Ipomovirus
Ipomovirus is a genus of positive-strand RNA viruses in the family Potyviridae. Member viruses infect plants and are transmitted by whiteflies (Bemisia tabaci). The name of the genus is derived from Ipomoea – the generic name of sweet potato. There are seven species in this genus.[1][2]
| Ipomovirus | |
|---|---|
| Ipomovirus virion | |
| Virus classification | |
| (unranked): | Virus |
| Realm: | Riboviria |
| Kingdom: | Orthornavirae |
| Phylum: | Pisuviricota |
| Class: | Stelpaviricetes |
| Order: | Patatavirales |
| Family: | Potyviridae |
| Genus: | Ipomovirus |
Structure
Viruses in genus Ipomovirus are non-enveloped, with flexuous and filamentous geometries. The diameter is around 12–15 nm, and may have a variety of lengths depending on the species (for single segmented species lengths of around 650–900 nm, or for double segmented species 200–300 nm and 500–600 nm). The capsid has helical symmetry with a pitch of 3.4 nm. They induce characteristic inclusion bodies (pinwheels) within infected plant cells.[1]
Genome
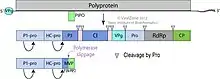
The genome is either monpartite or bipartite depending on the species. Member viruses have linear, single stranded RNA genome of positive polarity about 10-11 kilobases in length. The 3’ terminus has a poly (A) tract and the 5’ terminus has a genome linked protein (VPg).[1]
Member viruses encode a single polypeptide with a predicted molecular weight of 390 kiloDaltons (kDa) which is cleaved into ~10 proteins. In 5'–3' order these proteins are
- P1 (a serine protease): 83 kDa
- HC (a protease): 51 kDa
- P3: 34 kDa
- 6K1: 5 kDa
- Cl (helicase): 71 kDa
- 6K2: 6 kDa
- VPg (the 5' binding protein): 20 kDa
- NIa-Pro (a protease): 27 kDa
- NIb (RNA dependent RNA polymerase): 57 kDa
- Capsid protein: 34 kDa
There may be some variation in the number of the proteins depending on the species, for instance some ipomoviruses lack HC and have a P1 tandem. Inosine triphosphate pyrophosphatase (known as ITPase or HAM1) is an atypical protein domain identified in some ipomoviruses.[3]
Life cycle
Viral replication is cytoplasmic. Entry into the host cell is achieved by penetration into the host cell. Replication follows the positive stranded RNA virus replication model. Positive stranded RNA virus transcription is the method of transcription. The virus exits the host cell by tubule-guided viral movement. Plants serve as the natural host. The virus is transmitted via a vector (white fly). Transmission routes are vector and mechanical.[1]
Taxonomy
The genus contains the following species:[2]
- Cassava brown streak virus
- Coccinia mottle virus
- Cucumber vein yellowing virus
- Squash vein yellowing virus
- Sweet potato mild mottle virus
- Tomato mild mottle virus
- Ugandan cassava brown streak virus
References
- "Viral Zone". ExPASy. Retrieved 15 June 2015.
- "Virus Taxonomy: 2020 Release". International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV). March 2021. Retrieved 21 May 2021.
- Pasin, Fabio; Daròs, José-Antonio; Tzanetakis, Ioannis E (23 February 2022). "Proteome expansion in the Potyviridae evolutionary radiation". FEMS Microbiology Reviews: fuac011. doi:10.1093/femsre/fuac011. ISSN 1574-6976.