genus | Structure | Symmetry | Capsid | Genomic arrangement | Genomic segmentation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Betalipothrixvirus | Rod-shaped | Enveloped | Linear | Monopartite |
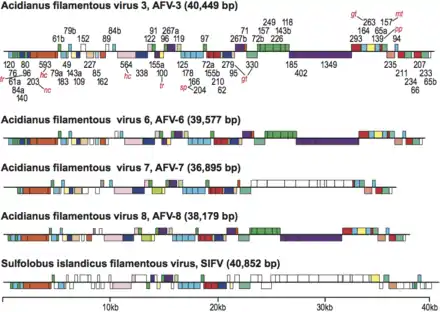
Genome map of AFV-3, AFV-6, AFV-7, AFV-8, all Betalipothrixvirus
Life cycle
Viral replication is cytoplasmic. Entry into the host cell is achieved by adsorption into the host cell. DNA templated transcription is the method of transcription. Archaea serve as the natural host. Transmission routes are passive diffusion.[1]
| Genus | Host details | Tissue tropism | Entry details | Release details | Replication site | Assembly site | Transmission |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Betalipothrixvirus | Archea | None | Injection | Budding | Cytoplasm | Cytoplasm | Passive diffusion |
References
- "Viral Zone". ExPASy. Retrieved 15 June 2015.
- "Virus Taxonomy: 2020 Release". International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV). March 2021. Retrieved 10 May 2021.
External links
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.