Chlamydiaceae
The Chlamydiaceae are a family of gram-negative bacteria that belongs to the phylum Chlamydiota, order Chlamydiales. Chlamydiaceae species express the family-specific lipopolysaccharide epitope αKdo-(2→8)-αKdo-(2→4)-αKdo (previously called the genus-specific epitope). Chlamydiaceae ribosomal RNA genes all have at least 90% DNA sequence identity. Chlamydiaceae species have varying inclusion morphology, varying extrachromosomal plasmid content, and varying sulfadiazine resistance.
| Chlamydiaceae | |
|---|---|
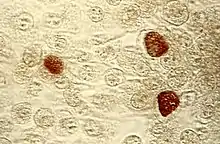 | |
| Chlamydia trachomatis inclusion bodies (brown) in a McCoy cell culture | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Bacteria |
| Phylum: | Chlamydiota |
| Class: | Chlamydiia |
| Order: | Chlamydiales |
| Family: | Chlamydiaceae Rake 1957 |
| Genera | |
| |
The family Chlamydiaceae currently includes one genus and one candidate genus: Chlamydia and candidatus Clavochlamydia.[1]
Chlamydia
Three species belong to Chlamydia: C. trachomatis, C. muridarum, and C. suis. C. trachomatis has been found only in humans, C. muridarum in hamsters and mice (family Muridae), and C. suis in swine. Chlamydia species produce a small amount of detectable glycogen and have two ribosomal operons.
Chlamydia trachomatis is the cause of an infection commonly transmitted sexually (often referred as just "Chlamydia") and also is the cause of trachoma, an infectious eye disease, spread by eye, nose, and throat secretions.
Phylogeny
| 16S rRNA based LTP_01_2022[2][3][4] | 120 marker proteins based GTDB 07-RS207[5][6][7] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
Taxonomy
The currently accepted taxonomy is based on the List of Prokaryotic names with Standing in Nomenclature (LPSN)[8] and National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI)[1]
- "Ca. Amphibiichlamydia" Martel et al. 2012
- Chlamydia Jones et al. 1945
- "Chlamydiifrater" Vorimore et al. 2021
- Chlamydophila Everett, Bush & Andersen 1999
- "Ca. Medusoplasma" Viver et al. 2017
References
- Sayers; et al. "Chlamydiae". National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) taxonomy database. Retrieved 2022-09-09.
- "The LTP". Retrieved 23 February 2022.
- "LTP_all tree in newick format". Retrieved 23 February 2022.
- "LTP_01_2022 Release Notes" (PDF). Retrieved 23 February 2022.
- "GTDB release 07-RS207". Genome Taxonomy Database. Retrieved 20 June 2022.
- "bac120_r207.sp_labels". Genome Taxonomy Database. Retrieved 20 June 2022.
- "Taxon History". Genome Taxonomy Database. Retrieved 20 June 2022.
- J.P. Euzéby. "Chlamydiota". List of Prokaryotic names with Standing in Nomenclature (LPSN). Retrieved 2022-09-09.